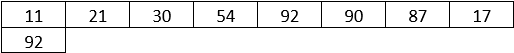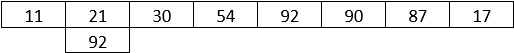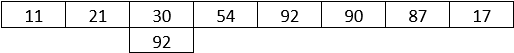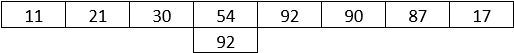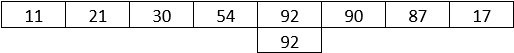Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Linear Search in Data Structure
One of the very simplest methods to search an element in an array is a linear search. This method uses a sequential approach to search the desired element in the list. If the element is successfully found in the list, then the index of that element is returned. The search starts from the first element and sequentially proceeds in the forward direction.
Algorithm for Linear Search in Data Structure
The algorithm for linear search is as shown below. It is a straightforward algorithm. Go through it and study it as we shall be building a computer program on the algorithm.
Algorithm:
function linear_search(integer array[], integer n, integer x)
{
integer k;
for (k = 0, k < n, k++)
if (array [k] = x)
return k;
return -1;
}
Example to Implement Linear Search
The program code to implement a linear search is as given below. This program has been written in C programming. Let’s go through the following program to understand how it helps us find the requisite element in the list using the linear search algorithm. Study each and every component of the code properly, including the statements, variables, loops, etc.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int linear_search(int arr[], int n, int x)
{
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
if(arr[i] == x)
return i + 1;
return -1;
}
void main()
{
int arr[50], n, i, x, res;
printf("Enter the number of elements in array: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("\nEnter the numbers: ");
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
printf("\nEnter the number to be searched: ");
scanf("%d", &x);
res = linear_search(arr, n, x);
if(res == -1)
printf("\n%d does not exist in the array.", x);
else
printf("\n%d is present at position %d in the array.", x, res);
getch();
}
Code Explanation: The above program first asks the user to specify the number of elements in the array along with the elements. It takes up to 50 elements. Once the array is specified, the user is asked to specify the element that needs to be searched in the array in the next step. The program using loop sequentially searches for the desired element. For this task, a function linear_search() has been used as seen in the code.
If the element is found in the array, then the function linear_search() returns the element’s position, and if the element is not found in the array, then -1 is returned. We must verify and validate the correctness of the implemented program. For this, the program should be checked by passing multiple parameters to it. We validate the program by passing multiple inputs. The inputs passed and the respective results obtained have been discussed in the below section.
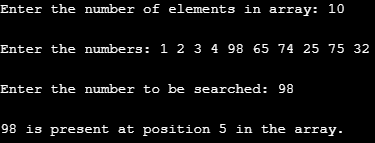
Input 1
In this case, we decided to have ten elements in the array, and so, specified 10 when asked to specify the number of elements in the array. Next, we passed ten different numeric elements in the array. The inputs must be passed carefully. Passing input of different data types may give incorrect results. Also, while passing elements, they must be separated by space. Once, we pass the entire array correctly; next, we will specify the number that we intend to search in the array. Here, we want 98 to be searched. As 98 is present in the array, its position has been returned correctly by the program. So, the program worked correctly.
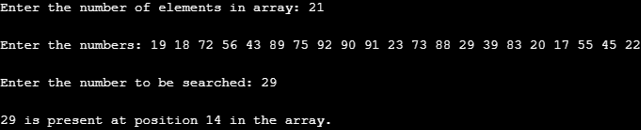
Input 2
In this case, we passed twenty-one elements into the array. Follow the steps and pass the inputs properly. After specifying the number of elements in the array, while passing the elements, ensure that the required number of elements are only passed. This is especially important when the number of elements in the array is high. Once done with the array, specify the requisite number to be searched. Here it is 29 as passed by us. 29 is present in the array, and the program successfully gave its position, which is 14. Go through the following output and see how the correct result has been obtained.
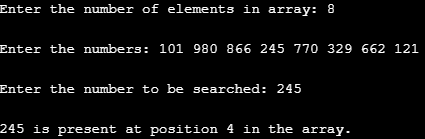
Input 3
Here, we passed eight three-digit numbers into the array. Then we specified number to be searched in the array, which is 245. As the number 245 is present in the list, so, the program correctly returned its position in the array. Go through the following program output.
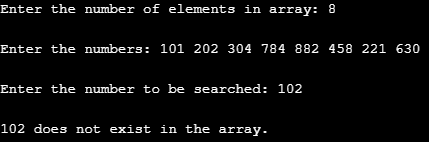
Input 4
Till now, we saw the program correctly returning the position of the element present in the array. However, the program should work correctly if the element is not present. The following program output shows this. As shown below, we decided to have eight elements in the array, and then specified the eight elements. After this, we specified the number to be searched, which is 102. 102 is not present in the array, and the program gave correct output saying that the number doesn’t exist in the array.
How Linear Search Algorithm Works
Let’s consider the following array to understand the working of the algorithm.
Now, suppose we want to search 92 in the above-mentioned array, the linear search algorithm shall follow the steps mentioned below.
Step 1: The algorithm begins from the left-hand side, and the element to be searched is matched with every element. In the first, the matching doesn’t happen.
Step 2: Now, the algorithm moves to the next element and compares the two elements to check if matching happens.
Step 3: Similarly, the searching happens until no match happens.
Step 4: Finally, when the match happens, the algorithm returns the position of the element.
Conclusion
Linear searches through a simple searching algorithm have vast applications. It is beneficial in situations that involve numerous elements. It is a straightforward methodology for searching requisite elements and can be implemented easily using any programming language.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Linear Search in Data Structure. Here we discuss the algorithm and working of Linear Search in Data Structure along with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –