Updated March 13, 2023
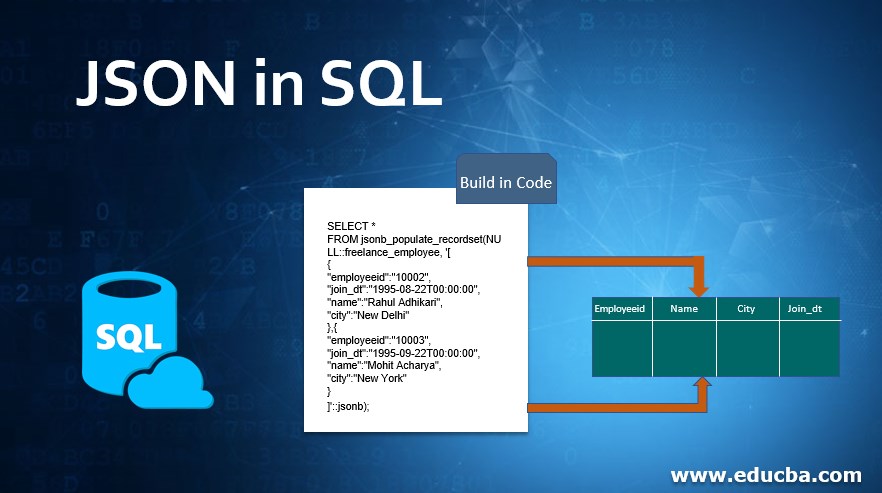
Introduction to JSON in SQL
JSON or JavaScript Object Notation is a standard file format that was derived from javascript and is used to store data in a serializable manner as key/attribute and value pairs or as array data types. It is a very commonly used data type as it is very easy for humans to read and understand.
Applications of JSON Data Type
- It is language independent. Hence, it finds application across multiple platforms and languages.
- JSON provides a wide range of browser compatibility with operating systems. Hence, the applications made with using JSON doesn’t require a lot of effort to make them compatible across a wide range of browsers.
- It is easy for machines to understand the data format.
- It is very light weight and hence it improves overall performance of the program or platform.
- It is faster than other file formats like CSV and XML.
However, we also have certain disadvantages of JSON file format. Since it is human readable and easy to parse, it might reduce the overall security of the database.
Syntax and Parameters
A standard JSON data is written as key/attribute and value pairs. The syntax is something like this :
{"key" : "value"}A key value pair consists of a “field name or attribute”,followed by a colon and finally the value of the attribute. Both the field name and value are written in double quotes.
Multiple records are written together within a set of square brackets,with each record written with a set of curly braces, separated by comma. The standard syntax is as follows :
{
column_name1":"value_a1",
"column_name2":"value_a2",
"column_name3":"value_a3",
"column_name4":"value_a4"
},{
"column_name1":"value_b1",
"column_name2":"value_b2",
"column_name3":"value_b3",
"column_name4":"value_b4"
}{An example of data in JSON file format is as follows :
[
{
"productid":"p1234",
"product_name":"Hershey's Milk Chocolate",
"category":"Chocolate",
"description":"Imported Milk Chocolate"
},{
"productid":"p1235",
"product_name":"Saffola Gold",
"category":"Cooking Oil",
"description":"Refined Vegetable Oil"
}
]Examples
Here are few examples to understand how json file format can be used in SQL.
Note : Parsing or reading data from JSON file format varies across the relational database servers. For example, in order to parse data in SQL Server 2008 and above, we use OPENJSON function which transforms a JSON array to a table. While in postgresQL, we use jsonb_to_recordset function.
For the purpose of this article, we have frequently used PostgreSQL and hence the corresponding functions.
Example#1 – Read or Parse JSON Data
Here is a simple example on how to parse data from a JSON file format. In this example , we are using jsonb_to_recordset function which parses data from a json code snippet and projects data as a temporary table with the mentioned column names.
SELECT * FROM jsonb_to_recordset('[
{
"employeeid":"10002",
"join_dt":"1995-08-22T00:00:00",
"name":"Rahul Adhikari",
"city":"New Delhi"
},{
"employeeid":"10003",
"join_dt":"1995-09-22T00:00:00",
"name":"Mohit Acharya",
"city":"New York"{
}{}">
]'::jsonb) AS t (employeeid integer, name text, city text, join_dt date);Next, suppose if we already have a table then we might not have to write that extra piece of code.
The first step is to create a table. Here, we are creating a freelance_employee table, using the following code snippet.
CREATE TABLE freelance_employee(
employeeid int NOT NULL,
name varchar(50) NOT NULL,
city varchar(50) NOT NULL,
join_dt date NOT NULL
);Output:
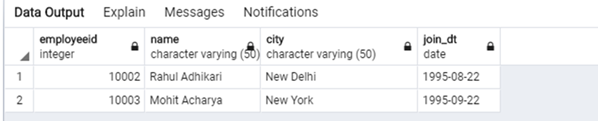
Next, we will populate the above mentioned “freelance_employee” table using jsonb_populate_recordset function using the following code snippet.
SELECT * FROM jsonb_populate_recordset(NULL::freelance_employee, '[
{
"employeeid":"10002",
"join_dt":"1995-08-22T00:00:00",
"name":"Rahul Adhikari",
"city":"New Delhi"
},{
"employeeid":"10003",
"join_dt":"1995-09-22T00:00:00",
"name":"Mohit Acharya",
"city":"New York"
}
]'::jsonb);Output:
Example#2 – Insert Data in a Relational Database Table
In this example, we will try insert data in JSON file format into the “freelance_employee” table mentioned in example 1. First we will be selecting from the JSON data using the SELECT statement and then populating it into the “freelance_employee” table using the INSERT statement as shown below.
INSERT INTO freelance_employee
SELECT * FROM jsonb_populate_recordset(NULL::freelance_employee, '[
{
"employeeid":"10002",
"join_dt":"1995-08-22T00:00:00",
"name":"Rahul Adhikari",-----------------------------------------
"city":"New Delhi"
},{
"employeeid":"10003",
"join_dt":"1995-09-22T00:00:00",
"name":"Mohit Acharya",
"city":"New York"
}
]'::jsonb);Output:
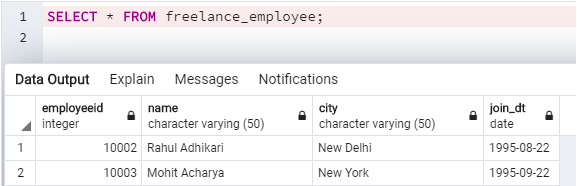
Let’s check if the data from the JSON file format has been successfully inserted in the table. We can do so using a SELECT statement as mentioned in the code snippet below.
SELECT * FROM freelance_employeeOutput:
Example#3 – Query Data in SQL
In this example, we will try to understand how to query JSON data in SQL. First we will be parsing JSON data using jsonb_to_recordset function and then using a SELECT statement we will query the data.
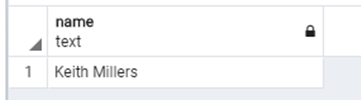
Suppose if we want to know the name of an employee who is from New Jersey. We can find it out as shown in the code snippet below.
SELECT name FROM jsonb_to_recordset('[
{
"employeeid":"10002",
"join_dt":"1995-08-22T00:00:00",
"name":"Rahul Adhikari",
"city":"New Delhi"
},{
"employeeid":"10003",
"join_dt":"1995-09-22T00:00:00",
"name":"Mohit Acharya",
"city":"New York"
},{
"employeeid":"10004",
"join_dt":"1997-09-22T00:00:00",
"name":"Keith Millers",
"city":"New Jersey"
<
]'::jsonb) AS t (employeeid integer, name text, city text, join_dt date)
WHERE t.city = 'New Jersey';Output:
Conclusion – JSON in SQL
JSON is a standard file format that can be used for storing data. It is a language independent file format that supports multiple platforms. Since it is lightweight and easy to understand format for both humans and machines, it is readily used across the industry for its faster performance and efficacy.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “JSON in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

