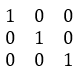Updated March 22, 2023
Introduction to Linear Algebra in Machine Learning
Linear Algebra in Machine learning is defined as the part of mathematics that uses vector space and matrices to represent the linear equations, from the implementation of algorithms and techniques in the code(such as Regularization, Deep learning, One hot encoding, Principal Component Analysis, Single Value Decomposition, etc.) to the notations that are used to describe the operations of the machine learning algorithm it acts as the key foundation in the field of machine learning.
Matrix: It is an array of numbers in a rectangular form represented by rows and columns.
Example:
Vector: A vector is a row or a column of a matrix.
Example:
Tensor: Tensors are an array of numbers or functions that transmute with certain rules when coordinate changes.
How does Linear Algebra work in Machine Learning?
As Machine Learning is the point of contact for Computer Science and Statistics, Linear Algebra helps in mixing science, technology, finance & accounts, and commerce altogether. Numpy is a library in Python which works on multidimensional arrays for scientific calculations in Data Science and ML.
Linear Algebra functions in various ways as is reflected in some examples listed below:
1. Dataset and Data Files
A data is a matrix or a data structure in Linear Algebra. A dataset contains a set of numbers or data in a tabular manner. Rows represent observations whereas columns represent features of it. Each row is of the same length. So, data is vectorized. Rows are pre-configured and are inserted to the model one at a time for easier and authentic calculations.
2. Images and Photographs
All images are tabular in structure. Each cell in black and white images comprises of height, width, and one-pixel value. Similarly, color images have 3-pixel values in it apart from height and width. It forms a matrix in Linear Algebra. All kinds of editing such as cropping, scaling, etc, and manipulation techniques are performed using algebraic operations.
3. Regularization
Regularization is a method that minimizes the size of coefficients while inserting it into data. L1 and L2 are of some common methods of implementation in regularization which are measures of the magnitude of coefficients in a vector.
4. Deep Learning
This method is mostly used in neural networks with various real-life solutions, such as machine translation, photo captioning, speech recognition, and many other fields. It works with vectors, matrices, and even tensors as it requires linear data structures added and multiplied together.
5. One Hot Encoding
It is a popular encoding for categorical variables for easier operations in algebra. A table is constructed with one column for each category and a row for each example. Digit 1 is added for categorical value succeeded by 0 in the rest and so on, as cited below:
6. Linear Regression
Linear regression, one of the statistical methods, is used for predicting numerical values for regression problems as well as describing the relationship among variables.
Example: y= A. b where A is dataset or matrix, b is coefficient and y is the output.
7. Principal Component Analysis or PCA
Principal Component Analysis is applicable while working with high-dimensional data for visualization and model operations. When we find irrelevant data, then we tend to remove the redundant column(s). So PCA acts as a solution. Matrix factorization is the main objective of PCA.
8. Single-Value Decomposition or SVD
It is also a matrix factorization method used generally in visualization, noise reduction, etc.
9. Latent Semantic Analysis
In this process, documents are represented as large matrices. Document processed in these matrices is easy to compare, query and use. A matrix is constructed where rows represent words and columns represent documents. SVD is used to reduce the number of columns while preserving the similarity.
10. Recommender Systems
Predictive models rely on the recommendation of products. With the help of Linear Algebra, SVD functions to purify data using Euclidean distance or dot products. For example, when we purchase a book on Amazon, recommendations come based on our purchase history keeping aside other irrelevant items.
Advantages of Linear Algebra in Machine Learning
Given below are the advantages mentioned:
- Acts as a solid foundation for Machine Learning with the inclusion of both mathematics and statistics.
Both tabular and images can be used in linear data structures. - It is distributive, associative, and communicative as well.
- It is a simple, constructive, and versatile approach in ML.
- Linear Algebra is applicable in many fields such as predictions, signal analysis, facial recognition, etc.
Linear Algebra functions in Machine Learning
There are some Linear Algebra functions that are vital in ML and Data Science operations as described below:
1. Linear Function
The linear regression algorithm uses a linear function where output is continuous and has a constant slope. Linear functions have a straight line in the graph.
F(x)=mx+b
Where,
- F(x) is the value of the function.
- m is the slope of the line.
- b is the value of the function when x=0.
- x is the value of x-coordinate..
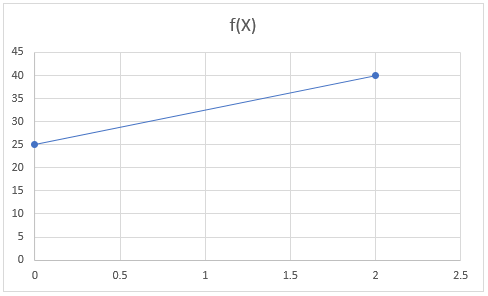
Example: y=5x+25
Let x=0, then y=5*1+25=25
Let x=2, then y=5*2+25=40
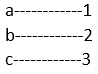
2. Identity Function
Identity function comes under the unsupervised algorithm and is mostly used in Neural Networks in ML where the output of the multilayer neural network is equal to its input, as cited below.
For every x, f(x) maps to x i.e x maps to itself.
Example: x+0=x
x/1=x
1——–>1
2——–>2
3——–>3
3. Composition
ML uses higher-order composition and pipelining functions in its algorithms for mathematical calculations and visualizations.
Composition function is described as below:
(g o f)(x)=g(f(x))
Example: let g(y)=y
f(x)=x+1
g o f(x+1)=x+1
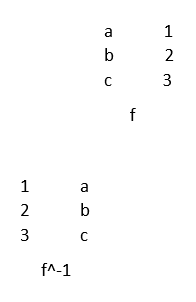
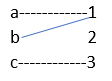
4. Inverse Function
The inverse is a function that reverses itself. Functions f and g inverse if f o g and g o f are defined and are identity functions.
Example:
5. Invertible Function
A function that has inverse is invertible.
one-to-one
onto
Conclusion
Linear Algebra is a subfield of mathematics. However, it has broader use in Machine Learning from notation to the implementation of algorithms in datasets and images. With the help of ML, algebra has got a larger impact in real-life applications such as search-engine analysis, facial recognition, predictions, computer graphics, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Linear Algebra in Machine Learning. Here we discuss how did linear algebra work in machine learning with the advantages and some examples. You may also look at the following article to learn more –