Updated May 11, 2023
Introduction Bar Charts in R
Bar Charts in R are the commonly used chart to create a graphical representation of the dataset. The Bar chart is represented as vertical or horizontal bars where the bar length or height indicates the count or frequency or any other calculated measure of the variable. As a best practice, a vector or a matrix can be used as input to the bar chat creation function in R for plotting bar charts. In addition, there are various labels, and color assignment features are available with the bar plot function, which is used to create the bar charts.
Syntax
The Basic syntax to create a Bar chart in R is shown below.
barplot (H, xlab, ylab, main, names.arg, col)
Description of the Parameters are:
H denotes height (vector or matrix). If H is a vector, the values determine the heights of the bars. If it is a matrix with option false corresponds to sub bars, and true denotes to create a horizontal bar.
- xlab: Label for X-axis
- ylab: Label for Y-axis
- main: Heading of the bar chart
- names. arg: Label to the bars a character vector.
- col: It gives color to the bars in the chart.
How to create a simple Bar Chart in R?
Here we shall discuss how to create Bar charts using function barplot () in R, which is very easy to implement with vertical and horizontal bars. In the below example, we will see creating charts using vectors.
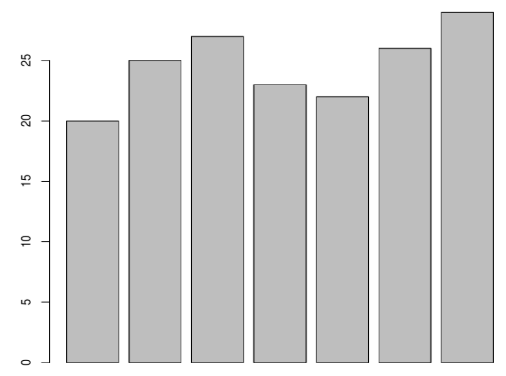
temp <- c(20, 25, 27, 23, 22, 26, 29)
barplot(temp)
Output:
The bar Plot should look like this:
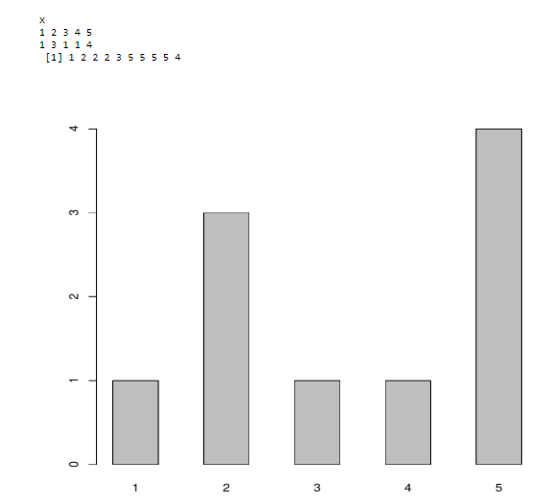
The next example comes with initializing some vector of numbers and creating a table () command to count them. The width of the bar can be adjusted using a parameter width () and space by space () in the barplot.
// Vector numbers are created using function c ()
x<- c (1,2,2,2,3,5,5,5,5,4)
cnt <- table(x)
cnt
x
barplot (cnt , space =1.0)
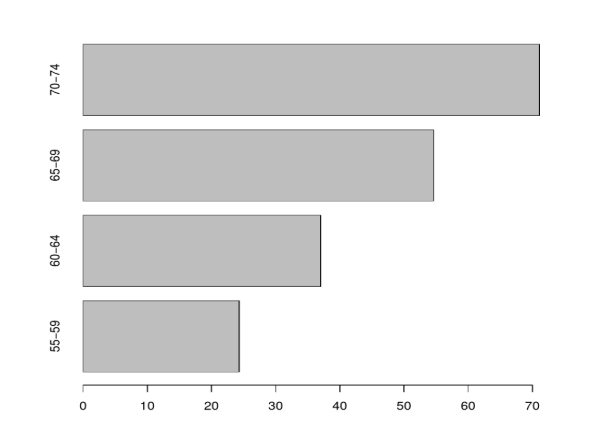
Creating a Bar chart using R built-in data set with a Horizontal bar. To do so, make horiz = TRUE or else vertical bars are drawn when horiz= FALSE (default option).
