Updated June 6, 2023
Introduction to J2EE Architecture
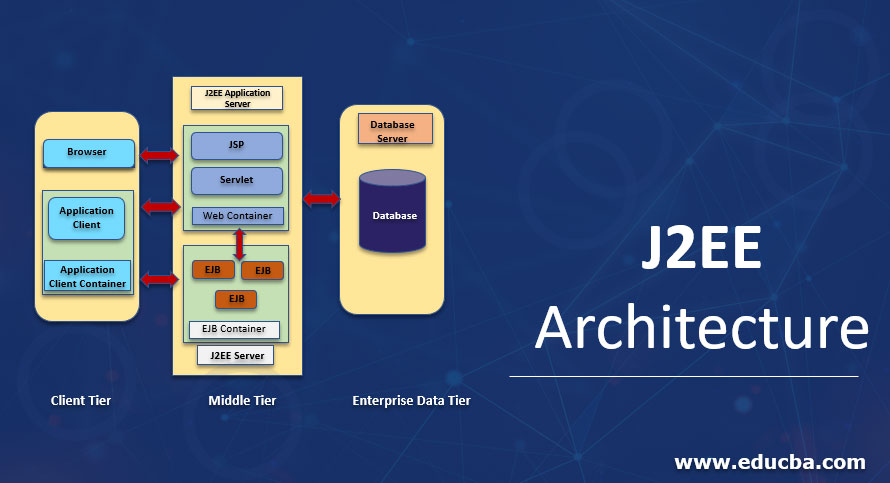
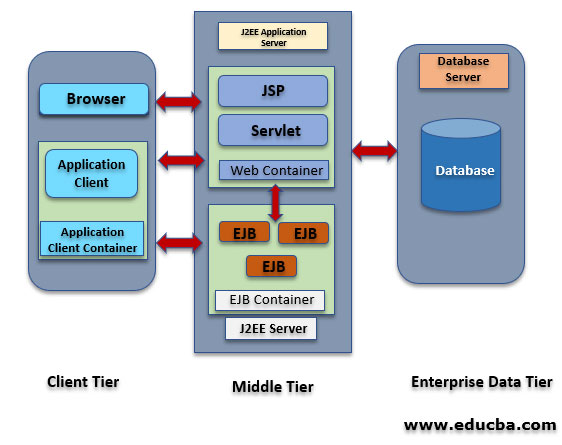
J2EE can be expanded as Java 2 Enterprise Edition, which offers a development environment for enterprise application creation and implementation. J2EE Architecture is made up of three tiers, such as the client tier is used as an interactive medium for the end user or the client & consists of web clients and application clients; the middle tier is used for defining logical functioning units & consists of web components and EJB components, and the enterprise data tier that is used for storage purposes in the form of relational database & consists of containers, components, and services.
J2EE Uses Three Tiers:
- Client Tier: The client tier consists of user programs that interact with the user for requests and responses.
- Middle Tier: Middle tier usually contains enterprise beans and web services that distribute business logic for the applications.
- Enterprise Data Tier: Enterprise data is stored in a relational database. This tier contains containers, components, and services.
Graphical Representation of J2EE Architecture
Usually, J2EE architecture consists of four tiers Client Tier, Web Tier, Enterprise JavaBean Tier, and Enterprise Information Tier. The middle tier consists of the Web Tier+EJB tier.
1. Client Tier
The client tier consists of programs or applications that interact with the user. Usually, they are located on a different machine from the server. Client tier prompts the user inputs into user requests, then forwarded to the J2EE server, then processed result returned to the client. A client can be a web browser, standalone application, or server on a different machine.
Clients can be classified as Web Clients and Application Clients.
Web Clients:
Web client consists of dynamic web pages of various mark-up languages generated by web components running in web tier or web browser, which renders pages received from the server. Web clients are also called thin clients that usually do not perform things like query databases or execute business rules. Thin clients offload heavy operations to enterprise beans that execute within the J2EE server.
Applets: Web pages received from the web tier embedded in an Applet. These run on a web browser. Web components are APIs for creating a web client program. Web components enable the user to design cleaner and more modular applications. They provide a way to separate application programming.
Application Clients:
The application client runs on the client machine and handles the tasks that give richer user interfaces. Typically the GUI is created by Swings or AWT. Application clients can access EJBs running in the business tier using an HTTP connection.
2. Middle Tier (Web tier & EJB Tier)
Below are the components of the Middle Tier:
Web Tier /Web Component:
Web components can be servlets or JSP pages. Servlets can dynamically process the request and generate the responses. Compared to JSP and servlets – servlets are dynamic pages to some extent, but JSP pages are static.
The Client’s Static HTML programs and applet codes are bundled in the web tier/ Web Component during the application assembly process. These HTML and applets are not considered elements of web components. Server-side utility classes are bundled with web components but are not considered web components themselves.
The web tier might include EJB components for processing user inputs and sending the input to Enterprise Bean running in the business tier.
EJB Tier /EJB Component:
Enterprise components usually handle business code that is logic to solve particular business domains such as banking or finance handled by enterprise bean running in the business tier.
If necessary, Enterprise Container receives data from client processes and sends it to the enterprise information system for storage. Enterprise Bean also retrieves data from storage, processes it, and sends it back to the client.
Three kinds of beans:
- Session Bean: The client uses a Session Bean for a conversation. Once the client finishes the execution, the session bean destroys.
- Entity Bean: Holds the particular data stored in a database. Once the server shuts down or the client finishes its execution, the data of the entity bean is preserved.
- Message Driven Bean: Message Bean combines the properties of Session Bean and JMS. Which benefits the business component to receive messages asynchronously.
3. Enterprise Information System
This tier comprises database servers, enterprise resource planning systems, and other data sources. Resources are typically located on a separate machine from the J2EE Server and accessed by components on the business tier.
Technologies used in EIS Tier:
- Java Database Connectivity API (JDBC).
- Java Persistence API.
- Java Connector Architecture.
- Java Transaction API.
Containers in J2EE Architecture
Given below are containers in J2EE Architecture:
1. Application Client Container
The container includes a set of classes, libraries, and other files required to execute client programs in their own JVM. Manages the execution of client components. It also provides services that enable Java client programs to execute. This container is specific to the EJB container. Compared to other containers in J2EE, this container is lightweight.
Features:
- Security: Responsible for collecting authentication Data such as User Name and Password and sending data over RMI/IIOP to the server. The server then processes the data using the JAAS module. Even though the client container provides authentication techniques, these are not under the control of the application client.
- Naming: Allows the application clients to use Java Naming and Directory Interface (JNDI).
2. Web Container
A web Container is a web server component that interacts with Java servlets. A web container is responsible for managing the servlet lifecycle and mapping URLs.Web container handles a request from Servlets, JSP files, and other files, including server-side code.
Web container implements a web component contract of the J2EE architecture. This provides a runtime environment for additional web components’ security, transaction, deployment, etc.
3. EJB Container
Enterprise Java bean container consists of server components that contain business logic. Provides local and remote access to enterprise beans.EJB container is responsible for creating enterprise bean and binding enterprise bean to the naming services.
Installing more than one module within a single EJB container is possible. It performs transactional actions like – Start Transaction, Commits or Rollback transactions, manages various connection pools for database resources, and synchronizes bean instance variables with corresponding data items stored in the database.
4. Applet Container
The container where the client’s Applet programs run may be in a web browser or other applications that support applet programming. Applets are subject to more restrictions due to the sandbox security model, which limits access to the client machine. Web servers download normal web pages and execute them on the client browser.
Conclusion
J2EE Three Tier Architecture which composed of three tiers of logical computing. This helps in developing specific client-server-based applications. It also helps development by separating the User Interface, business logic, and data storage layer. Gives greater flexibility for development for updating specific application parts without affecting the rest. This flexibility can improve overall development and upgrade and replace data from a specific tier without affecting the system.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to J2EE Architecture. Here we discuss the introduction, graphical representation, and containers in J2EE Architecture. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –