Introduction to JSON in Python
JSON in Python is a format for storing data. It is referred to as JavaScript Object Notation. It is a lightweight data frame as compared to XML or HTML format. JSON is easy to understand and resembles Python dictionaries with slight variations like, (Boolean notation and Null notation). It is a standard data format for storing/fetching data from APIs and configuration files. This format is language-independent and is adaptable in Python as well. In the case of Python, it has a separate library called JavaScript Object Notation.
How does it work?
As we know, JSON is a file format to store the data; now, we can use an existing file or create a new Python dataset and assign it in format. The syntax for each operation is discussed below.
1. Importing JSON Library
Python uses the JavaScript Object Notation library. To Install the library, the syntax is given below.
Syntax:
pip install jsonlib ;pip install demjsonOnce you have a library in Python, write the following command to import it into code.
import json;2. Get or Load JSON Format Dataset
To load JSON format data, the following syntax is used as given below.
Syntax:
My_json = json.load( Mason )In parentheses, write the name of the file you want to load.
3. Perform Operations on It
JSON format is like the dictionaries of Python, with some minor differences. We can perform several operations that we can perform on Python dictionaries, like viewing datasets, using loops, changing values, aggregating different keys to create a new key, etc.
4. Return JSON Format from Python
When Python loads the JSON file, it converts it into a readable format and works on it. Once the file is ready, it is again converted to the original JSON format.
To do this, we use the following syntax as given below:
Syntax:
My_json_output = json.dump( Mjson )In parenthesis, write the file name you would like to dump.
How to Convert JSON to Python and Vice Versa?
This is the essential part of this article. To convert a JSON document into Python, we perform Deserialization or Decoding. To convert a Python document into json string, we perform Serialization or Encoding. You need the demjson library to complete these two tasks.
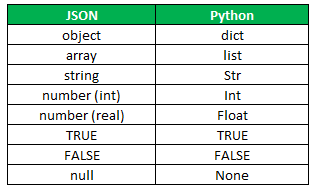
Serialization and Deserialization provide a translator that encodes and decodes the format. The below table shows the relationship between Python and JSON.
Here we can see some differences that we can identify clearly: numbers in JSON are treated as int and float, null in JSON is treated as None in Python, objects in JSON are dictionaries in Python, and so on. We will see the conversion in detail in the example section.
Examples of JSON in Python
Here are the examples as follows:
Encoding / Serialization to JSON File
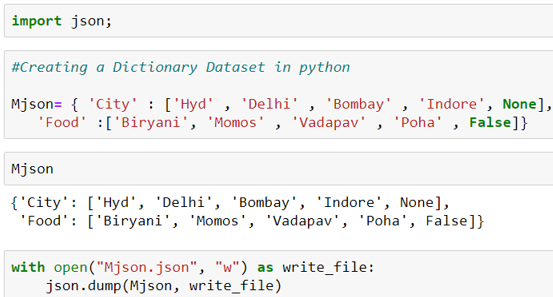
The task is to create one standard Python dictionary and then encode the same into a file. Here we will take the None and False types from Python and observe how the same has been changed in a file.
Code:
import json
#Creating a Dictionary Dataset in python
Mjson= { 'City' : ['Hyd' , 'Delhi' , 'Bombay' , 'Indore', None],
'Food' :['Biryani', 'Momos' , 'Vadapav' , 'Poha' , False]}
# Encoding to json file.
with open("Mjson.json", "w") as write_file:
json.dump(Mjson, write_file)After executing this code check in the directory of Python code, the Mjson.json file would have been created.
Output:
The conversion changes “None” to “null” and “False” to “false.”
Decoding / Deserialization to Python
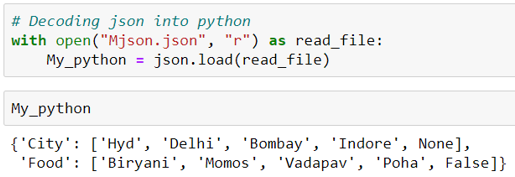
For the Mjson file, which we just now created, we will decode the same to Python again. We will observe the previous observation once again.
Code:
import json;
# Decoding json into python
with open("Mjson.json", "r") as read_file:
My_python = json.load(read_file)
My_pythonThe output of the above will be our Python dictionary. Observe the null again is converted to None.
Output:
Formatting of JSON String Using Python Encoder
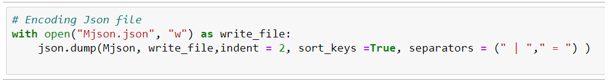
While encoding JSON, we can use some specified format defined to maintain clarity & format of data. Here we will use separators, indent, and sort keys. As we already have a JSON file, we will modify the existing one.
Code:
with open("Mjson.json", "w") as write_file:
json.dump(Mjson, write_file, indent= 4, sort_keys =True, separators = (" | " , " = " ) )Output:
It’s purely the choice of the coder how JSON format is required.
Advantages
Let’s see some of the advantages in detail given below:
- JSON is a formation to transfer data from server to client and vice versa. HTML and XML provide static data, while most of the data we need is dynamic; in this case, it can help.
- When an Asynchronous request is sent to a server via browser or application, the server receives the request and returns data (whatever format is acceptable, the client needs data oIfow; if the format is Html format, it will give design as well as data, but the client already has designed it; it requires only data.
- In the server, the data will be in the form of objects with properties, making data complex data-type objects. Now for this, we have JavaScript Object Notation. JavaScript Object Notation makes processing complex data with multiple classes and objects easy.
- It is of utmost need to use JSON type in DS and ML research; Python provides solutions for the same. The server Serialises the objects, and the client de-serializes and reads them.
Conclusion
Various JavaScripts and APIs commonly create the format known as JavaScript Object Notation. With Python, one can communicate JSON files. Deserialization or decoding converts a json object into a Python dictionary in Python. Serialization or encoding converts a Python doc into a json object. This article covers both formats.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “JSON in Python” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.