Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Get-Date
Get-Date cmdlet in PowerShell is used to get the Date and Time of the System. It uses the local computer system’s date and time. Its data type is DateTime. The output format of the Date and Time depends on the computer’s cultural settings that can be determined by the below syntax and command.
Syntax:
Following are the syntax for PowerShell Get-Date:
Get-Date
[[-Date] <DateTime>]
[-Year <Int32>]
[-Month <Int32>]
[-Day <Int32>]
[-Hour <Int32>]
[-Minute <Int32>]
[-Second <Int32>]
[-Millisecond <Int32>]
[-DisplayHint <DisplayHintType>]
[-Format <String>]
[-UFormat <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Code:
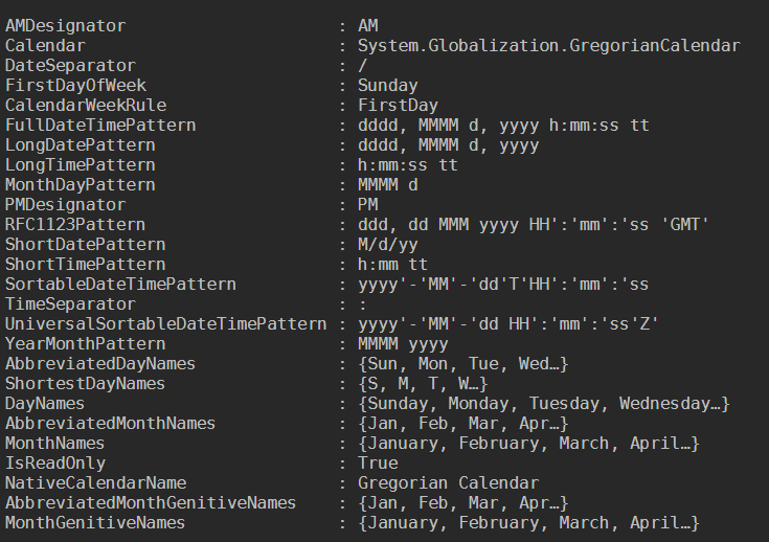
(Get-Culture).DateTimeFormat
Output:
Parameters of PowerShell Get-Date
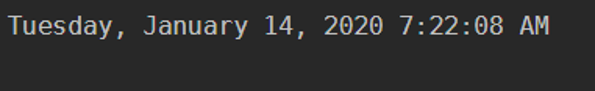
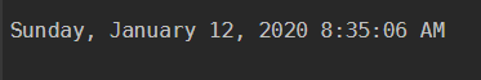
The default output of the command Get-Date is displayed in the below format.
Code:
get-date
Output:
Below parameters are used by Get-Date cmdlet to format the command output.
1. Date
When you use Date as a property like (Get-Date). Date, it specifies the date and time both. It displays the time 00:00:00 by default along with the system’s current date. Time property will give you the current system time. The output will be the DateTime data type only. And when you specify –Date parameter and date followed by it, it displays the specific date. For example Get-Date –Date “01/01/2010 22:00:00”. This action will not change the date/time of the system.
2. Year
When you specify Year as a property like (Get-Date). The year will provide the current system year. The output of the command is Int32 datatype. You can use –Year parameter to display the different year.
3. Month
When Month is mentioned as property like (Get-Date). Month it will display the current system’s month as an output. The output will be in the Int32 data type format. You can use –Month parameter to display the different month. The value should be between 1 to 12.
4. Day
When Day is specified as a property like (Get-Date).Day, it will display the current system’s day as an output. The output will be in the Int32 format. You can use –Day parameter to display a different day. The value should be between 1 to 31.
5. Hour
When Hour is specified as a property like (Get-Date).Hour, it will display the current system’s hour as an output. The output will be in the Int32 format. You can use –Hour parameter to display the different hours. The value should be between 1 to 24.
6. Minute
When Minute is specified as a property like (Get-Date).Minute, it will display the current system’s minute as an output. The output will be in the Int32 format. You can use –Minute parameter to display the different minutes. The values should be between 1 to 60.
7. Second
This parameter is to set and display the seconds of the current system and output will be in Int32 format. When you set seconds, it will just a temporary display of the seconds not setting it permanently. The value should be 1 to 60.
8. Millisecond
This parameter is to set and display the millisecond of the current system and output will be in Int32 format. When you set milliseconds, it will just a temporary display of the seconds not the setting permanently. The value should be 1 to 999.
