Difference Between HDFS and HBase
In the article HBase vs HDFS, the data volume is increasing daily, and organizations need to store and process this huge volume of data. HBase, as well as HDFS, are one of the essential components of the Hadoop ecosystem, which help in storing as well as processing huge datasets. HDFS and HBase can handle the data well, whether structured, semi-structured, or unstructured. HDFS stands for the Hadoop Distributed File System, which manages data storage across a network of machines, and the processing of huge datasets is done using MapReduce. HDFS is suitable for storing large files with a streaming access pattern i.e. write the data once to files and read as many times as required. In Hadoop, HBase is the NoSQL database that runs on top of HDFS. HBase stores the data in a column-oriented form known as the Hadoop database. HBase provides consistent reads and writes in real-time and horizontal scalability.
HDFS (Hadoop Distributed File System)HDFS allows you to store vast amounts of data in a distributed and redundant manner, which runs on commodity hardware. HBase (Hadoop’s database) is a NoSQL database that runs on your Hadoop cluster.
Let us take a look at the components and architecture of HDFS and HBase, respectively:
Components of HDFS
- NameNode
- DataNode
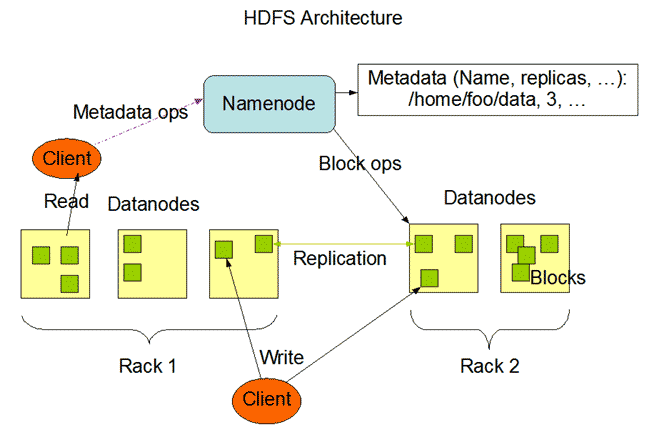
1. NameNode: NameNode can be considered as a master of the system. It maintains the file system tree and the metadata for all the files and directories present in the system. Two files, ‘Namespace image’ and the ‘edit log,’ store metadata information. Namenode knows all the data nodes containing data blocks for a given file. However, it does not store block locations persistently. The system reconstructs this information every time it starts from data nodes.
DataNode: DataNodes are slaves who reside on each machine in a cluster and provide the actual storage. It is responsible for serving, reading, and writing requests for clients.
HDFS Architecture:
Components of HBase
- Hbase master
- Region Server
- Region
- Zookeeper
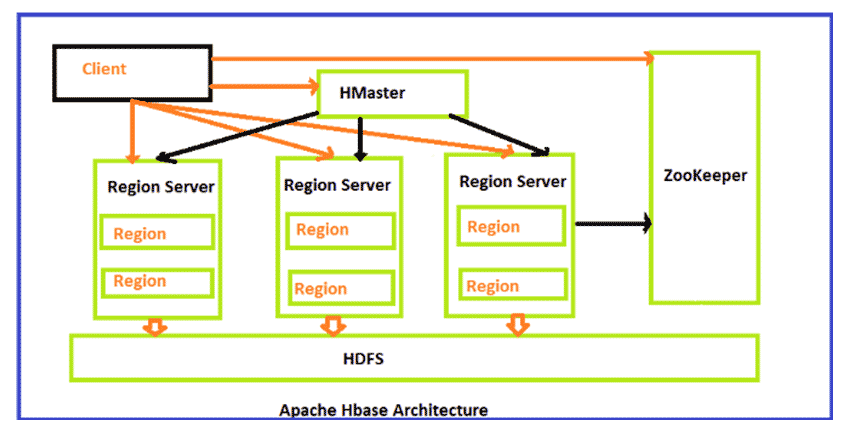
1. HMaster: It is the Master server in HBase architecture. It is the monitoring agent to monitor all Region Servers, and also it is the responsibility of HMaster to be the interface for all the metadata changes. It runs on NameNode.
2. Regions Servers: When Region Server receives, writes, and reads requests from the client, it assigns the request to a specific region where the actual column family resides. However, the client can directly contact Region servers; there is no need for HMaster’s mandatory permission to the client regarding communication with Region Servers. When client needs help with operations related to metadata and schema changes, they must request assistance from HMaster.
3. Regions: Regions are the essential building elements of the HBase cluster that consists of the distribution of tables and are comprised of Column families. It contains multiple stores, one for each column family. It consists of mainly two components, which are Memstore and Hfile.
4. ZooKeeper: In Hbase, Zookeeper is a centralized monitoring server that maintains configuration information and provides distributed synchronization. Distributed synchronization is to access the distributed applications running across the cluster to provide coordination services between nodes. If the client wants to communicate with regions, the server’s client has to approach ZooKeeper first.
HBase Architecture:
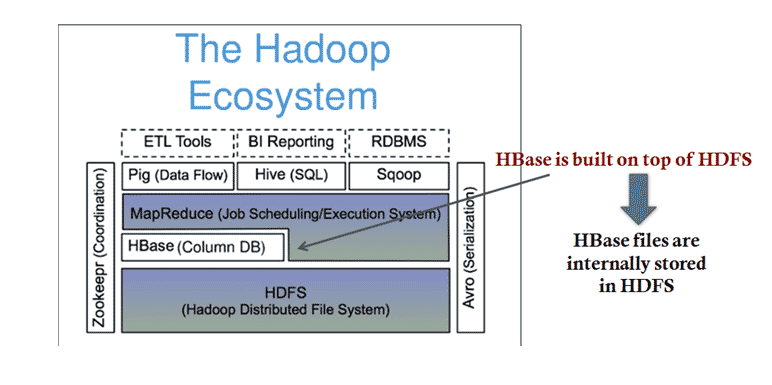
HBase is a part of Hadoop’s Ecosystem.
In-Depth Model:
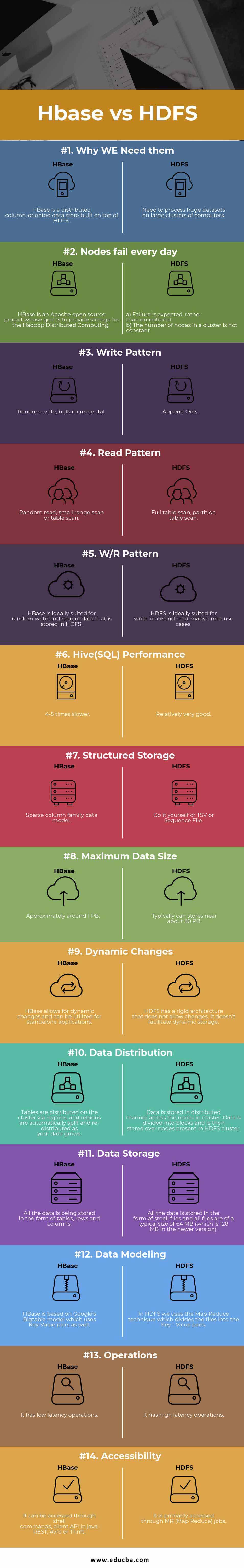
Head-to-Head Comparison Between HDFS vs HBase (Infographics)
Below are the Top 14 Comparison between HDFS vs HBase:
Key Differences Between HDFS vs HBase
Below is the difference between HDFS vs HBase:
- HDFS stores large files well because it is a distributed file system. HBase, however, is built on top of HDFS and offers fast record lookups (and updates) for large tables.
- HDFS has based on the GFS file system. But HBase is distributed – uses HDFS for storage, column – Oriented, Multi-Dimensional (Versions), and Storage System.
- HDFS uses HIVE as one of its components for the quire language, which is HIVE Query Language(HQL), but Hbase is NOT a SQL Database which means:- No Joins, no query engine, no datatypes, no (damn) SQL, No Schema and no DBA needed.
- As HDFS is a distributed storage unit hence has no specific language other than the commands used like the UNIX flavor like, for example:- Hadoop dfs -mkdir /foodir
- hadoop dfs -cat /foodir/myfile.txt
- hadoop dfs -rm /foodir/myfile.txt
But on the other hand, HBase has its interface in the form of HBase Shell, for example:
- hbase(main):003:0> create ‘test’, ‘cf’
0 row(s) in 1.2200 seconds
- hbase(main):004:0> put ‘test’, ‘row1’, ‘cf:a’, ‘value1’
0 row(s) in 0.0560 seconds
- hbase(main):005:0> put ‘test’, ‘row2’, ‘cf:b’, ‘value2’
0 row(s) in 0.0370 seconds
- hbase(main):006:0> put ‘test’, ‘row3’, ‘cf:c’, ‘value3’
0 row(s) in 0.0450 seconds
- hbase(main):007:0> scan ‘test’
ROW COLUMN+CELL
row1 column=cf:a, timestamp=1288380727188, value=value1
row2 column=cf:b, timestamp=1288380738440, value=value2
row3 column=cf:c, timestamp=1288380747365, value=value3
3 row(s) in 0.0590 seconds
HDFS vs HBase Comparision Table
Following is the comparison table between HDFS vs HBase
| Basis for Comparison | HDFS | HBase |
| Why We Need Them | Need to process huge datasets on large clusters of computers. | HBase is a distributed column-oriented data store built on top of HDFS. |
| Nodes Fail Every Day |
|
|
| Write Pattern | Append Only | Random write, bulk incremental |
| Read Pattern | Full table scan, partition table scan | Random read, small range scan, or table scan |
| W/R Pattern | HDFS ideally suits use cases where data is written once and read repeatedly. | HBase is ideally suited for random writing and reading of data stored in HDFS. |
| Hive(SQL) Performance | Relatively very good. | 4-5 times slower. |
| Structured Storage | Do it yourself or TSV or Sequence File. | Sparse column family data model. |
| Maximum Data Size | Typically can store near about 30 PB. | Approximately around 1 PB. |
| Dynamic Changes | HDFS has a rigid architecture that does not allow changes. It doesn’t facilitate dynamic storage. | You can use HBase for standalone applications and make dynamic changes to it. |
| Data Distribution | Data is stored in a distributed manner across the nodes in a cluster. Data is divided into blocks and then held over nodes in the HDFS cluster. | Tables are distributed on the cluster via regions, and regions are automatically split and re-distributed as your data grows. |
| Data Storage | All the data is stored in the form of small files, and all files are of a typical size of 64 MB (which is 128 MB in the newer version) | The data is stored in tables, each consisting of rows and columns. |
| Data Modeling | In HDFS, we use the Map Reduce technique, which divides the files into Key-Value pairs. | HBase is based on Google’s Big Table model, which uses Key-Value pairs. |
| Operations | It has high-latency operations. | It has low-latency operations. |
| Accessibility | It is primarily accessed through MR (Map Reduce) jobs. | You can access it through shell commands or client APIs in Java, REST, Avro, or Thrift. |
Conclusion
Overall, HDFS and HBase have excellent technologies on their own. The creators created HDFS and HBase to store the Big Data and make it easy to access and compute them. Both HDFS and HBase go side by side as one HDFS reserves the data, and the other one, HBase, puts a schema on the data on how to store and retrieve it later for the client’s usage.
Hbase is one of the NoSQL column-oriented distributed databases available in apache foundation. HBase gives more performance for retrieving fewer records rather than Hadoop or Hive. It’s straightforward to search for given any input value because it supports indexing, transactions, and updating. We can perform online real-time analytics using Hbase integrated with the Hadoop ecosystem. It has an automatic and configurable sharding for datasets or tables and provides restful APIs to perform the MapReduce jobs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to HDFS vs HBase. Here we have discussed HDFS vs HBase head-to-head comparison, key differences, and a comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –