Updated February 27, 2023
Introduction to B+ Tree in Data Structure
B+ Tree in Data Structure is an N-array tree in which a node has multiple children. Its components are root, internal nodes, and leaves. It allows very efficient insertion and deletion operation. Though a complex concept, It is a highly effective data structure for optimizing processing performance. It is quite useful in situations that involve large datasets where processing speed is very important.
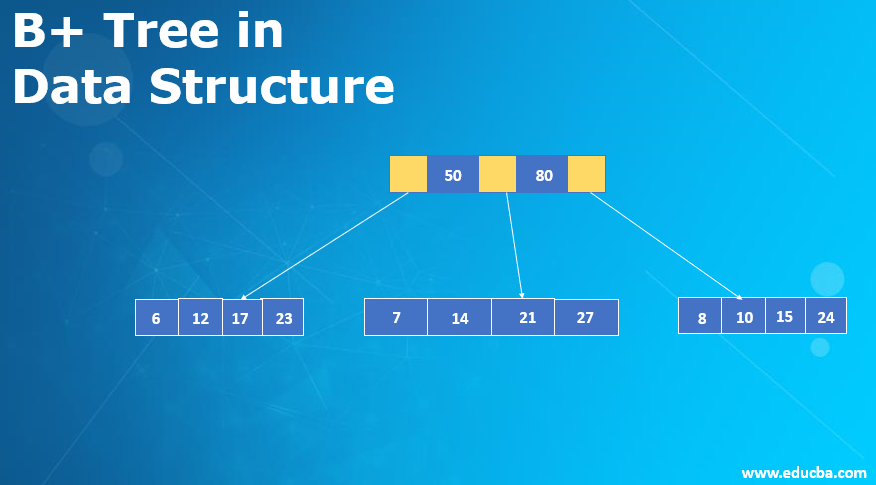
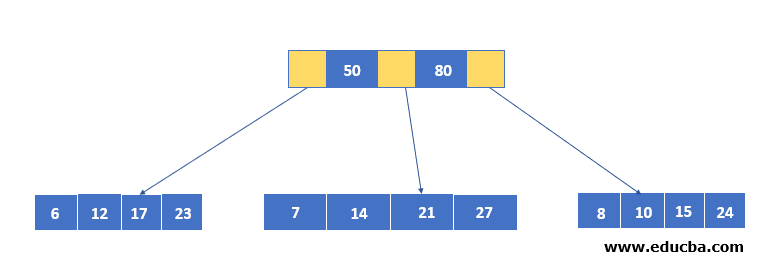
Visual Representation of B+ Tree in Data Structure
Below is the visual representation:
Implementation of B+ Tree
Below is the code:
Code:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
#define Macro 4
struct node
{
int n;
int keys[Macro - 1];
struct node *p[Macro];
}*root=NULL;
enum KeyStatus { dupl,SearchFailure,Success,insrit,LessKeys };
void insert(int x);
void display(struct node *root,int);
void delete(int x);
enum KeyStatus ins(struct node *r, int x, int* y, struct node** u);
int searchPos(int x,int *key_arr, int n);
enum KeyStatus del(struct node *r, int x);
void main()
{
int k;
int op;
for(;;)
{
printf("\n1.Insert");
printf("\n2.Delete");
printf("\n3.Display");
printf("\n4.Quit");
printf("\nEnter the option : ");
scanf("%d",&op);
switch(op)
{
case 1:
printf("\nEnter the element : ");
scanf("%d",&k);
insert(k);
break;
case 2:
printf("\nEnter the element : ");
scanf("%d",&k);
delete(k);
break;
case 3:
printf("\nB+ tree is :\n");
display(root,0);
break;
case 4:
exit(1);
default:
printf("\nInvalid Option.");
break;
}
}
}
void insert(int k)
{
struct node *newnode;
int upK;
enum KeyStatus val;
val = ins(root, k, &upK, &newnode);
if (val == dupl)
printf("\nElement already present.");
if (val == insrit)
{
struct node *uproot = root;
root=malloc(sizeof(struct node));
root -> n = 1;
root -> keys[0] = upK;
root -> p[0] = uproot;
root->p[1] = newnode;
}
}
enum KeyStatus ins(struct node *ptr, int k, int *upK,struct node **newnode)
{
struct node *nptr, *lptr;
int pos, i, n,splitPos;
int nK, lK;
enum KeyStatus val;
if (ptr == NULL)
{
*newnode = NULL;
*upK = k;
return insrit;
}
n = ptr -> n;
pos = searchPos(k, ptr->keys, n);
if (pos < n && k == ptr -> keys[pos])
return dupl;
val = ins(ptr->p[pos], k, &nK, &nptr);
if (val != insrit)
return val;
if (n < Macro - 1)
{
pos = searchPos(nK, ptr->keys, n);
for (i=n; i>pos; i--)
{
ptr -> keys[i] = ptr -> keys[i-1];
ptr -> p[i+1] = ptr -> p[i];
}
ptr -> keys[pos] = nK;
ptr -> p[pos+1] = nptr;
++ptr -> n;
return Success;
}
if (pos == Macro - 1)
{
lK = nK;
lptr = nptr;
}
else
{
lK = ptr -> keys[Macro-2];
lptr = ptr -> p[Macro-1];
for (i = Macro - 2; i > pos; i--)
{
ptr->keys[i] = ptr->keys[i-1];
ptr->p[i+1] = ptr->p[i];
}
ptr -> keys[pos] = nK;
ptr -> p[pos+1] = nptr;
}
splitPos = (Macro - 1)/2;
(*upK) = ptr->keys[splitPos];
(*newnode)=malloc(sizeof(struct node));
ptr -> n = splitPos;
(*newnode)->n = Macro - 1 - splitPos;
for (i=0; i < (*newnode)->n; i++)
{
(*newnode)->p[i] = ptr->p[i + splitPos + 1];
if(i < (*newnode)->n - 1)
(*newnode)->keys[i] = ptr->keys[i + splitPos + 1];
else
(*newnode)->keys[i] = lK;
}
(*newnode)->p[(*newnode)->n] = lptr;
return insert;
}
void display(struct node *ptr, int bl)
{
if (ptr)
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=bl;i++)
printf(" ");
for (i=0; i < ptr->n; i++)
printf("%d ",ptr->keys[i]);
printf("\n");
for (i=0; i <= ptr->n; i++)
display(ptr->p[i], bl + 10);
}
}
int searchPos(int k, int *k_arr, int n)
{
int pos = 0;
while (pos < n && k > k_arr[pos])
pos++;
return pos;
}
void delete(int key)
{
struct node *uproot;
enum KeyStatus value;
value = del(root,key);
switch (value)
{
case SearchFailure:
printf("Key %d is not available\n",key);
break;
case LessKeys:
uproot = root;
root = root->p[0];
free(uproot);
break;
}
}
enum KeyStatus del(struct node *ptr, int k)
{
int pos, i, piv, n ,min;
int *k_arr;
enum KeyStatus val;
struct node **p,*lptr,*rptr;
if (ptr == NULL)
return SearchFailure;
n = ptr -> n;
k_arr = ptr -> keys;
p = ptr->p;
min = (Macro - 1)/2;/*Minimum number of keys*/
pos = searchPos(k, k_arr, n);
if (p[0] == NULL)
{
if (pos == n || k < k_arr[pos])
return SearchFailure;
for (i=pos+1; i < n; i++)
{
k_arr[i-1] = k_arr[i];
p[i] = p[i+1];
}
return --ptr->n >= (ptr==root ? 1 : min) ? Success : LessKeys;
}
if (pos < n && k == k_arr[pos])
{
struct node *qp = p[pos], *qp1;
int nkey;
for(;;)
{
nkey = qp->n;
qp1 = qp->p[nkey];
if (qp1 == NULL)
break;
qp = qp1;
}
k_arr[pos] = qp -> keys[nkey-1];
qp -> keys[nkey - 1] = k;
}
val = del(p[pos], k);
if (val != LessKeys)
return val;
if (pos > 0 && p[pos-1]->n > min)
{
piv = pos - 1; /*pivot for left and right node*/
lptr = p[piv];
rptr = p[pos];
rptr -> p[rptr->n + 1] = rptr->p[rptr->n];
for (i=rptr->n; i>0; i--)
{
rptr->keys[i] = rptr->keys[i-1];
rptr->p[i] = rptr->p[i-1];
}
rptr->n++;
rptr->keys[0] = k_arr[piv];
rptr->p[0] = lptr->p[lptr->n];
k_arr[piv] = lptr->keys[--lptr->n];
return Success;
}
if (pos > min)
{
piv = pos; lptr = p[piv];
rptr = p[piv+1];
lptr->keys[lptr->n] = k_arr[piv];
lptr->p[lptr->n + 1] = rptr->p[0];
k_arr[piv] = rptr->keys[0];
lptr->n++;
rptr->n--;
for (i=0; i < rptr->n; i++)
{
rptr->keys[i] = rptr->keys[i+1];
rptr->p[i] = rptr->p[i+1];
}
rptr->p[rptr->n] = rptr->p[rptr->n + 1];
return Success;
}
if(pos == n)
piv = pos-1;
else
piv = pos;
lptr = p[piv];
rptr = p[piv+1];
lptr->keys[lptr->n] = k_arr[piv];
lptr->p[lptr->n + 1] = rptr->p[0];
for (i=0; i < rptr->n; i++)
{
lptr->keys[lptr->n + 1 + i] = rptr->keys[i];
lptr->p[lptr->n + 2 + i] = rptr->p[i+1];
}
lptr->n = lptr->n + rptr->n +1;
free(rptr);
for (i=pos+1; i < n; i++)
{
k_arr[i-1] = k_arr[i];
p[i] = p[i+1];
}
return --ptr->n >= (ptr == root ? 1 : min) ? Success : LessKeys;
}
Output:
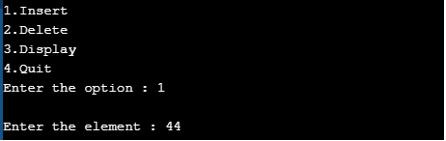
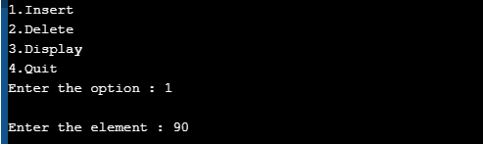
Output for Insert Operation:
We inserted elements one-by-one. Enter the proper option.
1. The first element passed into the tree is 23.
2. Similarly, we passed 44, 78, and 90, as shown by the following three screenshots.
Output for Delete Operation:
Now, let’s delete an element. We chose 44, as shown below.
Output for Display Operation:
Let’s display the tree now, as shown below.
Advantages of B+ Tree
- It offers a very effective mechanism to traverse through the data. It facilitates range as well as partial retrieval.
- It can be of any size and based on the number of records, its size changes.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to B+ Tree in Data Structure. Here we discuss an introduction to B+ Tree with Visual representation, implementation, and Advantages. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –