Updated March 17, 2023
What is IPv6?
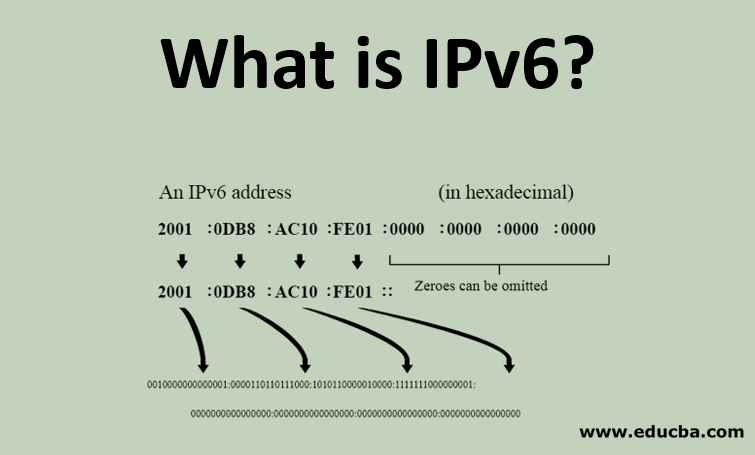
IPV6 is internet protocol version 6, which is used in the IP layer of TCP/IP protocol suite to identify each device connected to the internet, designed to provide more features than IPV4. IPV6 address is unique and universal, 128 bits or 16 bytes long having address space 2^128, uses four notation to show address, dotted-decimal notation, colon hexadecimal notation, mixed representation, and CIDR notation. IPV6 address can be unicast, anycast or multicast.
Need for IPv6
The explosive growth in technology and upgrade of various configurations in mobile devices, computers, tablets, wireless handheld devices has increased the need for address allocation. IPv6 is intended to replace the widely used IPv4, which was considered the backbone of the modern internet. IPv6 is developed to overcome IPv4’s address exhaustion. Before the detailed Explanation of IPv6’s need, Let’s Get an Overview of IPv4 and its Disadvantages.
IPv4’s Build & Its Disadvantages
IPv4 is the fourth version of the internet protocol development, and it stood as one of the core protocols of standards-based internetworking methods in the internet and packet-switching networks. It holds 32-bit addressing and still handles internet traffic.
It limits the addressing space to 2^32 and also reserves the blocks for private networks and multicast addresses. Mostly the addresses are written as four octets in decimal numbers separated by periods. It is also expressed in the dotted hex format. The allocation is divided into two parts: Network identifier and Host identifier. The network identifier holds the most significant octet of the address, and the host holds the rest of the address. The network classes are created to overcome the limit, and the system is revised using five classes.
<image>
The special-use addresses hold the address range with the number of addresses at different scopes, and it will be restricted for general use. It is mostly used for private networks to provide addressing space and for multicast traffic.
IPv4 Address got Depleted Because of the four main reasons.
- The rapid growth of internet users.
- Always on the device like cable modems.
- High usage in mobile devices, laptops, computers.
- Inefficient address use.
Because of address exhaustion, it developed as a threat and helped to identify and overcome with few methodologies like Classful networks, Classless Inter-Domain routing, network address translation, and policies also created for strict allocations. These technologies helped the problem to mitigate for some time by applying changes in the address allocation and routing infrastructure of the internet. The primary depletion in IPv4 caused insufficient capacity in the original design of internet infrastructure. Each of the problems increased in demand on the limited supply of addresses as follows:
1. Internet Regions: Development of the internet connectivity over the 15 years from 1990 brought high usage of broadband connection. Developing countries like India, China drives address exhaustion.
2. Inefficient Address Use: The Organizations that obtained IP addresses in the early 1980s allocated far more addresses than required. Because the initial classful network allocation method was inadequate to reflect reasonable usage, this had a restriction in IP addressing for devices that are not accessible outside their local network. This inefficiency exists in various scenarios from global address allocation also. Subnetting was the reason for inefficiency, and it did not allow us to use the addresses in a block.
3. Broadband-On Connections: Telephone modem dial-up was the predominant way for internet access. As the modem pool shares a common IP address and the pool gets assigned with IP addresses, and it was shared based on the consumer base. The rapid increase in the dialup networks increased the address consumption rates. As the year increased, the broadband connection has begun to exceed the 50% penetration of access as the connection always stays active as the gateways rarely turned off.
4. Mobile Devices: When the new tech has emerged in the mobile phone era, internet access demands increase. The digital communication and cost of embedding substantial computing power in hand-held devices were dropped. As it becomes viable and new specs of 4G/5G require IPv6 addressing for fast speed communication. These were the major reasons that started the address exhaustion. Mainly, Regional exhaustion was also the reason. The supply of RIR’s (Regional Internet Registries) exhausted at 1024 addresses. That begun the transition of IPv6 with the demand for change in internet infrastructure.
IPv6 Packets & Its Usage
To overcome the internetworking infrastructure of IPv4, IPv6 was built with extended octets to 40 octets and provided an opportunity to extend the protocol for the future without affecting the core packet structure. It introduced “Jumbograms”, which means the packet can handle over the limit of 2^32. Jumbograms improve performance over high MTU links and tackles the payload.
<image>
<image>
IPv6 holds 128 bits in addresses and its design in address space is large enough for future uses. The identifier is unique within the subnet to the host connected to the network. It is divided into 8 groups of 16 bits each. A colon separates each group in a hexadecimal format.
Usage of IPv6
Below are the points that explain the usages of IPv6:
- Comcast and AT&T have 63% & 65% in its network
- T-Mobile USA has more than 85% of traffic handling over IPv6.
- Alexa uses over 30% of access to their websites.
- IBM, first commercial vendor to support IPv6 through its AIX 4.3 OS
- The latest versions of Windows OS have IPv6 support enabled by default.
Benefits of IPv6
Below are the points that explain the Benefits of IPv6:
- IPv6 handles the packets more efficiently with a large address space.
- Improves the performances and increased security
- Hierarchical arrangement in routing table enables less space through internet service providers.
- IPv6 enables corporate machines with private IP addresses can send & receive packets from machines located outside the private network with public IP addresses.
- Stateless and Stateful address configuration both in the absence or presence of DHCP server
- Flow label field provides better support for prioritized delivery.
Development of IPv6
Below the points explain who developed IPv6:
- IPv6 was developed by Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
- The R&D networks with IPv6 infrastructure, services & applications in operations are AARNET (Australia), Abeline (US), Gigabit European Academic Network (Europe) & many others.
Conclusion – What is IPv6?
The findings and incorporation over IPv4 indicate that the IPv6 core is well supported and proven with its interoperability, and it is being deployed in the latest generations of routers & OS. Thus it is extended by the infrastructure to support complete enterprise transitions.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to What is IPv6? Here we discuss the needs of IPv6 with disadvantages of IPv4, usages, benefits, and who developed IPv6 in detail. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –