Updated September 6, 2023
Introduction to OSPF
When it comes to computer networking, transmitting data efficiently and reliably is crucial. Different routing protocols are used to enable seamless communication in complex networks. Open Shortest Path First is the most important and widely used among these protocols. This article will explore the specifics of OSPF, including its purpose, how it works, its advantages, and its role in modern networking architectures.
Table of Contents
What is OSPF?
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) dynamically finds the optimal route for routing data packets within an IP network in computer networking. It aims to efficiently route traffic by computing the shortest pathways considering metrics like link bandwidth, delay, and network topology changes.
OSPF Areas
An autonomous system can be divided into areas; this helps reduce the link state advertisements and other overhead traffic that will be otherwise sent to the network.
Let’s take a look:
- Backbone Area: It is also known as area 0 or area 0.0.0.0; it forms the core of an OSPF network, and all other areas of the network are connected to the backbone area. It distributes routing information between areas, not backbone area types.
- Standard Areas (Non-Backbone Areas): Standard areas refer to areas, not the backbone area (Area 0). They are useful for dividing larger networks into smaller, more manageable units. Routers within a standard area know the topology and routes within that particular area. Using standard areas reduces the amount of routing information that needs to be exchanged across the entire network.
- Stub Area: In the case of Stud Area, routing in the area is entirely based on a default route. It is an area that does not receive advertisements external to the autonomous system (AS).
- Totally Stubby Area: A “totally stubby area” expands the concept of a “stub area.” External routes are suppressed in this area, and inter-area routes are also summarized. The border router of the area introduces a default route, which simplifies routing and reduces the size of the routing table.
- Totally NSSA: The totally NSSA works similarly to the totally stubby area by blocking external and inter-area routes from entering the NSSA. External routes are condensed, and a default route is inserted into the area. The total NSSA offers improved management of external route distribution within the NSSA.
- Not So Stubby Areas: NSSA is a type of stub that can import AS external routes and send them to any other area. However, it cannot receive AS external routes from different areas of the network.
- Transit Areas: An area with two or more OSPF border routers can pass network traffic from one adjacent area to another. It does not originate traffic or the destination of any such traffic.
How does it work?
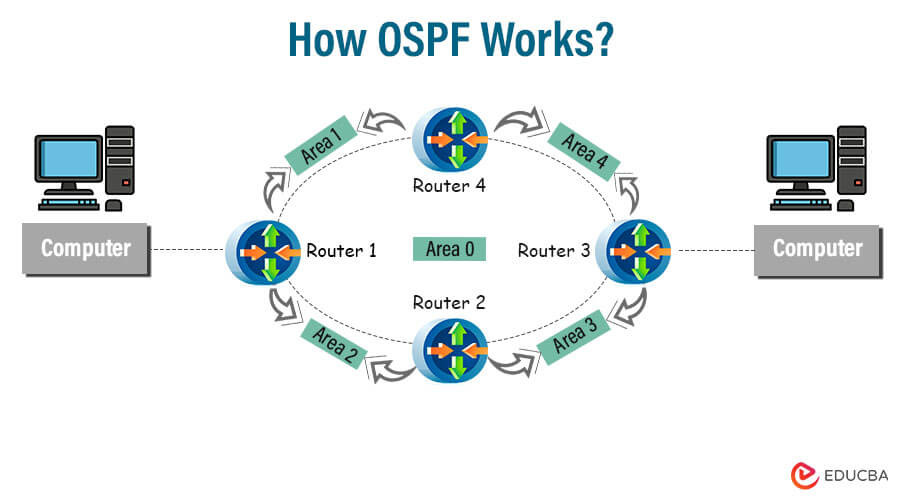
- Neighbor Discovery: To start, OSPF routers discover their neighboring routers on the same network segment by exchanging OSPF Hello packets. Routers on the same network then form OSPF neighbor relationships, which become the primary means for exchanging routing information.
- Router Types and Adjacencies: In OSPF networks, routers can be categorized as Designated Router (DR), Backup Designated Router (BDR), and ordinary routers. When it comes to Multi-access networks such as Ethernet, DR, and BDR are elected to minimize the number of adjacencies. Adjacencies link neighboring routers and facilitate the sharing of routing updates.
- Link-State Advertisement (LSA) Process: OSPF routers use Link-State Advertisements (LSAs) to exchange information regarding their interfaces, links, and states. Each router generates LSAs that describe the condition of its local links. The LSAs are spread across the network to share information about the status of the links with other routers.
- Database Synchronization: Routers using OSPF create and keep track of a database of LSAs they receive from their neighboring routers. This database holds essential information about the network’s topology. Routers exchange Database Description (DBD) packets during synchronization to ensure the databases are the same.
- Dijkstra’s Shortest Path Algorithm: After synchronizing their databases, OSPF routers utilize Dijkstra’s algorithm to determine the shortest path to all network destinations. This algorithm generates the SPF tree, representing the most efficient routes to different locations within the network.
- Route Calculation and Table Building: Using the SPF tree, routers in OSPF can establish the most efficient paths to different destinations based on metrics like link bandwidth and delay. After calculating these paths, routers populate their routing tables with the information, enabling them to make well-informed forwarding decisions for incoming packets.
OSPF creates tables:
- Routing Table: It contains the currently working best paths that will be used to forward traffic between two neighbors.
- Neighbour Table: This contains all discovered Open Short Path First neighbors.
- Topology Table: This one contains the entire road map of the network. This road map includes all the available Open Short Path First routers and keeps calculated data about best and alternative paths.
- Routing Updates and Convergence: OSPF routers are responsible for constantly monitoring the network and detecting changes in link states. Whenever a link goes down or comes up, the routers generate and send out LSAs to reflect these changes. They then recalculate the SPF tree to find out the new shortest routes. This fast exchange of information and recalculation guarantees network convergence, which means that any changes are quickly adjusted, and the best possible routes are re-established.
- Route Advertisement and Packet Forwarding: OSPF routers can send data packets using the most efficient paths after updating the routing tables. To do this, routers use OSPF Hello packets and LSAs to advertise the available routes to neighboring routers. This enables the neighboring routers to update their routing tables and know which available paths.
Router Types in OSPF
Here are the main router types in OSPF:
- Internal Router (IR): An internal router is a type of network device with all of its interfaces connected to the same OSPF area and no connections to external networks or different OSPF areas. The primary function of internal routers is to route traffic within their designated area efficiently.
- Backbone Router (BR): A backbone router, also known as an Area Border Router (ABR), connects several OSPF areas, including the backbone area (Area 0). It has at least one interface in the backbone area and one or more interfaces in other areas. Backbone routers are vital in interconnecting areas and propagating routing information between them.
- Area Border Router (ABR): ABR’s backbone router connects various OSPF areas. Its primary responsibility is summarizing routes from one area before advertising them to another. ABRs also facilitate the translation of routing information between areas with different numbering schemes.
- Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR): An ASBR is a type of router that establishes a connection between an OSPF area and external networks by utilizing a different routing protocol. Its primary function is to distribute external routes within the OSPF domain. ASBRs are instrumental in merging OSPF networks with various routing protocols.
- The Designated Router (DR) and Backup Designated Router (BDR): In networks like Ethernet with multiple routers sharing the same segment, DR and BDR are important. OSPF chooses a DR and BDR for each segment to minimize adjacencies. The DR is responsible for exchanging routing information with all routers on the segment and relaying it to other areas.
- Virtual Link Router (VLR): When a direct physical connection is not possible between two non-backbone areas, a virtual link router can establish connectivity through the backbone area. This is made possible by virtual links which extend OSPF routing information across areas.
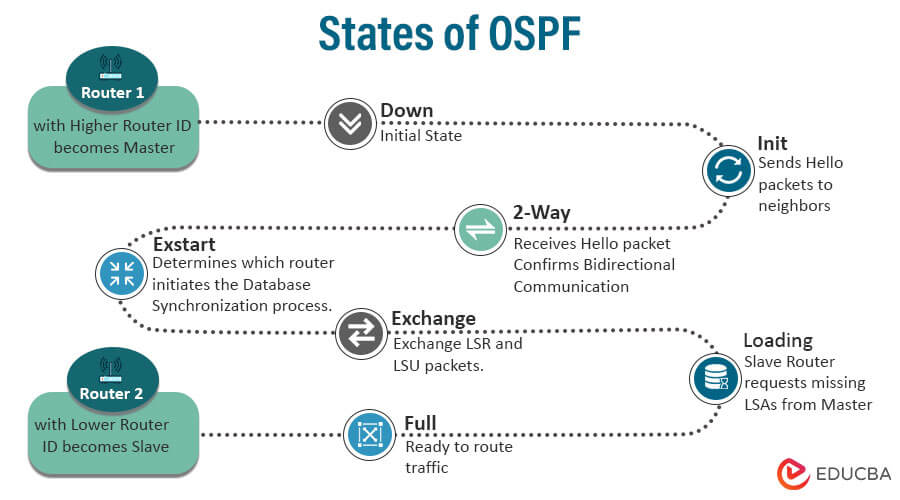
States of OSPF
Here are the main states of OSPF:
- Down: This represents the initial state where a router interface doesn’t engage in OSPF. The router isn’t actively seeking OSPF neighbors at this stage, and no OSPF messages get exchanged.
- Init: In this state, the router has identified an OSPF Hello packet from a possible neighbor. The router sends its Hello packet to the neighbor and enters the Init state. It’s an acknowledgment of receiving an OSPF Hello.
- 2-Way: Upon receiving a Hello packet from the neighbor and confirming the matching router ID and area ID, both routers transition into the 2-Way state. They mutually acknowledge each other, yet a full OSPF adjacency has yet to form.
- Exstart: During the Exstart state, routers negotiate to determine which router will exchange link-state information. The OSPF router ID of the router determines this negotiation.
- Exchange: Once the Exstart state is complete, routers exchange link-state database descriptors (LSDBDs) to identify which link-state information is necessary to synchronize their databases. This is a crucial step in achieving database synchronization.
- Loading: During the Loading state, routers share Link-State Request (LSR) and Link-State Update (LSU) packets to exchange the link-state information they identified in the Exchange state. This ensures that both routers possess identical database information.
- Full: Once the database synchronization concludes and the routers acquire all necessary link-state information, they transition to the Full state. At this state, the routers have a thorough and consistent understanding of the OSPF network and are fully connected. This enables them to precisely compute the shortest paths and send routing updates to each other.
Below is a diagrammatical representation:
OSPF Version
Over time, OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) has undergone multiple developments and standardizations, leading to the creation of two primary versions: OSPFv2 and OSPFv3.
- Open Shortest Path First version 2: OSPFv2 is designed explicitly for IPv4 networks and is currently the most commonly utilized version. It routes IPv4 packets within an OSPF domain. OSPFv2 employs IP version 4 for addressing and enjoys broad support across diverse router platforms.
- Open Shortest Path First version 3: OSPFv3 is created for IPv6 networks and is used to route IPv6 packets within an OSPF domain. OSPFv3 is an advancement of OSPFv2 and includes enhancements to support the different addressing structures and features of IPv6.
Real-World Applications
Here are some notable applications
- Enterprise Networks: Enterprise networks widely use OSPF for efficient and reliable routing. It suits large, sophisticated networks with multiple routers, switches, and subnets. OSPF’s hierarchical design and area segmentation empower organizations to manage routing effectively, attain rapid convergence, and ensure proper traffic distribution.
- Internet Service Provider (ISP) Networks: ISPs use OSPF to construct their backbone networks, divided into different areas. This allows for efficient traffic routing between other regions, and OSPF’s scalability is vital for ISP networks. It enables the seamless integration of new routers and the expansion of the network’s reach.
- Data Centers: In current data center designs, OSPF manages internal routing among server racks, switches, and infrastructure elements. OSPF facilitates load balancing, failover, and efficient traffic distribution within the data center, enhancing network reliability.
- Campus Networks: OSPF is a routing protocol applicable to campus networks of educational institutions or large organizations. It streamlines routing management across diverse departments, buildings, or campuses, allowing administrators to establish efficient paths and manage traffic flow effectively.
- Wireless Networks: Wireless networks employ OSPF to manage routing among access points, wireless controllers, and network devices. This capability ensures seamless roaming and handoff between various access points, providing uninterrupted connectivity for users.
- Telecommunications Networks: Telecom companies use OSPF to route traffic through their networks efficiently. OSPF’s scalability is especially advantageous in telecom networks, where many routers are interconnected to handle data, voice, and video traffic.
- Multi-Tenant Environments: OSPF permits logical network segmentation when multiple tenants utilize the same physical network infrastructure. Each tenant can have their own OSPF area, ensuring isolation while taking advantage of efficient routing within their domain.
- Hybrid Network Environments: Integrating OSPF into hybrid networks that utilize different routing protocols is possible. An enterprise’s internal network can use OSPF, while BGP can manage external connectivity with other autonomous systems.
Implementations of Open Short Path First
Here is a list of various OSPF implementations and platforms:
- Cisco IOS (Internetwork Operating System): The network operating system, Cisco’s IOS, is popularly used and supports OSPF as a dynamic routing protocol. OSPF is crucial to Cisco’s routing solutions and can be configured on Cisco routers and switches.
- Juniper Junos: The Junos operating system developed by Juniper offers strong support for OSPF. This system can configure OSPF on Juniper routers and switches, which helps enhance routing efficiency across different network settings.
- Quagga/Zebra: The Quagga project provides an open-source routing software implementation, which includes the Zebra routing suite. It supports the OSPF routing protocol and is often utilized on Unix-like operating systems.
- BIRD (BIRD Internet Routing Daemon): BIRD is a routing daemon available as open-source software. It supports both OSPFv2 and OSPFv3 protocols and is renowned for its flexibility. Its dynamic routing capabilities make it an ideal choice for various networking setups.
- OpenBSD and OpenOSPFD: OpenBSD, an open-source operating system, offers support for OSPF with the help of OpenOSPFD implementation. This feature enables OpenBSD users to set up OSPF routing for their network.
- VyOS: VyOS is an open-source network operating system that supports OSPF and other routing and networking features. It is useful for creating configurations for routers and firewalls.
- Linux with Quagga or FRRouting: If you’re using a Linux system, you can install routing software such as Quagga or FRRouting to implement OSPF. By doing so, your Linux machines can operate as routers with the ability to use OSPF.
- Packet Tracer and GNS3: With network simulation tools like Cisco Packet Tracer and GNS3, you can create virtual networks and practice configuring OSPF in a simulated environment.
Features
- Link-State Routing: Based on the link-state routing principle, OSPF requires routers to share information about their interfaces, states, and links. Routers communicate this data using Link-State Advertisements (LSAs), allowing them to construct a comprehensive network topology map.
- Hierarchical Design: Dividing OSPF networks into various areas, such as the backbone area (Area 0) and the non-backbone regions, is possible. This hierarchical structure improves scalability, simplifies network management, and mitigates the impact of changes in specific areas on the entire network.
- Fast Convergence: It is a highly effective protocol for quickly adapting to changes in a network, such as link failures or new connections. Frequent LSA updates and the SPF (Shortest Path First) algorithm allow routers to efficiently calculate and adapt to the shortest paths within the network.
- Scalability: Its hierarchical design and area-based architecture enhance OSPF’s scalability.OSPF reduces the processing and memory requirements on individual routers by dividing a large network into smaller areas, which limits the scope of exchanged routing information.
- Flexible Metrics and Path Selection: It allows multiple criteria (e.g., link bandwidth, delay, and cost) to select the best path for data packets. This adaptability enables network administrators to fine-tune path selection based on individual network requirements and priorities.
- Security and Authentication: It offers ways to secure routing exchanges and prevent unauthorized devices from participating in OSPF processes. Administrators can use authentication mechanisms to ensure that only trusted routers contribute to routing decisions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of OSPF
Below are the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
Below are the advantages:
- Open Short Path First is easily scalable, which means with very little amount of hassle, we can scale it to use in a very big network.
- Open Shortest Path First Protocol has full support for subnets.
- It sends small hello packets to verify link operations, ignoring transferring large tables.
- In Open Short Path First, routes can be tagged to ease interoperation with arbitrary values.
- Open Short Path First can route packets based on their type of service field.
Disadvantages
Below are the disadvantages:
- It is a processor-intensive protocol to use.
- Consumes more memory because it maintains more than one copy of routing information.
- It is a more complex protocol to understand and learn than other Internet Protocols.
Comparison with Other Routing Protocols
1. OSPF vs. RIP
| Aspect | OSPF | RIP |
| Routing Type | Link-State Routing Protocol | Distance-Vector Routing Protocol |
| Metric | Uses configurable metrics (cost) | It uses hop count as the metric |
| Convergence | Faster convergence due to SPF algorithm | Slower convergence due to periodic updates |
| Scalability | More scalable, suitable for larger networks | Less scalable, best for small to medium networks |
| Network Size | Suited for larger and more complex networks | Best for small to medium-sized networks |
2. OSPF vs. EIGRP
| Aspect | OSPF | EIGRP |
| Routing Type | Link-State Routing Protocol | Advanced Distance-Vector Protocol |
| Convergence | Faster convergence due to SPF algorithm | Rapid convergence with DUAL algorithm |
| Metrics | Uses configurable metrics (cost) | Uses composite metrics |
| Vendor Specificity | Standardized protocol, interoperable | Cisco proprietary protocol |
| Design Purpose | Designed for larger, complex networks | Designed for efficient, stable networks |
3. OSPF vs. BGP
| Aspect | OSPF | BGP |
| Routing Scope | Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) | Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) |
| Path Selection | Optimizes paths within an AS | Optimizes paths between ASes |
| Route Information | Distributes detailed route information | Distributes high-level reachability info |
| Convergence | Faster convergence within an AS | Slower convergence due to complexity |
| Primary Use Case | Routing within an autonomous system | Routing between different autonomous systems |
Conclusion
Open Shortest Path First, as a routing protocol, is important in internet infrastructure. Finding the shortest path easily and quickly helps reduce unnecessary network load, and the ability to find another path in case of error at the optimal one helps increase the stability of the network.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “What is OSPF” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

