Updated July 6, 2023
Introduction to JDBC
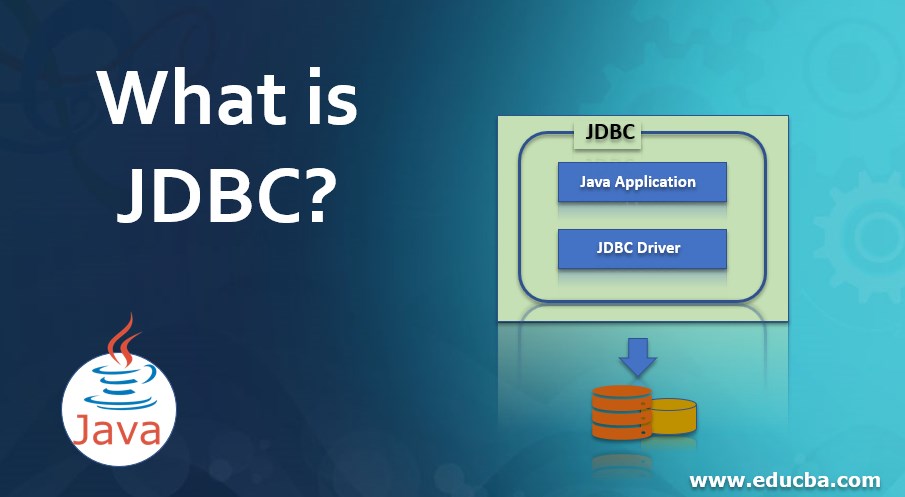
JDBC’s full form is Java Database Connectivity. It is a Java API that executes and connects queries with the database. It is considered part of Java SE, Java Standard Edition. API of JDBC makes use of drivers of JDBC to get connected along with the database. We can consider four types of JDBC drivers mentioned below :
- JDBC-ODBC Bridge Driver
- Thin Driver
- Native Driver and
- Network Protocol Driver
Developers can utilize the JDBC API to access tabular data stored in various relational databases. Using JDBC API, you can save, update, delete, and fetch the data from the database. Therefore, Microsoft provides Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) as the standard for database connectivity.
- Definition
- Understanding JDBC
How does it work?
Establishing a connection with an application or a data source, sending queries, updating statements, and processing results can be easily done using JDBC or Java Database Connectivity. It has made all the things mentioned below possible within a Java application –
- It helps in establishing a connection easily with a data source
- Sending queries and updating statements are made possible by it.
- It helps fetch data from the database and process the fetched results.
The SQL statements and queries can be submitted, and results can be retrieved by calling the JDBC classes and interfaces with the help of the Java application. It is the JDBC driver that helps in the implementation of the JDBC API. This driver constitutes a set of classes that will implement the JDBC interfaces. This will further assist in processing the JDBC calls and sending output/results to the Java application. The database serves as a data store where the Java application, utilizing the JDBC driver, retrieves and stores all the data.
Why should we use JDBC?
Before it came into existence, we used the ODBC API database to connect and execute queries along with the database. However, ODBC API makes use of ODBC drive in C language. Also, it is platform-dependent and, in addition, unsecured. Java defined its API, known as JDBC API, in the Java language using JDBC drivers. This design choice enables compatibility and ease of use within the Java ecosystem.
We can perform various activities using the JDBC API required to handle the database:
- Connection to database
- Execution of queries as well as update statements to the database
- Retrieving results fetched from the database.
Architecture of JDBBC
It supports two-tier as well as three-tier processing models for availing database access. However, generally speaking, Its Architecture has two layers listed below:
- JDBC API: This layer supports the connection to application-to-JDBC Manager. It uses the driver manager and database-specific drivers to give transparent connectivity to heterogeneous databases.
- JDBC Driver API: This layer connects JDBC Manager to Driver. The driver manager ensures it uses the correct driver to access each data source. It can also support concurrent connections to various heterogeneous databases using multiple drivers.
JDBC Components
It consists of the following interfaces as well as classes which can be termed components as well :
- Driver Manager: As the name suggests, the driver Manager class manages the list of drivers in the database. It also matches the connection requests from the java application and the database driver with the help of a sub-protocol of communication. The first driver, which recognizes subprotocol under the JDBC, establishes a database connection.
- Driver: The driver is the interface that manages communications between the application and the database server. The chances of interacting with the driver object directly are very rare as, most of the time, the objects of the Driver Manager are generally used to manage objects of this type. It extracts all the detail=[]- associated with the working of Driver objects.
- Connection: Developers use a connection interface and its methods to establish contact with the database. The object of connection represents the context of communication; that is, all communication with the database is only through the object of connection.
- Statement: The objects created from this interface will make it possible to submit the SQL statements to the database. Some of the derived interfaces also accept parameters while executing some stored procedures.
- ResultSet: ResultSet objects hold the data retrieved from the database, but this occurs after executing an SQL query using Statement objects. It also acts as an iterator that allows us to move through the data.
- SQL Exception: The SQL Exception class handles errors in the database application.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Below are the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
Some of the advantages of using are mentioned below:
- It is capable of reading any database. The only requirement for it to do so is properly installing all the drivers.
- It automatically creates the XML format of data from the database.
- The conversion of material is not necessary.
- It provides full support to query and stored procedures.
- Both synchronous and asynchronous processing are supported.
- It supports modules.
Disadvantages
Just like most of the APIs, It also has some cons. Some of these disadvantages are mentioned below:
- It is susceptible when it comes to the driver. Hence, installing the correct drivers and deploying them for each database type is essential. This is a time taking task and challenging at times.
- It does not allow a single sequence to update or insert multiple tables.
Conclusion
Thus, It helps you connect to a database and execute SQL statements against the database. JDBC API also, as discussed, gives a set of interfaces and also different implementations respective to their databases.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to What is JDBC. Here we have discussed JDBC’s Architecture, Components, Advantages, and Disadvantages. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –

