Updated June 26, 2023
Introduction to RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is one of the most widely used open-source message brokers. It was originally based on the Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP). Later, it was modified to support Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT), Streaming Text Oriented Messaging Protocol (STOMP), and several other standard protocols. RabbitMQ has been designed to be used for a variety of messaging scenarios that have developed over the last 25 years. It is well-known for Reliability and Interoperability. Many languages have implemented it, positioning it as one of the best choices for building reliable, large-scale, clustered, resilient messaging infrastructure.
What is RabbitMQ?
The hybrid broker, known as RabbitMQ, is a traditional messaging broker that supports multiple messaging protocols such as AMQP, MQTT, and STOMP. Our platform provides various messaging techniques, such as pub-sub, points-to-point, and request-reply, to meet your requirements. It uses a smart broker/dumb consumer model and focuses on delivering messages to consumers consistently. It offers excellent performance if appropriately configured, supports client libraries in Java, Ruby, .NET, PHP, and many other languages, and offers several plugins that can be added to extend use cases and integration scenarios. Both synchronous and asynchronous modes of communication are available.
It supports a variety of acknowledgments for different use cases and supports transactions across messaging queues. It also allows the segregation of the various transactional semantics (if required). Furthermore, it supports distributed transactions like X/Open XA transactions. It also supports message grouping and idempotent messages. It helps a lot of fine-grain control in terms of accessing queues. One can restrict access to specific queues, manage the depth, and more.
Operations and Security are areas of strength for RabbitMQ. RabbitMQ management plugin offers a browser-based UI for monitoring and management, HTTP UI, and CLI tools for operations. In addition to TLS support, RabbitMQ comes with RBAC having a built-in data store, LDAP, or external HTTPS-based providers.
Why We Use RabbitMQ?
Many web servers utilize RabbitMQ, a messaging broker, extensively to obtain rapid responses instead of executing resource-intensive operations that would otherwise cause users to wait for results. It is also suitable for distributing messages among more than one consumer or load balancing among consumers under high load.
Following are some scenarios where one would prefer using RabbitMQ:
- Your application needs to use a combination of different messaging protocols like STOMP, AMQP, MQTT, etc.
- It would help to have finer and more consistent control on a per-message basis.
- Your application needs multiple messaging techniques like pub/sub, point-to-point, request/reply, etc.
- It is useful when running the same job on a specific server, group of servers, or all servers. The application sends one message, and the exchange will route it. This is possible due to the powerful routing capability of RabbitMQ.
- If you need to integrate your messaging broker with existing IT infrastructure, RabbitMQ is the one to go with.
RabbitMQ can also be used with Cassandra (No-SQL) if your application is required to run on stream history, and you can also use LevelDB plugin if your application needs to use Infinite Queue.
What Can We Do with RabbitMQ?
Messaging allows applications to connect and scale up. Applications can connect as parts of a larger application or end-user devices and data. RabbitMQ is a messaging broker- an intermediate entity for messaging. It provides a common platform for your applications to send and receive messages and a safe place for your messages to live until consumed.
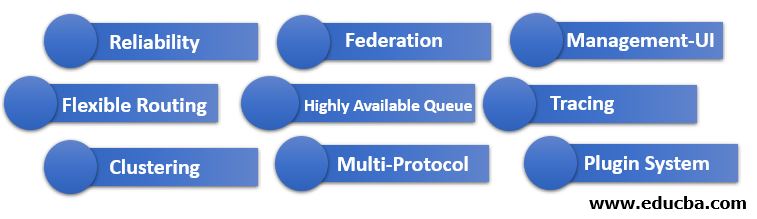
It offers the following features:
- Reliability: It offers several features that allow you to trade off performance with reliability, and delivery acknowledgments, including persistence, high availability, and publish confirms.
- Flexible Routing: Exchanges receive messages and then route them to queues. It offers several predefined exchanges for various use cases. You can define more complex routing by binding exchanges or defining your exchange type as a plugin.
- Clustering: Two or more RabbitMQ servers on the local network can be clustered together, forming a single large broker.
- Federation: For certain use cases, servers may require a looser and less reliable connection than what clustering allows. RabbitMQ offers a federation model for such cases.
- Highly Available Queue: Queues can be replicated across several cluster nodes, ensuring that messages are safe even during hardware failure.
- Multi-Protocol: It supports several of the messaging protocols.
- Management-UI: RabbitMQ has an easy-to-use Management UI that helps smooth control and monitor every broker aspect.
- Tracing: If the system misbehaves, RabbitMQ offers to trace support to find out what is breaking the system.
- Plugin System: It comes with various plugins; you can also write a custom plugin to meet requirements.
Conclusion
The industry widely uses RabbitMQ due to its support for complex routing. It has been adopted by many big companies/organizations like JP Morgan, NASA (for Nebula Cloud Computing), and Google. It also finds usage in India’s Aadhar Project, the largest biometric database in the world.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to What is RabbitMQ. Here we discuss why we use RabbitMQ, what we can do with it, and its features. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –