Updated May 23, 2023
Introduction to What is PL/SQL?
PL/SQL or Procedural Language for SQL is an extended version of SQL programming, designed specifically by Oracle for its relational databases, to be programmed alongside SQL and Java. As a programming language, it derives from SQL and incorporates object-oriented programming (OOPS) concepts such as procedures, functions, loops, conditional statements, and more. Also, this programming language consents to variables & constants declaration, similar to Java and other OOPS-based programming languages.
PL/SQL
- PL/SQL is an extension of SQL that allows developers to combine the power of SQL with procedural statements. Oracle Corporation developed it in the early ’90s. It will enable writing a piece of code, including the SQL query in a block (which is the basic unit of it).
- It is a high-standard and readable language that is easy to understand and learn. It can be used exclusively with Oracle Database Systems and is incompatible with a standalone application like C, C++, Java, etc. It allows developers to use loops, conditions, object-oriented concepts, and SQL like other database languages.
- Before this, only one query is sent to the Oracle server, which increases the load and time. But through this, multiple SQL statements are grouped and sent in a single block or subprogram, increasing the processing speed and decreasing traffic on Oracle Server.
Why Should We Use PL/SQL?
- Although PL/SQL executes and processes the SQL statements at the end, consider a scenario of updating the salary record with a hike of 20% of all employees in the Employee table having 1000+ values. Is it practical to write the update command 1000+ times and fire the SQL query each time to update the records? For this, it came into the picture as though it was looping; it can be done in 2 lines of code without any interruption in between
- Moreover, it is fundamental for any web application to hide the implementation logic from the end users. It is done through Interfaces in programming languages like Java and C++. Similarly, the database is the main module in Database intensive applications, and the SQL queries and tables are its implementation data.
- All these modules are hidden behind the PL/SQL interface. This way, it maintains the correctness, maintainability, security, and abstraction for developers and end-users.
- The system offers a specialized feature for working with triggers, which fire as unique events when specific situations are met. This deals with various triggers like View level triggers, Database level triggers, Session level Triggers, and Table level triggers.
Advantages of PL/SQL
Below given are some of the advantages:
- It allows the users/developers to run multiple SQL statements at once by wrapping them in a block.
- It is compatible with SQL. It allows us to use all the SQL statements, data manipulation, cursor handling, and transaction statements in PL/SQL blocks. There is no need for conversion between the two of them.
- Maintaining the subprogram is easy because all the clients and applications can access a single copy stored in the database server.
- It supports scalability by accessing centralized processing on database servers, allowing multiple concurrent users to access it on a single node.
- It supports Portability, as the applications are written in PL/SQL, and is portable to computer Operating systems and hardware where the Oracle database is present and working correctly.
- It provides straightforward and expressive syntax, which is easy to understand if someone is familiar with any programming language.
- Users can automatically define triggers that will fire when a specific situation is met.
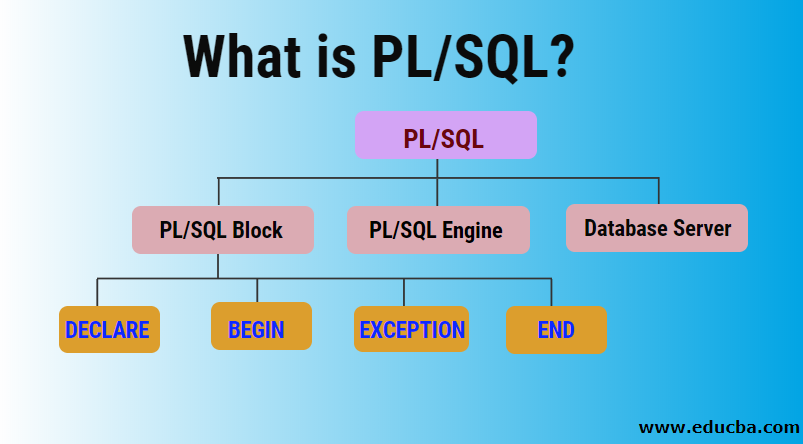
The Architecture of PL/SQL
This architecture consists of 3 components:
1. PL/SQL Block
It is the main part that contains all the code. The input includes the SQL statements and the instructions that will interact with the database.
It mainly consists of 4 parts, i.e.
- DECLARE: This part of the code is optional. The DECLARE section starts with the DECLARE keyword, which contains all the variables, constants, and records that must be declared. Then, it temporarily stores the data.
- BEGIN: It is the main section of the PL/SQL block and is mandatory. It contains all the logic written and tasks that must be performed using the SQL queries through DDL and DML statements. It starts with the BEGIN keyword and ends with END.
- EXCEPTION: This part of the block is optional, and it handles the exception. It contains the code to execute when a runtime exception occurs. This section starts with an EXCEPTION keyword.
- END: This keyword specifies the end of PL/SQL. Writing in PL/SQL block is mandatory as it indicates the code’s end.
2. PL/SQL Engine
This Engine is responsible for processing the PL/SQL statement. It compiles the code into bytecode and executes it. Then, it separates the PL/SQL and SQL code and sends the actual SQL code to the database server, where it interacts with the database. The PL/SQL engine handles the remaining code.
3. Database Server
The PL/SQL Engine uses SQL queries to interact with the data stored in the database, which serves as the component responsible for storing the data. It consists of an SQL executor that parses and processes further the SQL
How will this Technology Help you in Career Growth?
- If we talk about any web application, 98% of the application deals with the data, either handling, storing, or manipulating it. There is a high demand for people in the market with good database knowledge to organize and manage vastThe database and serves as the component responsible for storing the data. At the same time, the PL/SQL Engine utilizes SQL queries to interact with the data stored within the database amounts of data.
- As for the big applications, all the code cannot be kept in the application layer because it can degrade the overall performance of the application when it comes to sending a large number of requests to the database server at a time, so database professionals start implementing server-side coding which has wide scope in the market as it is implementing in all database-intensive applications and all this demands a good knowledge of database languages like SQL, PL/SQL, Oracle, etc.
- Companies are ready to give great packages to DBAs, as security and maintainability of data are their foremost priority.
Conclusion
The above discussion clearly shows the importance and the use of PL/SQL language in the field of database development and so on the application. It can help to deal with the database’s data, but It helps to fire that SQL procedurally. So, good language knowledge is mandatory to dive deep into the database field.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is PL/SQL? Here we have discussed why we should use it, how this technology will help you in career growth, advantages, and architecture. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –

