Updated March 22, 2023
Introduction to Variables in PowerShell
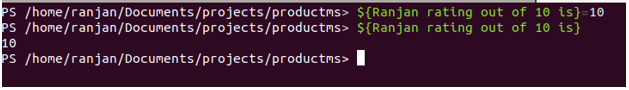
Variables in PowerShell are automatic by default, that means according to your assigned data it will select a data type, for example, if it is $age=1 than it will be int32 and if It is $student =” Ranjan” than it will be a string. Variable in PowerShell starts with $ symbol. Variables in PowerShell are not case sensitive and they may contain any letters, numbers and special characters. In the case of special characters they need to enclose with {}, for example, ${Ranjan rating out of 10 is}=10. And we can get output from variable ${Ranjan rating out of 10 is} is 10. In the very simple word variable is a placeholder for any important data like any string or any integer. An example in the below screen with variable with special characters.
How to Declare Variables in Powershell?
The variable declaration means, naming a variable with its data type or its basic property. In PowerShell Naming a variable is just informing about the variable to memory. Once we assign something like string or integer, it will be informed to memory about the data type of variable And according to that, it’s allocation in memory done at that time only.
By declaration, we are informing the system about the variable type and its names only, in the declaration we are not defining memory size needed to hold variable. Memory size needs to hold any variable part is done by the system at the time of initializations.
PowerShell supports many other data types other than string and integer, such as floating-point numbers, decimal, and Boolean values, etc. You don’t have to explicitly declare the data type of a variable; PowerShell automatically chooses the data type at the time of initialization. PowerShell also provides data type conversion at the time of initialization.
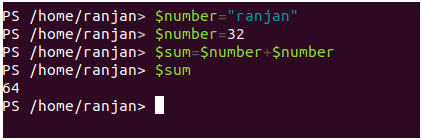
$number ="Ranjan"//string
$number =34//int32
$sum=$number+$number
In PowerShell, we can strictly defined data type for any variables. Below example, we have defined variable strictly so we can only assign those data which are relevant to its data type.
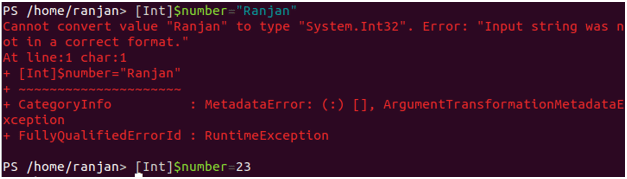
[Int]$number="Ranjan"//throw an error as we defined it as Int and assigning the value of the string
[Int]$number=23
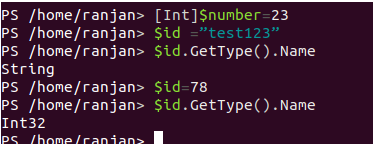
Automatic conversion of the variable in PowerShell. In the below example Initially, we assigned a string and we checked it’s data type we found it was a string and we assigned an integer value and we checked it’s data type and we found it was int32.
$id ="test123"
$id.GetType().Name
$id=78
$id.GetType().Name
How to Initialize Variables in Powershell?
Initialization means telling the system about the size of memory needed to hold the variable as we are initially assigning something. We can initialize our variable according to our further uses.
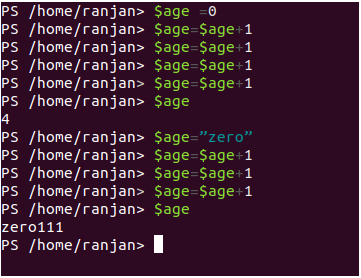
For example, each year age is increasing below.
$age =0
$age=$age+1
$age=$age+1
$age=$age+1
$age=$age+1
So on. But if we Initialise like below
$age="zero"
$age=$age+1
$age=$age+1
$age=$age+1
$age=$age+1
Hence we found at the time of initialization we should initialize with integer value or string according to our users in further programming.
Rules and Regulations for Variables in Powershell
Let’s discuss some rules of PowerShell variables. PowerShell variables always start with $ symbol and it can contain a combination of letters, numbers, and underscores. If you really feel it is important to use characters other than this, you have to enclose them in curly braces. You should not use the name of variables that have been pre-defined and try not to assign the string to a strictly int defined variable else it will throw an error.PowerShell has reserved variables such as $$, $?, $^, and $_ that contain alphanumeric and special characters.
Here are examples of valid variable names:
$schoolType, $schoolType_1, ${school-type not known}
Below is some wrong way for variable naming.
schoolName, $school-type, $school type
Example:
Let us look at the example mentioned below:
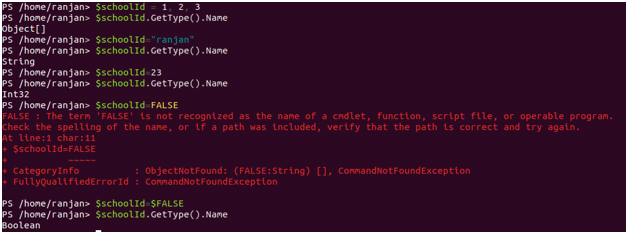
$schoolId = 1, 2, 3 //assigning array to variable
//Checking it’s data type , we can see it is an Object type
$schoolId.GetType().Name
Object[]
$schoolId="ranjan" //assigning string to same variable
//Checking it’s data type , we can see it is a String type
$schoolId.GetType().Name
String
$schoolId=23 //assigning int value to same variable
//Checking its data type, we can see it is a Int32 type
$schoolId.GetType().Name
Int32
$schoolId=FALSE //wrong way of assignment throw an error
$schoolId=$FALSE //correct way of assignment
//Checking its data type, we can see it is a Boolean type
$schoolId.GetType().Name
Boolean
In the above example, we first assigned array to a variable than string name and then numeric suddenly it throws an error when we assigned FALSE as $FALSE is the correct way to assign any boolean value.
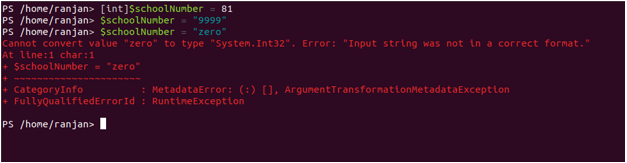
[int]$schoolNumber = 81 //Strictly defining data type of variable to integer
$schoolNumber = "9999" //Here string of numeric will be converted to an integer
$schoolNumber = "zero" //As we have defined integer so we can not assign string
It will throw an error, see in the below screen.
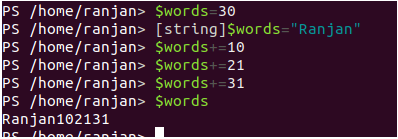
[string]$words = "Ranjan"
$words = 30 // The integer is converted to a string.
$words += 10 //Treat $words as string only
$words+= 21 //keep concatenate as string
$words+= 31
In the above code block, because we have defined $words as a string so it will not perform any arithmetic operation here it will treat all these variables as a string and concat them as a string. The screens of the above execution are given below.
Let’s understand Date datatypes in PowerShell,
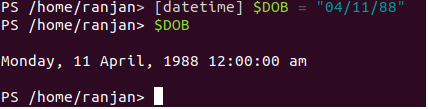
[datetime] $DOB = "04/11/88" //It will convert string of date to Date objects.
$DOB
Output: Monday, 11 April, 1988 12:00:00 am
The screen is given below,
In the above example, we are just passing date as a string variable and PowerShell converts it to date and time object.
Conclusion
To conclude, I hope I was able to explain variables in the simplest way. PowerShell gives a lot of flexibility for variable defining and it provides auto type casting which makes it very powerful and easy to use.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Variables. Here we discuss how to declare and initialize variables in Powershell along with the rules and regulations. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –