Introduction to Breadth First Search
Breadth First Search is an algorithm which is a part of an uninformed search strategy. This is used for searching for the desired node in a tree. The algorithm works in a way where breadth wise traversal is done under the nodes. It starts operating by searching starting from the root nodes, thereby expanding the successor nodes at that level. Then it moves to the other node by expanding along with its neighbouring breadth. The algorithm requires a considerable amount of memory space and time for its execution in the case where the required node lies at the bottom of the tree or graph. The BFS algorithm requires the usage of First in First Out queue for its implementation. The BFS strategy works without any domain knowledge.
Now we shall put our glance at the steps involved in the BFS strategy.
Step 1: We take an empty queue.
Step 2: Then, we select a starting point or root node to start with and insert the data from the node into the queue.
Step 3: If the queue is not empty, then we extract the node from the neighbouring nodes in breadth wise fashion and insert its child nodes into the queue.
Step 4: Then, we can print the extracted nodes.
Example of Breadth First Search
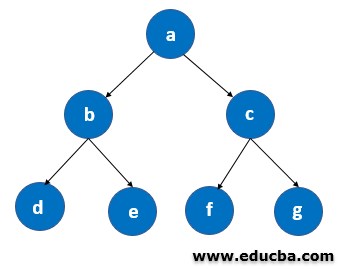
We will now see the steps of the above BFS strategy into this example. We take a look at the graph below. We will use the BFS strategy to traverse the graph.
We can allocate ‘a’ as the root node. Then we start searching for the goal node in the downward direction following the steps mentioned above.
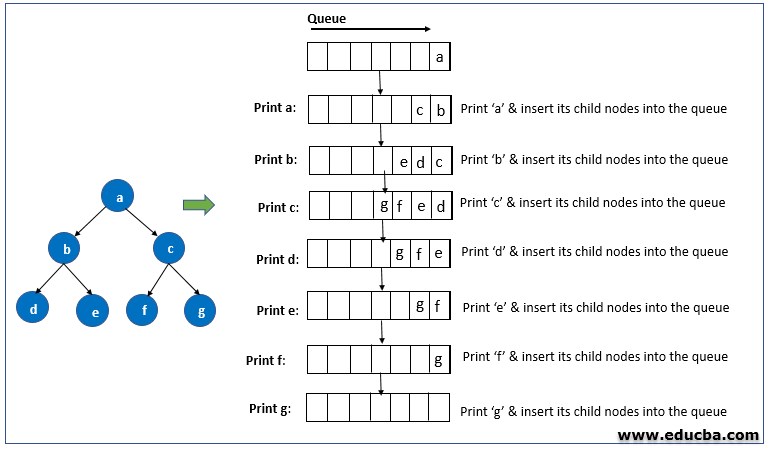
The figure illustrates the steps involved in BFS, which binds in the end to end process. The steps are executed in the following manner.
- We allocate node ‘a’ as a starting root node and insert it into the queue.
- Then ‘a’ node is extracted and the child nodes of ‘a’ which are ‘b’ and ‘c’ put into the queue.
- Then we Print ‘a’.
- Then the first node in the queue is extracted again similarly.
- Next, the child of ‘b’ which are ‘d’ and ‘e’ are inserted into the queue and extracted for printing.
- Then we recursively repeat the steps until the queue is empty.
- We cannot repeat the steps for already visited nodes.
Now let us see below the pseudo-code of the algorithm.
- Input: s as the source node
- BFS (G, s)
- let Q be the queue.
- enqueue( s )
- mark s as visited
- while ( Q is not empty)
- v = Q.dequeue( )
- for all neighbours w of v in Graph G
- if w is not visited
- enqueue( w )
- mark was visited
Applications of Breadth-First Search
We can say that there are numerous applications of BFS in data sciences, one of them being in finding the shortest path using a minimum spanning tree. There are various applications in networking, broadcasting, GPS navigation, etc. The range of applications surprises us though the execution time might not allow us to choose it sometimes. The BFS is one of the main algorithms used in indexing web pages.
The Program in C language for BFS implementation is as follows:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define MAX 200
#define initial 1
#define waiting 2
#define visited 3
int m;
int adj[MAX][MAX];
int state[MAX];
void create_graph();
void BF_Traversal();
void BFS(int x);
int queue[MAX], front = -1,rear = -1;
void insert_queue(int vertex);
int delete_queue();
int isEmpty_queue();
int main()
{
create_graph();
BF_Traversal();
return 0;
}
void BF_Traversal()
{
int x;
for(x=0; x<m; x++)
state[x] = initial;
printf("Enter the starting vertex for doing BFS: \n");
scanf("%d", &x);
BFS(x);
}
void BFS(int x)
{
int i;
insert_queue(x);
state[x] = waiting;
while(!isEmpty_queue())
{
x = delete_queue( );
printf("%d ",x);
state[x] = visited;
for(i=0; i<m; i++)
{
if(adj[x][i] == 1 && state[i] == initial)
{
insert_queue(i);
state[i] = waiting;
}
}
}
printf("\n");
}
void insert_queue(int vert)
{
if(rear == MAX-1)
printf("Queue is overflowing\n");
else
{
if(front == -1)
front = 0;
rear = rear+1;
queue[rear] = vert ;
}
}
int isEmpty_queue()
{
if(front == -1 || front > rear)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int delete_queue()
{
int delete_item;
if(front == -1 || front > rear)
{
printf("Queue is underflowing\n");
exit(1);
}
delete_item = queue[front];
front = front+1;
return delete_item;
}
void create_graph()
{
int count,m_edge,ori,dest;
printf("Enter number of vertices : ");
scanf("%d",&m);
m_edge = m*(m-1);
for(count=1; count<=m_edge; count++)
{
printf("Enter edge %d( -1 -1 to quit ) : ",count);
scanf("%d %d",&ori,&dest);
if((ori == -1) && (dest == -1))
break;
if(ori>=m || dest>=m || ori<0 || dest<0)
{
printf("Invalid edge!\n");
count--;
}
else
{
adj[ori][dest] = 1;
}
}
}
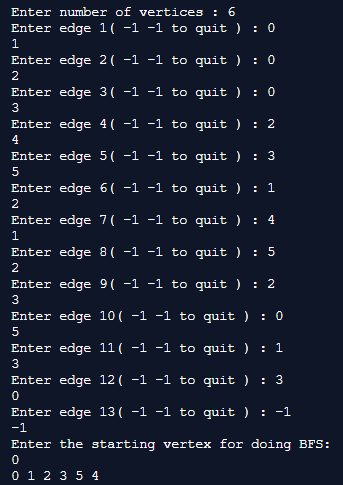
Output
The run time of the code is given by O (V+E) where V =Number of vertices and E=Number of edges.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Breadth First Search
Below are the advantages and disadvantages of BFS
Advantages
- The breadth-first search algorithm is complete.
- The optimal solution is possible to obtain from BFS.
- There is a vast number of applications of the BFS algorithm in data science.
- Optimality means admissibility if all the operators used in the code are having the same cost and the goal node can be reached in time. The other possibility is that the solution is found with the shortest length without optimality.
- The execution time is exponential, and the memory space complexity can be expressed as O(b^d), where d=depth of the search space and b=branching factor(child nodes)
Disadvantages
- The run time may exceed when the goal node is not known.
- The execution time might get into an infinite loop.
- The main demerit looks to exist in the time taken to find the solution with large data and thus it gives priority to look at shorter lengths first.
Conclusion
The Breadth-first search is a simple algorithm for implementing the search operation breadth wise and using FIFO queues. The memory space requirements might rise high, but yet it proves to be high in demand. It is used in determining the levels of a tree using its node information. From this basic application to higher range usages in networking, peer to peer networking, we may find the applications of BFS. Thus, we may say that BFS is an important uninformed search algorithm that opens the research gateway as well.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Breadth First Search. Here we discuss Breadth First Search’s examples along with the steps involved in the BFS strategy and advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –