Updated March 16, 2023

Introduction to Arrays in C++
Arrays in C++ are a collection of similar data types like int, char, float, double, etc., that are stored using the index value and can easily be accessed by index value only. Moreover, it stores all the instances of variables into one single variable. In C++, an array can be declared using three methods: by specifying the size of an array, by initializing array elements directly, and by specifying the array’s size with its elements.
To let the data be processed using any application, we first need to bring the data into the application. This means there should be some space in the application where the value should be stored until the program runs. To serve the purpose of storing the values, the programming language offers us a variable. Variables are used to store the values so that they can be used by the application to generate the expected outcome. As variables are stored, some value occupies space in the memory allocated to the application. So the optimal approach to coding is to ensure the usage of the variable should be as low as possible. The concept of array came into existence to mitigate the memory allocation issue due to the creation of a high number of variables. The array can be considered the list of values belonging to the same data type. In this article, we will learn about the array using the C++ programming language.
How Arrays work in C++?
Below is the explanation of how arrays work:
- The array is to store the values of the datatype. It is supposed to work the same way as the variable. It can hold multiple values, creating the array in C++ or programming languages. We must state the number of variables we want to store in the array.
- It has to be noted that the size of the array remains fixed throughout the application runtime and cannot be changed dynamically. Once the size of the array is defined, we can store the same count of values in it. If the data type of the array is defined as an integer, it will not accept any value that is not an integer. One will need to use the index to locate the value held by the array, and one will need to use the index.
- For instance, if the array can hold two values, then the second value will be stored at the array’s one index as the array’s index begins with zero. In the next section, we will learn array creation.
How to Create Arrays in C++?
Below explanation shows how to create arrays in c++:
The approach of creating the array is exactly similar to variable creation. The first step is to declare the array. Once the array is declared, we can either initialize the array at the same time, or it could be initialized later. While declaring the array, we have to mention three things: the datatype of the array, the name of the array, and its size. Below is the syntax that shows how to declare the array merely.
Syntax:
Datatype array_name[size];Ex.
int first_array[10];The array defined here can have ten integer values. The name of the array is first_array, and the number defined inside the large bracket states the size of the array. Now let’s see how to declare and initialize the variable simultaneously.
Code:
int first_array[4] = { 1,2,3,4}
int first_array[]= {1,2,3,4,5,6}In the above example, we have seen that the array that has defined the size 4 has accepted the 4 values. If one tries to submit more than 4 values, it will throw an error. Also, if you do not specify the size of the variable, you can store as much value as you want.
Types of Arrays in C++
In the C++ programming language, we mainly have two types of variables: Single Dimensional Arrays and multidimensional Arrays. The single-dimensional stores values in the form of the list, while the multidimensional array store the value in the matrix. Below we will see each of the types using an example.
1. Single Dimensional Array
The single-dimensional array may be defined as the type of array capable of holding the values of the same data center in the form of a list. It is the simplest form of an array as it doesn’t require much effort to define and initialize such an array. It can be defined as int a[10], where int is the data type, the array name, and the array size is 10. The example below will make things more clear.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
void main()
{
int val_array[3];
int int_val=1,counter;
cout<<"Please enter three numbers that you want to multiply"<<endl;
for(counter=0;counter<3;counter++)
{
cin>>val_array[counter];
int_val = int_val*val_array[counter];
}
cout<<"The multiplication of these three numbers is = "<<int_val;
getch();
}The above program is written to accept three values from the user, which will then be processed to generate the multiplication value of all of them. The array user here is name val_array, and the array can hold three values. The loop is used to intake the value in the array, which is multiplied. The result of the multiplication has been stored in the int_val variable. As the function is void, it will not return any value.
Output:
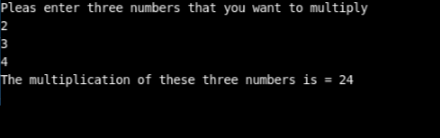
2. Multidimensional array
The multidimensional array may be defined as the array that holds the values as a matrix does. The two-dimensional array is used very often, and the array gets complicated with the increase in dimension size, the array gets complicated. For instance, working with a two-dimensional array is easier than working with a three-dimensional one. The two-dimensional array needs two sizes to be defined for one dimension each. The two-dimensional array can be in the program as int a[5][3]. This array will hold the value in the form of a matrix with 5 rows and three columns. Let us understand this with the help of an example.
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <conio.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int val_array[5][5];
int count_rows,count_cols,counter1,counter2;
cout<<"Please enter the size of the rows and columns that you want to input: ";
cin>>count_rows>>count_cols;
cout<<"PLease enter the values for matrics in row wise manner"<<endl;
for(counter1=0;counter1<count_rows;counter1++)
for(counter2=0;counter2<count_cols;counter2++)
cin>>val_array[counter1][counter2];
cout<<"The matrix will be as follows"<<endl;
for(counter1=0;counter1<count_rows;counter1++)
{
for(counter2=0;counter2<count_cols;counter2++)
cout<<val_array[counter1][counter2]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
getch();
return 0;
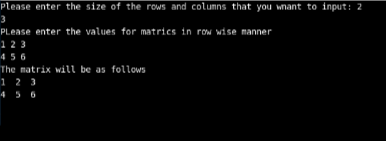
}In this program, we have used a two-dimensional array. The way the array was defined using two sizes states that the array used is two dimensional. If there would have been three sizes, then the array would be three-dimensional. The user is asked to input the number of rows and columns they want in the matrix. Once the user specifies the numbers, they are asked to input the values they want in the rows and columns of the matrix. Here the user has submitted 2 3, which means they want two rows and three columns in the matrix. They had to offer six values as the matrix with two rows and three columns with six values. When all the values have been submitted, they have been represented in the form of a matrix. The entire program is implemented using the two-dimensional array.
Output:
Method of Passing Array
Methods are shown below:
To pass the variable in any method as a parameter needs to accept the value from where it is called datatype and the name of the variable holding the Value. The approach of passing the array to the method is similar to how any normal variable is passed. The only difference is that rather than mentioning a single variable, we will need to use the array with a specific size in the place of the array. Let’s understand this using syntax.
Syntax:
//defining method that accepts an array as a parameter.
int handle_array(int a[6]);Here the method name is handle_array, which has an array as a parameter. The name of an array is a, and the array can hold six values. Now let’s see how the argument can be passed to the method handle_array.
Syntax:
int arrr[6] = {1,2,3,4,5,6};
handle_array(arr) ;First, we must assign the values to other variables that we must pass to the handle_array method. Once the values are assigned, we need to pass the array as an argument while calling the handle_array function. In the above snippet, it is clear how the array has been assigned with the values and passed as an argument to pass the values that the handle_array function has been defined.
Conclusion
The array in C++ is an essential feature for memory management and improves the program’s efficiency. It can be used in several algorithms to die to offer multidimensional data storage. It is always optimal to use an array when storing values of the same datatype is needed. It does not just help in conserving resources but also reduces the program execution time.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Arrays in C++. Here we have discussed how Arrays work in C++, how to create, types of Arrays, passing, codes, syntax, outputs, etc. You can also go through our given articles to learn more-


