Updated May 20, 2023

What is Cryptosystems?
A cryptosystem is also called a cipher system. It implements cryptographic techniques using various cryptographic components such as plain text, encryption algorithm, cipher text, decryption algorithm, and encryption key to provide information security services. There are two types of cryptosystems: Symmetric Key Encryption and Asymmetric Key Encryption.
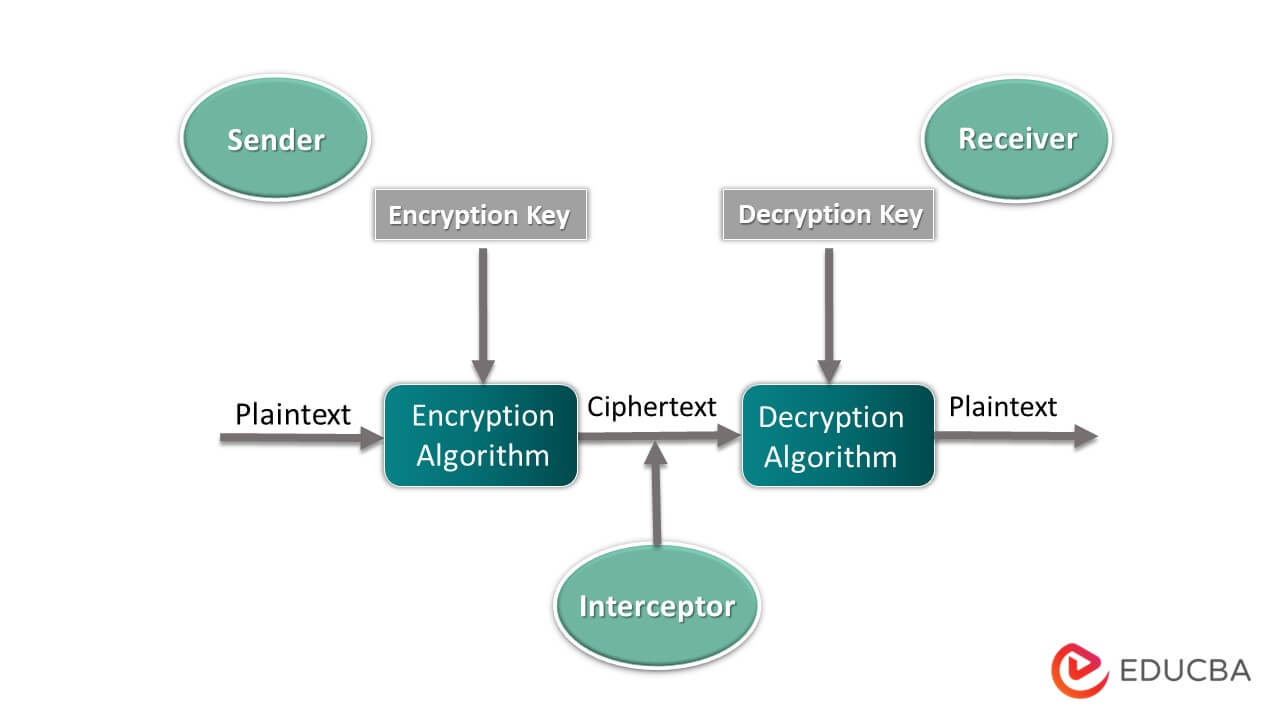
The sender wants to secretly send a message to a receiver without revealing it to any third party in the diagram above. To accomplish that, the cryptosystem comes into the picture. At the sender system, the cryptosystem takes the sender Message i. Plain text using a secret key (encryption key) performs some encryption algorithm, forms a ciphertext, and then sends it to the receiver. After receiving ciphertext at the receiver side cryptosystem performs decryption algorithms using a secret key (decryption key) and converts cipher text into plain text. The cryptosystem’s goal is to send private data from sender to receiver without the interpretation of any third party.
Components of Cryptosystem
Let us discuss some of the components below.
1. Plain Text
Plain text is a message or data which can understand by anyone.
2. Ciphertext
The ciphertext is a message or data that is not readable; it is accomplished by performing the encryption algorithm on plain text using an encryption key.
3. Encryption Algorithm
It converts plain text into ciphertext using an encryption key. It takes two inputs, i.e,. plain text and encryption key, to produce ciphertext.
4. Decryption Algorithm
It is an opposite process of an encryption algorithm; it converts cipher text into plain text using the decryption key. It takes two inputs, i.e,. ciphertext and decryption key to produce plain text.
5. Encryption Key
It is key that the sender uses to convert plain text into ciphertext.
6. Decryption Key
It is a key that the receiver uses to convert ciphertext into plain text.
Types of Cryptosystems
There are two types of Cryptosystems – Symmetric Key Encryption and Asymmetric key encryption.
Let’s discuss these two types in detail.
1. Symmetric Key Encryption
- In symmetric key encryption, the sender and the receiver use the same secret key, i.e., the encryption key, to perform encryption and decryption. Symmetric key encryption is also known as symmetric cryptography.
- Some algorithms use symmetric key concepts to achieve security. For example, DES (Data Encryption Standard), IDEA (International Data Encryption Algorithm), 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard), and Blowfish.
- All cryptosystems mostly use symmetric key encryption.
- In Symmetric-key encryption, the sender and receiver agree on the same secret key. The sender encrypts the private data, i.e., plain text, using a secret key and sends it to the receiver. After receiving data, the receiver uses the same secret key the sender uses to encrypt data. Using this secret key, it converts cipher text into plain text.
In the below picture, we can see the working of Symmetric key encryption.

Features of cryptosystem in case of Symmetric-key encryption:
- They have to share that secret key as they use the same key for encryption and decryption.
- To prevent any attack, you need to update a secret key at regular intervals of time.
- The length of the secret key in symmetric key encryption is small; hence, encryption and decryption are faster.
- A mechanism must share a secret key between the sender and receiver.
Challenges for symmetric key encryption:
- Generating secret key: To share the Secret key, the sender and receiver must agree on the symmetric key, which requires a key generation mechanism.
- Trust issue: There must be trust between the sender and the receiver as they share the symmetric key. E.g., suppose the receiver lost his secret key to attackers, and he does not inform the sender.
2. Asymmetric Key Encryption
In asymmetric key encryption, the sender and receiver use two different keys for encryption and decryption processes. Asymmetric key encryption is also known as public-key encryption.
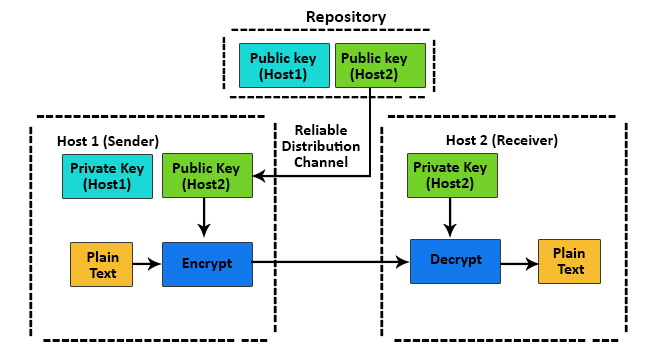
In the above picture, we can see how asymmetric key encryption works.
- In asymmetric key encryption, two keys are used. i.e., public key and private key. These two keys are mathematically related to each other. A public key is stored in a public repository, and private keys are stored in a remote repository.
- The receiver’s public key sender encrypts the private data and sends it to the receiver. After receiving private data, the receiver uses his private to decrypt private data.
- The length of keys in asymmetric key encryption is considerable; hence encryption and decryption processes in asymmetric key encryption become slow compared to symmetric key encryption.
- Calculating the private key based on the public key is computationally difficult. As a result, public keys can be freely shared, allowing users to easily and conveniently encrypt content and verify digital signatures and private keys can be kept secret, ensuring that content can be decrypted and private key owners can only create digital signatures. Asymmetric key cryptosystems face the challenge, i.e., the user must be confident that the public key he is using for transmission with an individual is that person’s public key and was not handled by an attacker.
- Also, because public keys need to be shared, they are large; hence, they are difficult to remember, so they are stored on digital certificates for secure transmission and sharing. You store private keys in the cloud software or operating system you use or on hardware devices. Many internet protocols like SSH, OpenPGP, and SSL/TLS used in asymmetric cryptography for encryption and digital signature functions.
Conclusion
This article has seen how cryptosystem helps encrypt and decrypt messages securely and conveniently.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Cryptosystems. Here we discussed the introduction, components, and types of Cryptosystems. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –


