Updated May 15, 2023
What is Gray Box Testing?
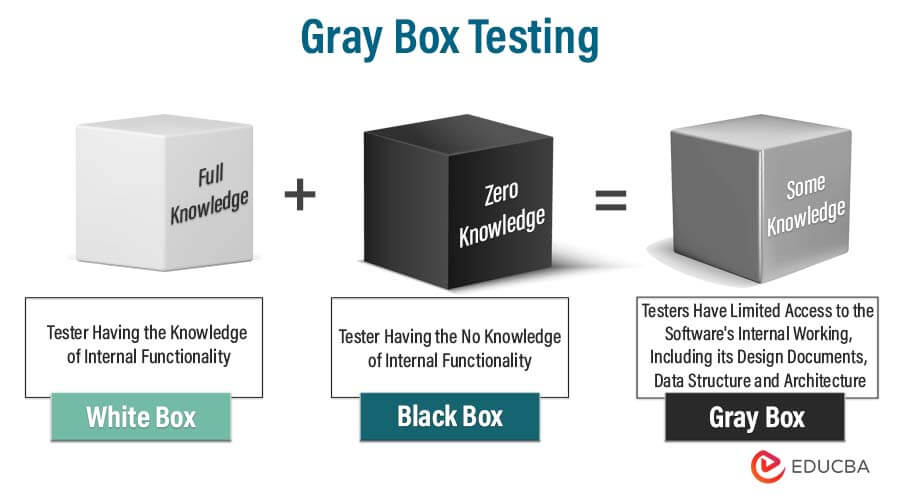
The term “Gray Box Testing” refers to a testing technique that combines aspects of both white-box and black-box testing. It is also sometimes called “Transparent Box Testing.” This approach involves testing an application’s software with limited knowledge of the underlying code that the application is built upon.
Gray Box Testing is a type of functional testing that aims to verify the behavior of an application’s code to some degree while considering its expected internal functionality. This testing method typically involves multiple stages throughout the Testing Life Cycle, as it encompasses both code and functionality testing.
Overall, Gray Box Testing provides a balance between the in-depth analysis of white-box testing and the external perspective of black-box testing. By utilizing this approach, testers can uncover potential issues in an application while also ensuring that it meets the expected functional requirements.
Understanding Gray Box Testing
Gray box testing is a product of Black Box Testing and White-box Testing. Black Box Testing means the tester has no knowledge of how the software works inside. Testers conduct this type of testing at the user level, verifying whether the software achieves the desired end result, without having knowledge of whether the code is functioning correctly at the level of loops and breaks within the software. So, the Software Testers are the ones who generally are responsible for Black Box Testing. Exactly opposite is White Box Testing. This type of testing is done mostly by the Software Developers as they check whether a particular result is being obtained at a particular break. In white-box testing, the testers (generally developers) have the knowledge of how the software is internally working.
As told earlier, in Transparent Box, for testing purposes, the tester enters some dummy values to check the correct flow of the output. So for using Transparent Box, the tester needs to have knowledge of both software development and testing so as to check the correct flow.
Examples
As we know by now, only a partial part of the logic is known to the tester in Transparent Box; it becomes a middle way in which the user can test the logic or software. The best example to explain the same would be; in certain software, the user needs to use some third-party application. Developers are only given access to a portion of the application when it is in use. So, now this can only be checked using the input data and some of the part which has been exposed. This is a perfect example of how Transparent Box works.
Another example would be the working of HTML links. The tester checks for the links. Some of the links he may click may or may not open the correct page. When the link does not go to the expected page, the tester can change the link address from the partially exposed code and correct it.
Another example of Transparent Box testing is the use of data input validations. Many of us have encountered this while entering information online, where errors occur if we enter incorrect data, such as ‘[email protected].’ In such cases, the input is identified as incorrect, and an error message is displayed. The tester will rectify this at their end by disabling the code.
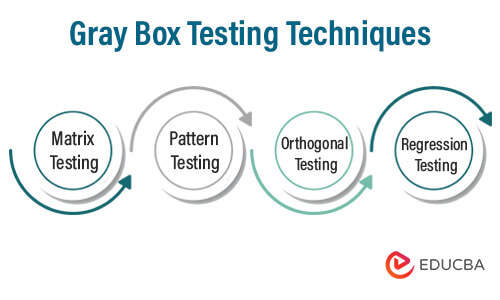
Gray Box Testing Techniques
Some of the techniques are listed below:
- Matrix Testing: Developers define the entire variable that might be used during the execution of the software. Each of these variables has a technical and business risk associated with it. During the matrix testing phase, testers assess the risks associated with the software.
- Pattern Testing: The team performs an analysis on the software’s past failures. Why and how the software has failed is taken into account and logged for future reference. This helps in designing test cases in the future, which will not let the software fail.
- Orthogonal Testing: Developers typically use this method when dealing with complex software systems that have a relatively small data set. Testers use all possible permutations and combinations to evaluate the software and assess its performance.
- Regression Testing: When making specific changes to the software to achieve the desired output, testers perform regression testing to ensure that the modifications do not affect the output, and the software continues to work as expected, producing the desired result.
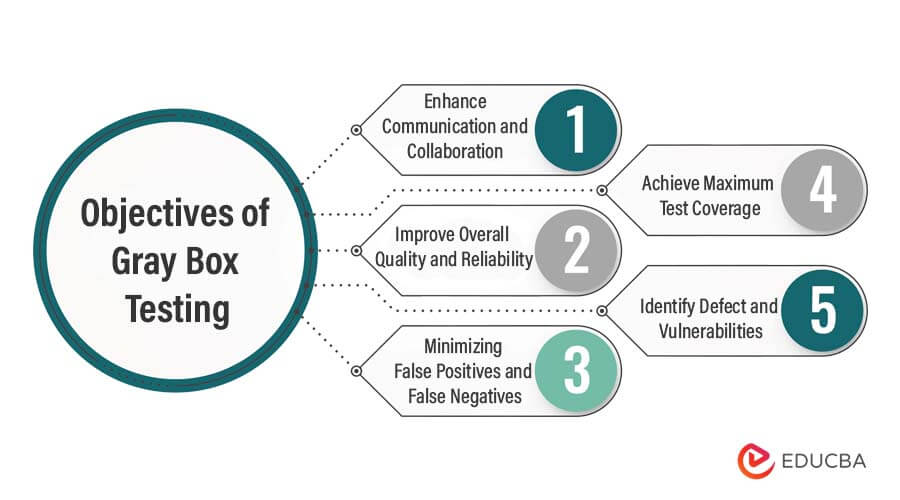
Objectives of Gray Box Testing
- While retaining a certain level of objectivity, providing information into the internal workings of the software.
- Identifying vulnerabilities and issues in the software being tested.
- Minimizing the risk of false negatives and false positives in testing.
- Enhancing the overall quality and reliability of the software, websites, and mobile applications.
- Enhance communication and collaboration between testers, developers, and other stakeholders.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Given below are some advantages and disadvantages mentioned:
Advantages:
- As it is a derivative of Black Box and White Box Testing methods, it adds more of both testing techniques’ advantages.
- Testers approach testing from a user perspective, rather than from a developer’s perspective.
- The testers need not have access to all of the code/logic.
- Instant fixes can be done, as a partial code is available.
- The system manages and maintains the flow of data correctly.
- The developers and testers conduct a fair review of the software, and they don’t have any conflicts.
Disadvantages:
- As only limited access to code/logic is available, complete fixes cannot be done sometimes, which means, sometimes the software can remain as it is.
- Other white box testing types, like algorithm testing, cannot be done, as complete logic is not available.
- Difficult to perform this type of testing on distributed architected software systems.
- It is sometimes challenging to communicate testing results and finding stakeholders who may not be familiar with the methodology.
- For all testing scenarios, gray box testing might not be the ideal choice.
Why Should we use Gray Box Testing?
As of now, we all know that it is very effective with not only web applications but with business applications, too, so it’ll rectify most of the software solutions. The name “Gray Box Testing” is also referred to as “Transparent Box Testing” as well; the tester need not have a full understanding of the system. This testing method certainly penetrates through the application and gets to the core of the problem, and without knowledge of the whole code, it can be fixed.
Conclusion
With so many usage advantages, one will necessarily require Gray Box Testing. You can perform gray box testing to evaluate a product’s effectiveness by examining the effects on the product’s performance and usage. You can conduct these tests before, after, and during the use of the product by comparing results with a suitable baseline.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Gray Box Testing. Here we discussed how gray box testing is performed with the help of examples and different black box testing techniques. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –