Updated June 19, 2023
Differences Between Java and Ruby
Java is a programming language.Java is a platform-independent language. That means Java is not specific to any processor or runs on most operating systems, including Mac OS, Windows, and Linux. As mentioned earlier, Java is also a computing platform. The Java platform is a collection of programs that helps develop and run programs written in Java. Java platform also includes an execution engine, compiler, and a set of libraries. Ruby is a scripting language. Ruby is an object-oriented programming language and is a powerful, dynamic, flexible, interpreted, reflective, object-oriented, and general-purpose programming language with complex but, at the same time, expressive grammar. It also has core class libraries with rich and robust APIs.
Java
Java is a programming language and a computing platform for application development first released by developed by Sun Microsystems, which Oracle Corporation later acquired in 2009. Java is swift, robust, reliable, and secure.t is a general-purpose programming language with a lot of features in it which makes the language suitable for use on the WWW (World Wide Web).
Ruby
Ruby is a scripting language designed and developed by Yukihiro Matsumoto in the mid-1990. Ruby is open-source and freely available on the Web, which is subject to a license. Ruby has many similar features that Python and Perl scripting languages possess. Ruby’s programming language mainly focuses on simplicity and productivity, with an elegant syntax that is natural to read and easy to write. Every code in Ruby has its properties and actions. Here properties mean variables, and actions mean methods. Ruby follows the principle of POLA – Principle of Least Astonishment, which means that the Ruby language behaves in such a way as to minimize confusion for experienced users.
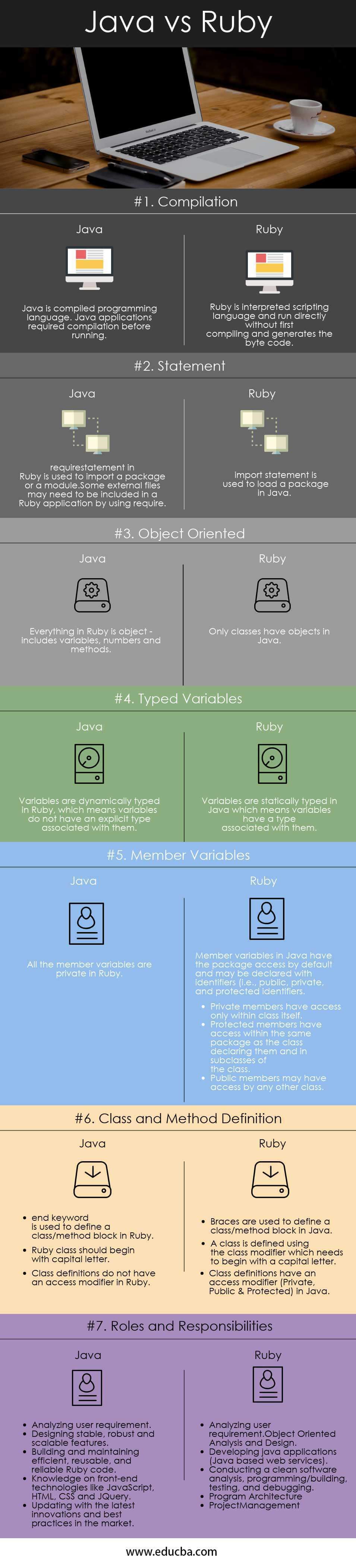
Head to Head Comparison Between Java and Ruby (Infographics)
Below is the Top 7 Comparison Between the Java vs Ruby:
Key Differences Between Java and Ruby
Below are the lists of points; describe the key differences:
- Java must be compiled before running the application, whereas in Ruby, there is no need to collect the code.
- Only classes are objects, whereas everything in Ruby is Object.
- Variables in Java are statically typed, whereas in Ruby, variables are dynamically typed.
- Member variables have access identifiers (Private, Public, and Protected) in Java, whereas in Ruby, all the member variables are private by default.
- In Java, methods will have package access by default and require a return type, whereas methods in Ruby begin with defend and end with an end.
- Parentheses in method invocation are mandatory in Java. For example, define a method hello that returns a Hello message by the below program.
public class Hello {
public String hello(String name){
return "Hello "+ name;
}
}
But in Ruby, parentheses in method invocation are not mandatory, which is optional. For example, define a method hello that takes a name argument and returns a Hello message.
class Hello
def hello(name)
return "Hello " +name
end
end
- A class can extend to another class both in Java and Ruby. In Java, a class can be extended using the keyword – extends as follows:
public class LinkedHashSet extends HashSet{}
But in Ruby, a class can extend to another class using ‘<‘. For example, the Catalog class extends the ActiveRecord:: Base class.
class Catalog < ActiveRecord::Base
end
In Java, exceptions are handled using the try-catch-finally construct, which consists of a try block followed by one or more catch blocks and, optionally, a final block. On the other hand, in Ruby, exceptions are handled using the begin-rescue-ensure-end construct.
Java vs Ruby Comparison Table
Below is the comparison table between Java vs Ruby
| Basis for Comparison |
Java | Ruby |
| Compilation | Java has compiled programming language. Java applications required compilation before running. | Ruby has interpreted scripting language and runs directly without first compiling and generating the bytecode. |
| Statement | require a statement in Ruby that imports a package or a module.
Some external files may need to be included in a Ruby application by using require. |
import statement is used to load a package in Java. |
|
Object-Oriented
|
Everything in Ruby is an object – including variables, numbers, and methods. | Only classes have objects in Java. |
| Typed Variables | In Ruby, variables are dynamically typed, which means they do not have an explicit type associated with them. | In Java, variables are statically typed, which means they have a type associated with them. |
| Member Variables | All the member variables are private in Ruby. |
|
| Class and Method Definition
|
|
|
| Roles and Responsibilities |
|
|
Conclusion
Both Java and Ruby are similar and share a lot of parallel features. At the same time, they both have their own specific features which help with a specific requirement. But definitely, Ruby is not a replacement for Java. Java EE is the enterprise framework that is used to develop Model-View-Controller applications with Java and Ruby; Ruby on Rails is the Model-View-Controller framework.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Java vs Ruby” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.