Differences Between Hadoop vs Teradata
Hadoop
Hadoop is an open-source Apache project which provides the framework to store, process and analyze a large volume of data. Hadoop’s core components are the Java programming model for processing data and HDFS (Hadoop distributed file system) for storing the data in a distributed manner.
Hadoop cluster consists of 1 ton (may vary as per the requirement) number of nodes of commodity (less expensive) hardware, and the task is performed on the same node on which data is present and if suppose the data is distributed on 10 different nodes than the same job will run on all 10 nodes.
Hadoop works on the principle that if one node (computer) will complete a task in 10 hours, then 10 nodes should complete the task in one hour. Hadoop does not increase the processing of tasks. Rather, it distributes the task to multiple nodes, and all nodes work in parallel to complete the task in much lesser time; once all the jobs are completed, the data from each node is collected and combined back to give the output.
Teradata
Teradata consists of tables like any other traditional database and can be queried using query language similar to traditional databases.
Teradata utilizes a patented software called PDE (Parallel Database Extension), which is installed on the Teradata hardware component; this PDE divides the processor of a system into multiple virtual software processors where each virtual processor acts as an individual processor and is capable of performing all tasks independently.
Now, whenever data is queried, each processor will look for it only in its corresponding virtual memory. All virtual processors will work in parallel to search the data in their corresponding virtual memory. Due to its parallel processing, Teradata is faster with a great margin as compared to traditional databases.
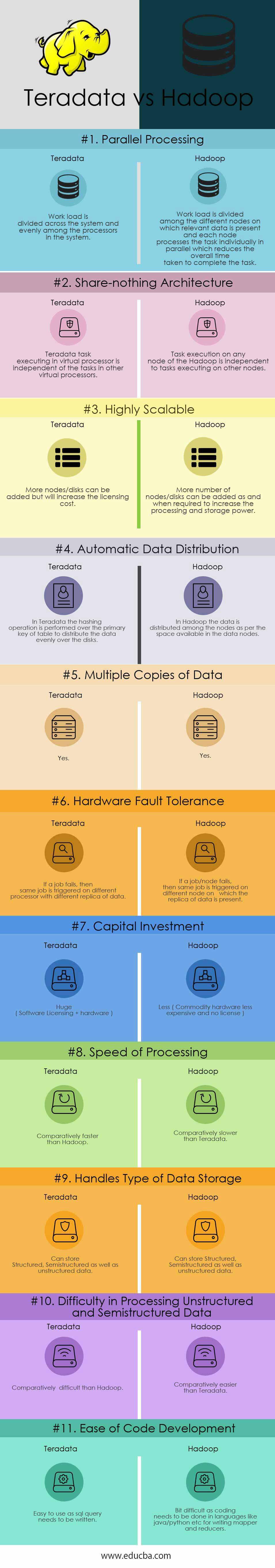
Head to Head Comparison Between Hadoop and Teradata (Infographics)
Below is the top 11 Comparison Between Hadoop and Teradata:
Key Differences Between Hadoop and Teradata
Below are the key differences between Hadoop and Teradata :
Technology difference:
Hadoop is a big data technology that stores a large amount of data in a distributed manner among multiple nodes. On the other hand, Teradata is a relational database warehouse that is implemented in a single RDBMS and serves as a central repository.
Cost factor:
The hardware used in the Hadoop Ecosystem is commodity hardware, so the overall cost of the Hadoop ecosystem is very less; on the other hand, Teradata has a licensing cost and hardware used is also comparatively expensive which makes the Teradata more expensive than Hadoop.
Type of data:
Hadoop can store and process any type of data by using multiple open-source BigData tools specially designed for the Hadoop ecosystem. Hadoop has many tools to process structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, whereas Teradata mainly deals with structured tabular format data.
Multiple languages support:
Hadoop supports multiple programming language executions in parallel in the Hadoop ecosystem, unlike Teradata, which uses a query language to perform the operations over data.
Performance:
Hadoop has its own data warehousing tool called Hive. Hive also does not have any concept of a primary key. At the same time, Teradata here gets the advantage as it supports a primary key, which also pushes the performance of querying data using Teradata.
Data security:
Teradata is much more secure as compared to Hadoop.
Schema:
A well-defined schema is required before loading the data into Teradata, whereas there is no such concern in Hadoop.
Comparison Table Between Hadoop vs Teradata
Below are the lists of points that describe the Differences between Hadoop and Teradata :
| Basis of Comparison | Teradata | Hadoop |
| Parallel Processing | The system divides the workload across its processors, distributing it evenly among them.
|
The system divides the workload among different nodes, each containing the relevant data. Each node independently processes its assigned task in parallel, resulting in a reduction in the overall time required to complete the task. |
| Share-nothing Architecture | Teradata task executing in a virtual processor is independent of the tasks in other virtual processors.
|
Task execution on any node of the Hadoop is independent to tasks executing on other nodes. |
| Highly Scalable | Adding more nodes or disks to the system is possible, but it will result in an increase in the licensing cost. | The processing and storage power can be increased by adding more nodes or disks as and when required. |
| Automatic Data Distribution | In Teradata, the hashing operation is performed on the primary key of a table to evenly distribute the data across the disks. | In Hadoop, the data is distributed among the nodes based on the available space in the data nodes. |
| Multiple Copies of the Data | Yes | Yes |
| Hardware Fault Tolerance | If a job fails, it will be automatically triggered on a different processor with a different replica of the data.
|
If a job or node fails, the same job will be triggered on a different node where a replica of the data is present. |
| Capital Investment | Huge( Software Licensing + hardware )
|
Less ( Commodity hardware ( less expensive ) and no license ). |
| Speed of Processing | Comparatively faster than Hadoop. | Comparatively slower than Teradata. |
| Handles type of Data Storage | Can store Structured, Semi-structured as well as unstructured data.
|
Can store Structured, Semi-structured as well as unstructured data. |
| Difficulty in processing Unstructured and Semi-structured data | Comparatively difficult than Hadoop. | Comparatively easier than Teradata. |
| Ease of Code Development | Easy to use as SQL query needs to be written. | Bit difficult as coding needs to be done in languages like Java/python etc, for writing mappers and reducers. |
Conclusion
So, here now, we can conclude whether one should go for Hadoop vs Teradata based on three major factors, i.e. investment cost, execution time, and type of data dealing with. If less investment cost is the major factor and users can compromise with execution time, then one must choose Hadoop over Teradata. If fast execution is a priority of the user and one can invest in the licensing cost of Teradata, then one must go for Teradata.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Hadoop vs Teradata” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.