Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to SQL REGEXP
A regular expression in standard query language (SQL) is a special rule that is used to define or describe a search pattern or characters that a particular expression can hold. For example, a phone number can only have 10 digits, so in order to check if a string of numbers is a phone number or not, we can create a regular expression for it. It is an in-built specification supported in almost all SQL databases.
Regular expressions are very helpful as they let us place multiple lines of code or information in just 1 line. It is particularly helpful in SQL databases when we want to perform validation tasks like if the information provided is a valid PIN code, Contact No, email address, etc. Regular expressions also help in pattern matching or searching the database.
List of Operators Used for REGEXP in SQL
Here is the list of some of the most frequently used operators or metacharacters for making regular expressions in SQL.
|
Operator |
Operator Name |
Function |
| (.) | Any character – Dot Quantifier | Matches any single character in the character set of the database. |
| (*) | Asterisk or Star Quantifier | Matches zero or more occurrences of the subexpression/ strings preceding to it. |
| (+) | Plus Quantifier | Matches one or more occurrences of the subexpression/ strings preceding to it. |
| (?) | Question mark Quantifier | Matches zero or one occurrence of the subexpression/ strings preceding to it. |
| [ABC] / [abc] | Matching Character List | Matches any character mentioned in the list. |
| [^ABC] / [^abc] | Non-Matching Character List | Matches any character except the ones mentioned in the list. |
| [0-9] | Digit List | Matches any digit from 0 to 9. |
| {a} | Exact count Interval | Matches exact ‘a’ occurrences of subexpression or string preceding to it. |
| {a,} | At Least one count Interval | Matches at least ‘a’ occurrences of subexpression or string preceding to it. |
| {a,b} | Between count Interval | Matches at least ‘a’ occurrences of subexpression or string preceding to it but not more than ‘b’ occurrences. |
| (^) | Caret Quantifier | Matches an expression only if it occurs at the beginning of a line. |
| ($) | Dollar or End Quantifier | Matches an expression only if it occurs at the end of a line. |
| (|) | Vertical Bar Quantifier | It is used to isolate different alternatives in a regular expression. |
| [[:class:]] | Class Quantifier | Matches the character class , for example , matches [[:digit:]] to digits, [[:space:]] to space, [[:alnum:]_] to alpha numerics, etc. |
In the table above, we have tried to incorporate the most basic and frequently used meta-characters or quantifiers used for creating complex regular expressions. On the basis of this table, you can create other quantifiers such as +? Or *? for non-greedy versions of plus (+) quantifier and asterisk (+) quantifier, i.e matching just zero or one occurrences.
Examples of SQL REGEXP
Here are a few examples to illustrate the use and functions of different quantifiers in regular expressions.
In order to do so, let us first create a ‘customer_details’ table which contains customer id, his or her name, contact details, and the city where they live. We can use the following SQL statements to perform the task.
CREATE TABLE customer_details
(
customer_id integer,
customer_name character varying(255),
city character varying(255),
contact_no character varying(255),
email_address character varying(255)
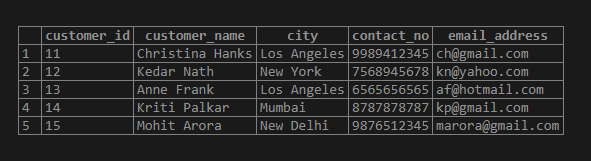
);Having created the customer_details table, let us now feed some information into the table columns using insert statements as shown below.
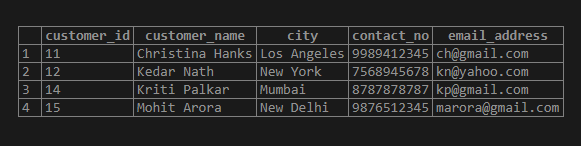
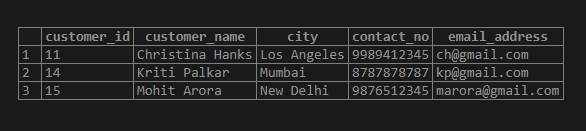
INSERT INTO customer_details
VALUES (11,'Christina Hanks','Los Angeles','9989412345','[email protected]'),
(12,'Kedar Nath','New York', '7568945678','[email protected]'),
(13,'Anne Frank','Los Angeles','6565656565', '[email protected]' ),
(14,'Kriti Palkar','Mumbai','8787878787', '[email protected]'),
(15,'Mohit Arora', 'New Delhi', '9876512345','[email protected]');select * from customer_detailsOutput:
Example #1
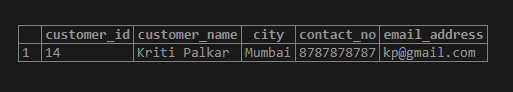
SQL query to Illustrate the use of Dot (.) quantifier.
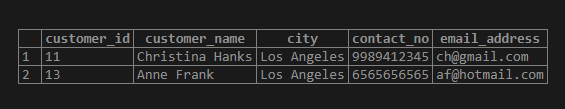
SELECT * FROM customer_details
WHERE customer_name ~ 'K.';Output:
Any Character Dot (.) quantifier matches with any string containing that character. In this example, customer_names with capital ‘K’ in them will be matched.
Example #2
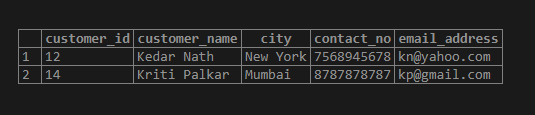
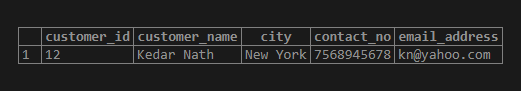
SQL query to Illustrate use of Star (*) quantifier.
SELECT * FROM customer_details
WHERE customer_name ~ 'Ked*';Output:
Example #3
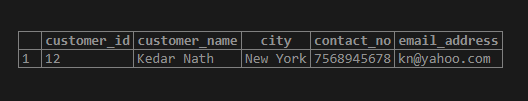
SQL query to Illustrate the use of Plus(+) quantifier.
SELECT * FROM customer_details
WHERE email_address ~ 'gmail+';Output:
Example #4
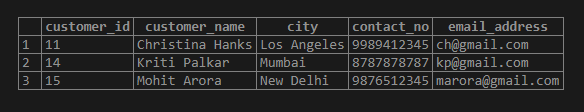
SQL query to Illustrate the use of Question Mark (?) quantifier.
SELECT * FROM customer_details
WHERE city ~ 'Los?';Output:
? quantifier matches with zero or one occurrence of the string preceding to it. Here, Cities with ‘Los’ will be matched.
Example #5
SQL query to Illustrate the use of [… ] Character List quantifier.
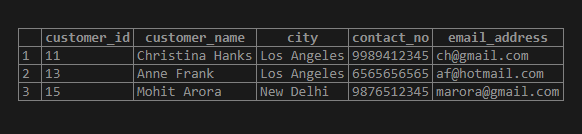
SELECT * FROM customer_details
WHERE customer_name ~ '[CA]';Output:
Example #6
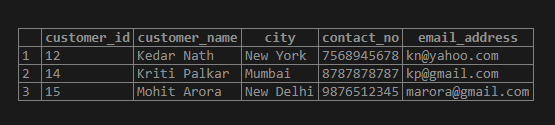
SQL query to Illustrate the use of [^…] non-matching character list quantifier.
SELECT * FROM customer_details
WHERE customer_name ~ '^[^CA]';Output:
Example #7
SQL query to Illustrate the use of Digit [0-9] quantifier.
SELECT * FROM customer_details
WHERE contact_no ~ '[8-9]';Output:
Example #8
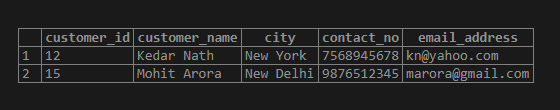
SQL query to Illustrate the use of the Caret (^) quantifier.
SELECT * FROM customer_details
WHERE contact_no ~ '^[8]';Output:
SELECT * FROM customer_details
WHERE city ~ '^New';Output:
‘^’ quantifier matches an expression if and only if a string or line begins with it. For example, contact_no starting with 8 and cities starting with ‘New’.
Example #9
SQL query to Illustrate the use of Vertical Bar (|) quantifier.
SELECT * FROM customer_details
WHERE contact_no ~ '^[8]|^[9]';Output:
The vertical bar is used to create one or more versions of the matching subexpression. For example, in this case, matching those contact numbers which starts with 8 or 9.
Example #10
SQL query to Illustrate the use of Dollar or End ($) quantifier.
SELECT * FROM customer_details
WHERE contact_no ~ '8$';Output:
$ matches an expression when it occurs at the end of a string. In this case, we are trying to find those contact numbers which end in digit 8.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL REGEXP” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.