Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to SQL For loop
SQL provides us with the language that can be used to convey the instructions and give the commands to the SQL server. This language comes with many statements and functionalities to implement the conditional and looping behavior of the execution of multiple statements. Looping statements are used to perform a certain task repetitively. There are many looping statements available in SQL such as while loop, looping using the simple loop and exit keywords and labels, etc. However, there is no presence of functionality to use for loop in SQL. It is still possible to simulate the behavior of for loop using while loop.
In this article, we will learn about the syntax of the for loop like implementation using while loop, it’s working and internal implementation and illustrate with some of the examples that will enhance the grip on the usage of while loop to execute the statements multiple times in for loop fashion as per our requirement.
Syntax:
WHILE condition
BEGIN
[statements inside the loop];
END;Syntax of simple customized WHILE loop for implementing for loop functionality in SQL:
counting variable = beginning value;
WHILE condition usually counting variable < ending value
BEGIN
[statements inside the loop];
counting variable = counting variable + step value
END;Usually, we maintain a counter variable that will be incremented or decremented inside the while loop to implement the for loop like functionality using while loop in SQL. The condition is provided in such a way that the execution of statements inside the while loop continues until the value of the counter variable reaches the ending value.
- name of counting variable – This can be any variable that will hold the value as the counter to maintain which value is being iterated and to know the number of times the looping has been done and statements have been executed at any point in time. In short, it can be considered as the temporary variable that stores the value of the looping counter.
- beginning value – This is the starting value from where the looping will begin and the first value of the counting variable that it will hold.
- ending value – This is the last value of the counting variable up to which the while loop will iterate and execute the statements.
- step value – This is the incremental value with which the counting variable will increase from the beginning value until the value of the counting variable reaches the ending value.
- Statements inside the loop – We can specify multiple statements to be executed repetitively while iterating the while loop each time. All the statements that should be executed while each of the iterations of the while loop should is specified between BEGIN and END keywords.
We can loop by decrementing the value of the counter variable from beginning value up to which the decrementation leads to counting variable to reach to the value of ending value by simply mentioning the condition as the condition usually counting variable > ending value instead of the above one and decrementing the counter variable by decreasing step value by using counting variable = counting variable – step value.
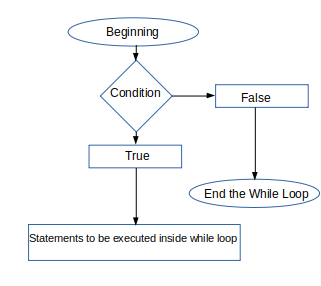
Working of while Loop
The execution begins by assigning the beginning value to the counter variable and then begins the execution of statements. The while loop internally executes the statements declared inside the loop body which begins from the BEGIN and ends with the END keyword. After the execution of statements inside the looping keywords the execution of while loop again increments the value of the counting variable by step value in case if we are not decrementing the counter variable. If we are decrementing the counter variable then the value of the counting variable is decremented by the step value and then the execution of the looping statements is executed again. This process keeps on repeating until the value of the counter variable reaches the value specified in the ending value part and then the execution of looping statements is done for the last time. Refer to the below figure to know how the while loop works:
Example
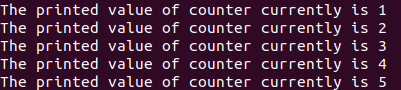
Consider one example where we will print the value of the counter variable by using the while loop and giving it the functionality like for loop by simply declaring the counter variable outside the loop to 1 and iterating the while loop until the counter variable has a value less than 5 and inside the while loop body we will print the value of the current counter and then increment its value by one as we do it in for loop of other languages. Our code will be as follows –
DECLARE @counterVariable INT
SET @counterVariable=1
WHILE ( @counterVariable <= 5)
BEGIN
PRINT 'The printed value of counter currently is ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR,@counterVariable)
SET @counterVariable = @counterVariable + 1
ENDThe execution of the above statements inside the stored procedure of function and then calling the same will give the following output after execution with the value of the counter variable being printed from 1 to 5 as we have looped the while loop specifying those conditions –
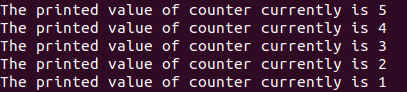
Let us now use the while loop to implement for loop like functionality with decrementing counter variable as follows –
DECLARE @counterVariable INT
SET @counterVariable=5
WHILE ( @counterVariable >= 5)
BEGIN
PRINT 'The printed value of counter currently is ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR,@counterVariable)
SET @counterVariable = @counterVariable - 1
ENDOutput:
Conclusion
We can implement the functionality of for loop inside the SQL even though for loop statement is not available in SQL using the while loop statement. All we need to do is maintain a counter variable and then specify the condition in the while loop the same as that we specify it in the for loop of other languages and then increment or decrement the counter variable inside the body of the while loop to iterate the counter variable. We can simulate the working of for loop functionality using the simple while loop in SQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL for loop” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.