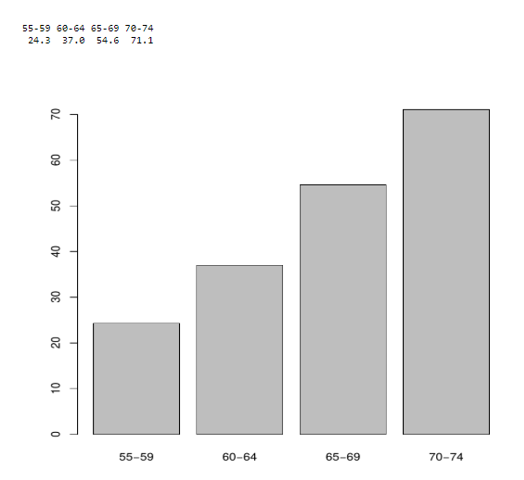
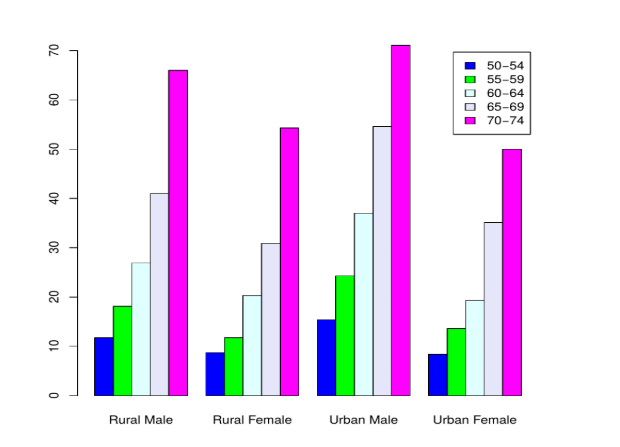
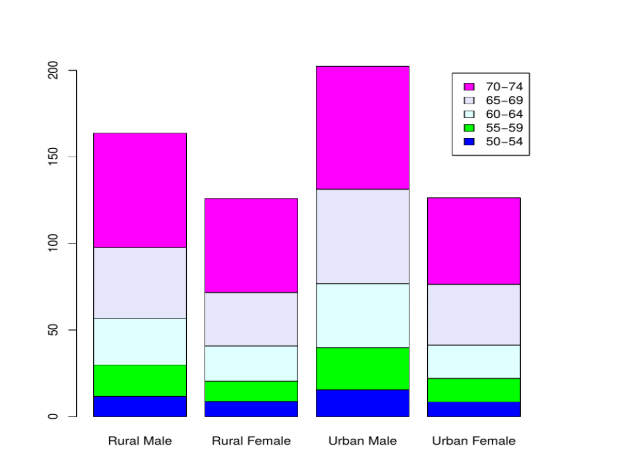
We shall consider a R data set as:
Rural Male Rural Female Urban Male Urban Female
## 50-54 11.7 8.7 15.4 8.4
## 55-59 18.1 11.7 24.3 13.6
## 60-64 26.9 20.3 37.0 19.3
## 65-69 41.0 30.9 54.6 35.1
## 70-74 66.0 54.3 71.1 50.0
Here comes an example to plot the built-in data set of R.
a<- VADeaths [2:5, "Urban Male"]
barplot(a)
# Horizontal bar plot
barplot (a, horiz = TRUE)
Output:
Creating a Bar Chart with Labels & Title
The bar chart could look more elegant by adding more parameters to the bar plot.
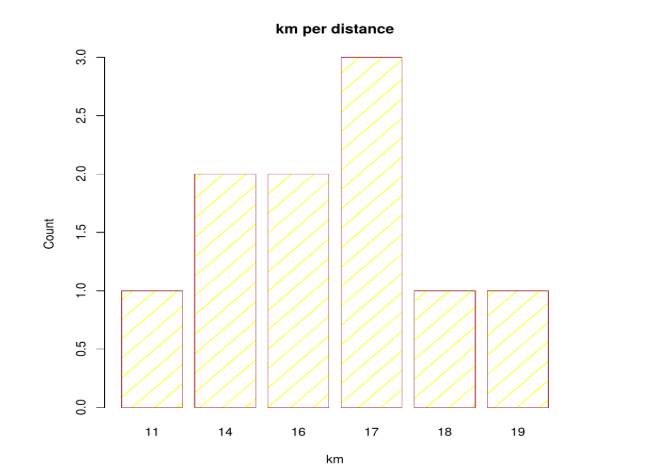
Assigning titles and labels
Titles here are assigned using main arguments as “ Km per distance”, and x-axis as “km and y-axis as “ count” (labels) and the parameter col is for adding colors to the bar( either in hexadecimal or RGB format). also, care should be taken a number of bars should be equal to the number of colours assigned in the character vector; if not, the colors get repeated, density is for shading lines on the bars. Titles and labels can be modified and added to the bar charts.
The following example plots kilometer per count using different parameters.
km <- c(11,14,14,16,17,19,17,16,17,18)
table (km)
km
barplot(table(km),
main="km per distance",
xlab="km",
ylab="Count",
border="brown",
col="yellow",
density=5)
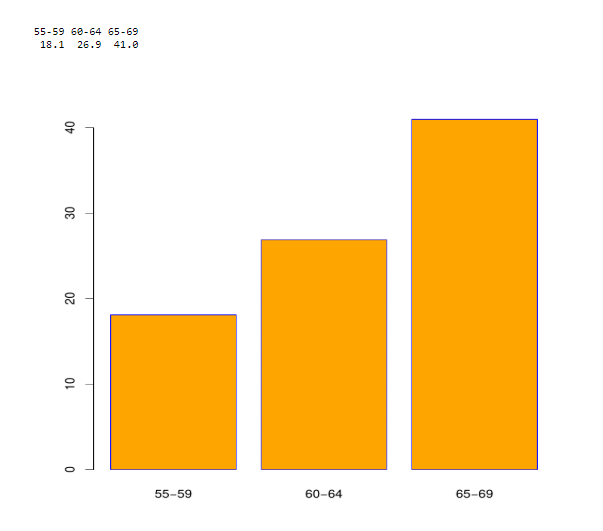
Assigning and changing colors
x <- VADeaths [2:4, "Rural Male"]
barplot (x, col = "orange", border = "blue")
The bar chart for the above code is given here:
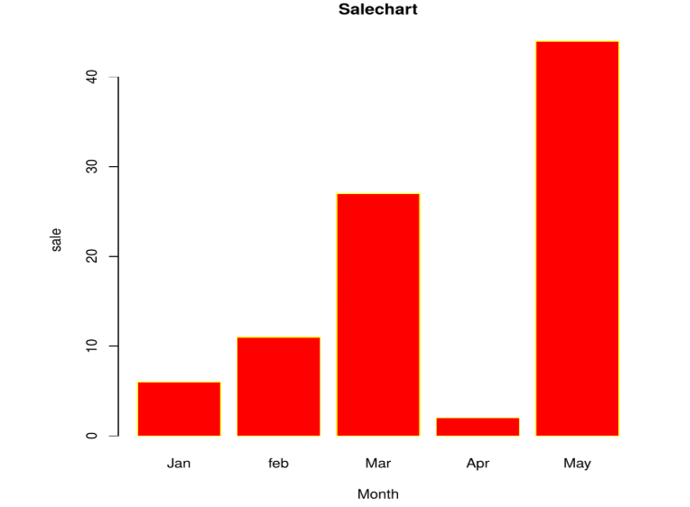
And each of the bars can be assigned different colors. Here, we will fix some labels.
H <- c (6,11,27,2,44)
D <- c("Jan","feb","Mar","Apr","May")
barplot(H,names.arg=D,xlab="Month",ylab="sale",col="Red",main="Salechart",border="yellow")
When executed, we get the following Output:
Using various Arguments
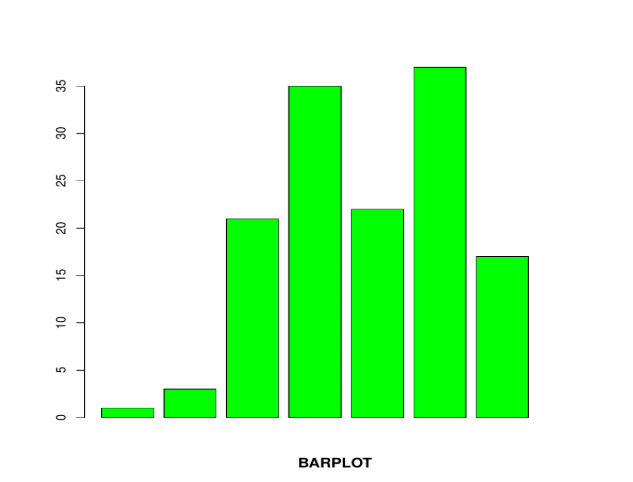
B <- c (1, 3, 21, 35, 22, 37, 17)
barplot (B, col="green")
barplot (B, main="BARPLOT", xlab="LETTERS", ylab="VALUES", names.arg=c("A","B","C","D","E","F","G"),
border="yellow", density=c (90, 70, 50, 40, 30, 20, 10))
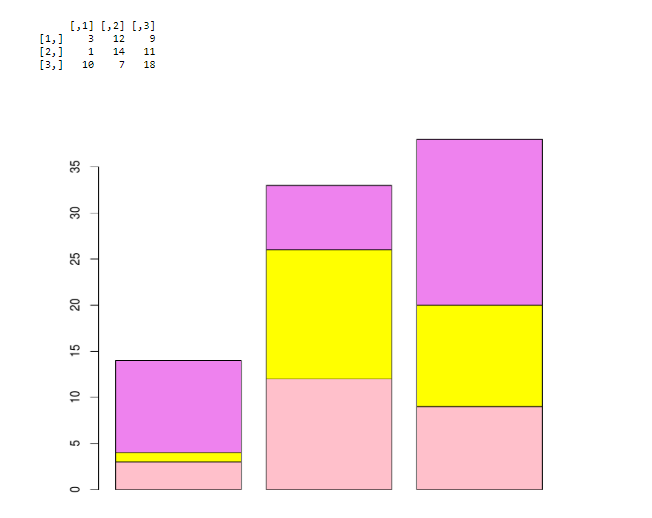
Using Matrix
mt <- c (3, 1, 10, 12, 14, 7, 9, 11, 18)
val <- matrix (mt, nrow = 3, ncol = 3)
val
barplot (val, col = c ("pink", "yellow", "violet"))
Multiple comparisons
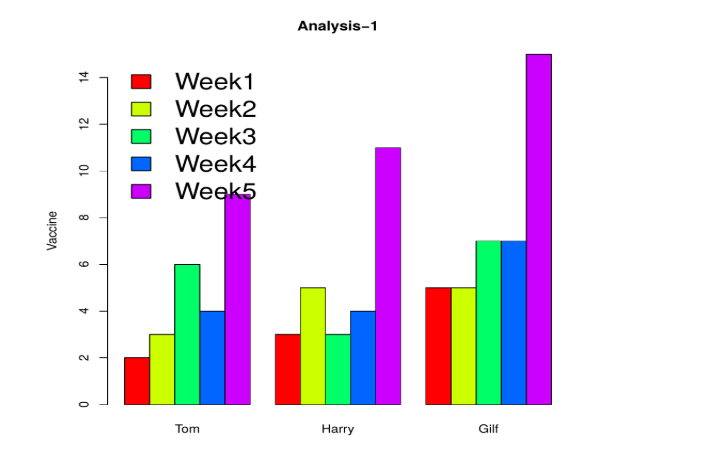
In the below example, we have created a matrix for three vectors representing five points, and a comparison between them is done using a bar chart. Here, we are using the legend function to display the legends. Bty argument is meant for legend borders. The data has been plotted as follows.
A <- c (2,3,6,4,9)
B <- c (3,5,3,4,11)
C <- c (5,5,7,7,15)
data<- data.frame(A, B, C)
names(data)<- c("Tom","Harry","Gilf")
barplot(height=as.matrix(data),main="Analysis-1",ylab="Vaccine", beside=TRUE,col=rainbow (5))
legend ("topleft",c("Week1","Week2","Week3","Week4","Week5"),cex=2.0,bty="n",fill=rainbow (5))
Grouped Bar Plots
Bar charts are created for all the columns. (columns are grouped together). Group chart makes use of matrix as input values.
barplot (VADeaths,col = c("blue", "green", "lightcyan","lavender", "magenta"),
legend = rownames(VADeaths),beside = TRUE)
// Now Making beside = FALSE
barplot (VADeaths, col = c("blue","green","light cyan","lavender","magenta"),
legend = rownames(VADeaths), beside = FALSE)
Stacked Bar Plot
Instead of assigning the bars continuously, it is effective to stack them in order.
Example:
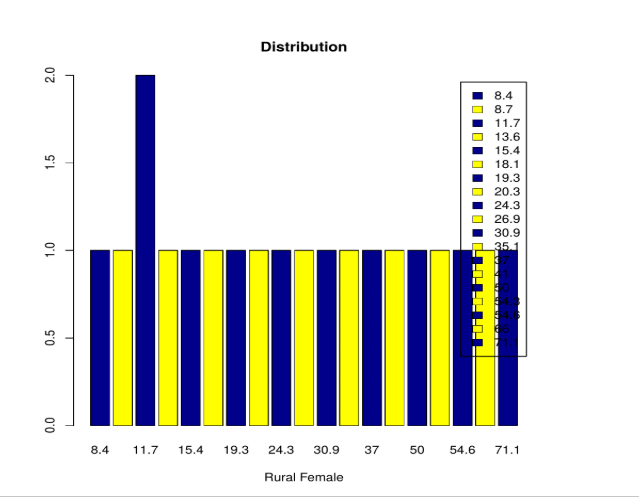
counts <- table (VADeaths)
barplot(counts, main="Distribution",
xlab="Rural Female",col=c("darkblue","yellow"), legend = rownames(counts))
Conclusion
Hence, we have discussed the basics of creating bar charts in R. this will help you to understand real-time concepts for quantitative comparison. Bar charts play an essential role in data visualizations. We have seen some real-time scenarios on bar charts for categorical values and monitoring variation of a process for the given data set. New variations of bar charts include plotting using dots. Bar charts help in grouping values at several levels.