9. DisplayHint
This parameter displays only Date or only Time or DateTime, depends on the specified argument.
Accepted values are,
- Date: Display only system current date.
- Time: Display the only system current time.
- DateTime: Display only system DateTime
Examples to Implement PowerShell Get-Date
Below are the examples that implement PowerShell Get-Date:
Example #1
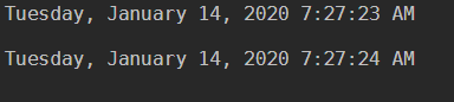
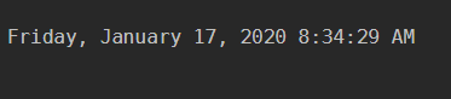
The get-date command will give you the current Date and Time of the system. A similar output can be fetched by the below commands.
Code:
(Get-Date).DateTime
Get-Date -DisplayHint DateTime
Output:
Example #2
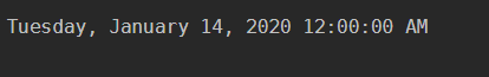
To display the Date, you can use two commands.
1. (Get-Date).Date: This command will display the date along with 00:00:00 or 12:00:00 time format.
Code:
(Get-Date).Date
Output:
2. Get-Date -DisplayHint Date: This command will display only the date of the system.
Code:
Get-Date -DisplayHint Date
Output:
3. To display the Time, below command can be used
Code:
Get-Date -DisplayHint Time
Output:
Example #3
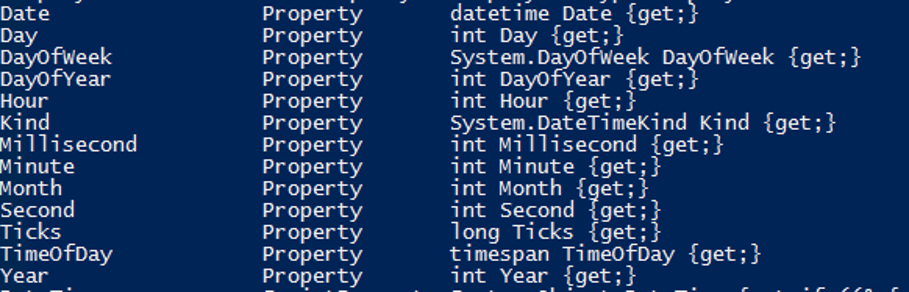
Below properties are supported by the Get-Date command.
Above each property has the following commands:
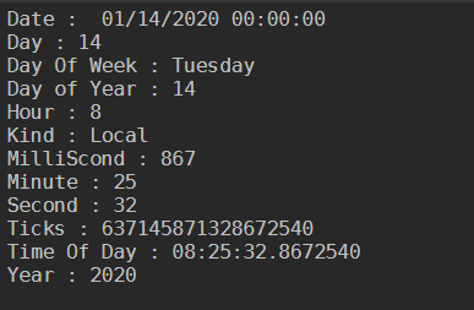
Code:
$d = Get-Date
"Date : " + $d.Date
"Day : " + $d.Day
"Day Of Week : "+ $d.DayOfWeek
"Day of Year : "+ $d.DayOfYear
"Hour : " + $d.Hour
"Kind : " + $d.Kind
"MilliScond : " + $d.Millisecond
"Minute : " +$d.Minute
"Second : " +$d.Second
"Ticks : " + $d.Ticks
"Time Of Day : " + $d.TimeOfDay
"Year : " + $d.Year
Output:
Example #4
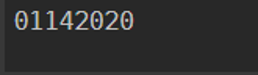
To format the output using -Format parameter, Here, we will display Date in “MMddyyyy”
Code:
Get-Date -Format "MMddyyyy"
Output:
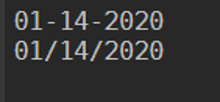
You can also put the separator between them, For example,
Code:
Get-Date -Format "MM-dd-yyyy"
Get-Date -Format "MM/dd/yyyy"
Outputs:
All of the above outputs will be in String format.
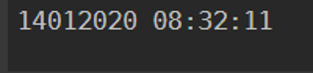
Example #5
To get the output including hours, minutes and seconds,
Code:
Get-Date -Format "ddMMyyyy HH:mm:ss"
Outputs:
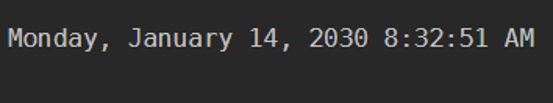
Example #6
You can use the Get-Date command to temporarily change in time or date. For example, the below command will display the year 2030 in output, the rest date and time will remain the same.
Code:
Get-Date -Year 2030
Output:
Similarly, you can change the day, hour, date, minute, seconds, etc.
Example #7
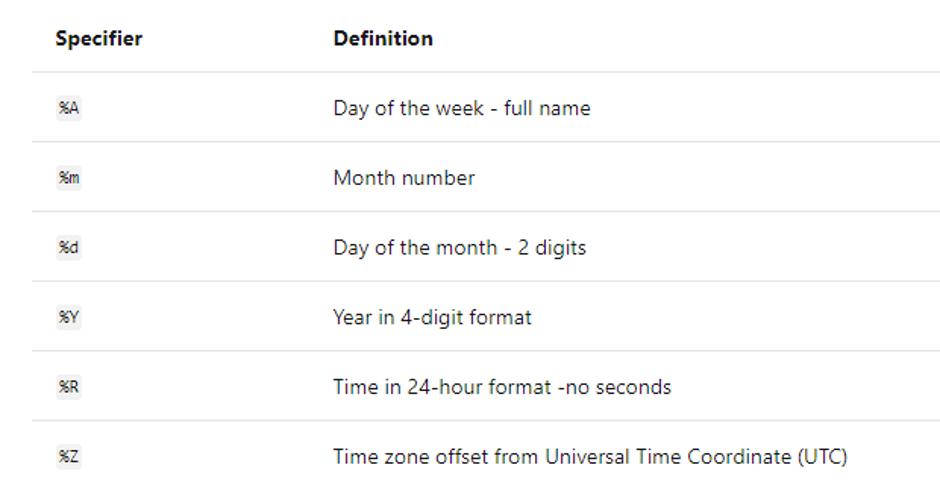
To change output in UFormat, The table mentioned below will describe UFormat.
Code:
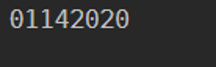
Get-Date -UFormat "%m%d%Y"
Output:
Similarly, you can use different combinations below.
Example #8
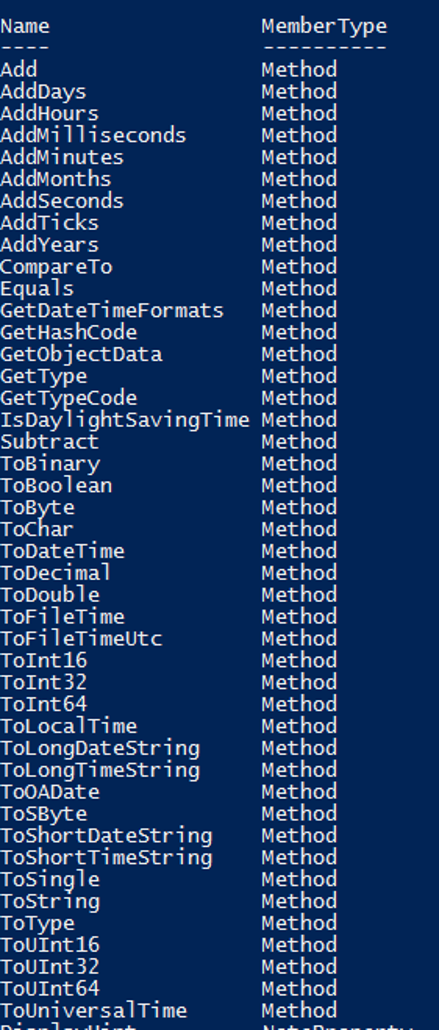
There are also methods available for Get-Date as below.
If you want to get the Date and time after 3 days,
Code:
(Get-Date).AddDays(+3)
Output:
To get the date/time of 2 days back,
Code:
(Get-Date).AddDays(-2)
Output:
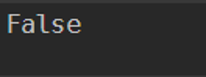
Similarly, you can use other methods to add/minus the hours, months, seconds, etc with the methods described in the snapshot above. You can also check if daylight saving is enabled for the current date with IsDaylightSavingTime() and output will be in the boolean format (True or False).
Code:
(Get-Date).IsDaylightSavingTime()
Output:
Conclusion
Get-Date is useful when formatting outputs that involve date and time. You can extract data by modifying dates as well, which is assigned to a temporary variable. To set the date of the system, use the Set-Date command.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Get-Date. Here we discuss syntax, the parameters are used by Get-Date cmdlet and the examples that implement PowerShell Get-Date. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –