Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Set-Variable in PowerShell
The following article provides an outline of the set-variable in Powershell. A variable is a block of memory that can be used to store values. PowerShell variables are denoted using the “$” symbol. A variable name can be anything from numbers, alphabets or even underscores. PowerShell variables are not case sensitive. PowerShell variables are not just text-based, instead, they are objects like that of Microsoft.Net objects. There are different types of variables like User-Created variables, automatic variable and preference variables. Set-variable is the cmdlet to set the value of a variable. In case if the variable doesn’t exist, the set-variable cmdlet creates one and then assigns the value to it.
Syntax for Set Variable in PowerShell
The following is the syntax of the set-variable cmdlet.
Input:
Get-Help Set-Variable
Output:
Example:
Set-Variable -Name "test" -Value "test variable"
The above cmdlet sets the value of a variable called test to “test variable”. If the variable doesn’t exist, it will be created.
Parameters of Set Variable in PowerShell
The following parameters are given below:
1. Confirm: This is used to get confirmation before running the cmdlet. This is an optional parameter. Its type is a switch. Its default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wildcard characters.
2. Exclude: This specifies the list of items that should be excluded while executing the cmdlet. It can be a path or a pattern. Its type is a string. Its type is a switch. Its default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input whereas it can accept wildcard characters. It is also an optional parameter.
3. Force: This allows the creation of a variable as same as an existing read-only variable. It can also be used to change the value of a read-only variable. This is an optional parameter. Its type is the switch. Its default value is false. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wildcard characters.
4. Include: This specifies the list of items that should be included while executing the cmdlet. It can be a path or a pattern. Its type is a string. Its type is the switch. Its default value is none. It doesn’t accept pipeline input whereas it can accept wildcard characters. It is also an optional parameter.
5. Name: This specifies the variable name and it’s a mandatory parameter. Its type is a string. Its default value is none. It accepts pipeline input whereas wild card characters are not permitted.
6. Option: This is used to specify the variable’s options property. It is default value is none. Its type is the scope of items. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wildcard characters. This is an optional parameter.
Its applicable values are as follows
- Note: This is the default value; no options are set.
- Readonly: The variable’s value cannot be changed except using the force parameter. The variable can also not be deleted.
- Constant: The variable’s value cannot be changed or deleted. A variable can be made constant only during its creation.
- Private: The variable is valid only in the current scope.
- AllScope: The variable can be copied to any scope that may be created.
7. Scope: This parameter specifies the scope of the variable. The available scopes are Global, local, script and Private. Local is the default scope of a variable. Its type is a string. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wildcard characters. This is an optional parameter.
8. Value: This is used to specify the variable’s value. Its type is the object and default value is none. It can accept pipeline input but doesn’t accept wild card characters.
9. Visibility: This denotes whether the variable created is available for outside the session in which it is created. Its value is either public or private. By default, it is public, which means it is available even outside the session. Private denotes the variable is not available outside the session. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wildcard characters.
10. WhatIf: This shows the actual output if the cmdlet is run. It’s like a demo of the cmdlet. Type is a switch. The default value is false. It doesn’t accept pipeline input and wildcard characters.
Examples of Set-Variable in PowerShell
Below are the examples for the set-variable in PowerShell
Example #1
Set and Get a Variable
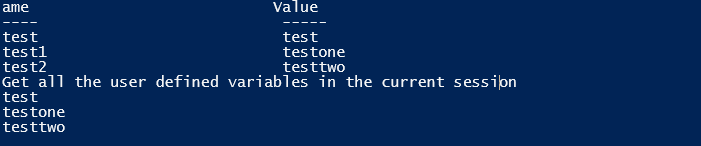
Input:
Set-Variable -Name "test" -Value "test"
Get-Variable -Name "test"
Set-Variable -Name "test1" -Value "testone"
Get-Variable -Name "test1"
Set-Variable -Name "test2" -Value "testtwo"
Get-Variable -Name "test2"
Write-Host "Get all the user-defined variables in the current session"
Get-Variable test* -ValueOnly
Output:
Example #2
Difference between Private and Public Variable
Input:
Write-Host "Example of the public variable"
Set-Variable -Name "PubVar" -Visibility Public -Value "This is a Public Variable"
$pubvar
Write-Host "Example of the private variable"
Set-Variable -Name "PriVar" -Visibility private -Value "This is a private Variable"
$PriVar
Output:
Working with Environment Variables
Below are the two examples for working with environment variables
1. Creating a local scoped Environment Variable
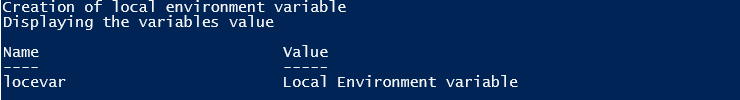
Input:
Write-Host "Creation of local environment variable"
$env:locevar = 'Local Environment variable'
Write-Host "Displaying the value of the variable"
Get-ChildItem Env:locevar
Output:
In the above example, the created variable will be available only for the current PowerShell session. Once the session is closed, the variable will vanish.
2. Creating an environment variable for the machine
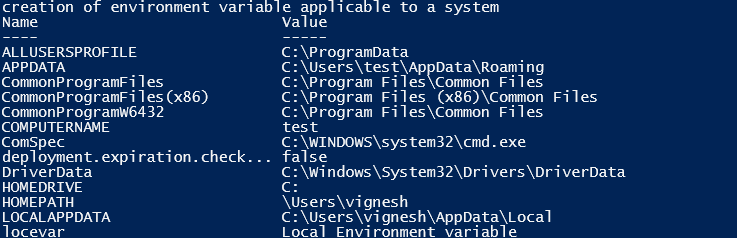
Input:
Write-Host "creation of environment variable applies to a system"
[System.Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('envvar','environment variable',[System.EnvironmentVariableTarget]::Machine)
Set-Location Env:
Get-ChildItem
Output:
Conclusion – Set-Variable in PowerShell
Thus, the article explained in detail about the set-variable cmdlet along with its different scopes. It also explained about environment variables, how to create and access them. To learn in-depth about the cmdlet it is advisable to create sample programs and have fun working around them.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Set Variable in PowerShell. Here we discuss the parameters of Set Variable in PowerShell along with working with Environment Variables and respective examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more–