Table of Contents
- What is Java Inheritance?
- Inheriting from Object
- Types of Java Inheritance
- Stopping Inheritance with the final keyword
- Importance of Inheritance in Java
- Creating Constants with final keyword
- Advantages
- Why should we use it?
- Why do we need it?
- Who is the right audience for learning Java Inheritance technologies?
- How will this technology help you in career growth?
What is Java Inheritance?
When it comes to Java, Inheritance can be used when a class desires to inherit the characteristics of another existing class. The class which usually aims to utilize the feature of another class is known as the subclass, while the class whose features have to be used is known as the superclass.
That leads to the query, “Where will it all start?” The top-most class, the derived class, is an Object class described in java.lang. The object is a root structure of classes.
The below figure shows those two types of classes:

The subclass follows conditions and behavior, such as variables and methods from the superclass. The subclass may use just the items inherited from the superclass, and the subclass may change or override this. Therefore, as you fall into the hierarchy, the classes become more and more specific:
Inheriting from Object
Every class inherits directly from the Object class
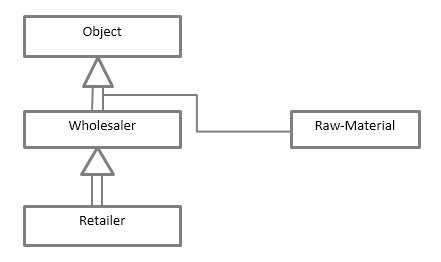
In the above diagram
public class Wholesaler extends Object { …….. }
public class Retailer extends Wholesaler { …….. }
public class Raw-Material { …………}
The extended keyword shows the parent class that the subclass is usually inherited and cannot be applied as identifiers.
In a public class, Raw-Material no need to extend the keyword; it is directly accessing the Object class.
Types of Java Inheritance
Inheritance denotes an IS-A relationship, also referred to as a parent-child relationship, as mentioned in the introduction.
Before moving to the types of Inheritance in Java, first, let us see the syntax of Inheritance.
Syntax:
class apple extends fruit
{
//methods and fields
}
Here, apple is the subclass, and fruit is the parent class. This means Apple has specific unique properties, and it also has the properties of the fruit.
Different types are given below.
1. Single Inheritance
A class that extends only one class. In the following example, class apple extends class fruit.

i.e., Fruit is the superclass, and Apple is the subclass that extends the properties and behavior of the Fruit class.
public class Fruit {
………..
}
public class Apple extends Fruit {
………..
}Following is the demonstration of single Inheritance in Java.
Code:
//Java program to demonstrate Single Inheritance
//parent class
class fruit {
public void taste()
{
System.out.println("Fruits are sweet");
}
}
//child class of fruit
class apple extends fruit
{
public void shape()
{
System.out.println("Apple is round");
}
}
public class InheritanceExample
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
apple fr = new apple(); //object of child class
fr.taste(); //call method of parent class
fr.shape(); //call method of child class
}
}Output:

2. Multi-Level Inheritance
Multilevel inheritance occurs when a class extends another class, which, in turn, can be extended by yet another class.
public class A { ……………… }
public class B extends A { ……………… }
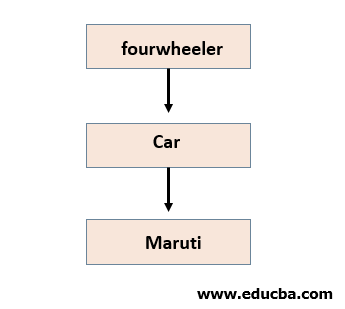
public class C extends B { ……………… }In this type of inheritance, a class will be extended from another class, and the derived class acts as the base class for some other class.
For example, in the figure, a class four-wheeler is the parent class, and the car is the derived class of the four-wheeler class. At the same time, the class car can be the base class for class Maruti.
Code:
//Java program to demonstrate Multiple Inheritance
//parent class
class fourwheeler {
public void wheels()
{
System.out.println("I have 4 wheels");
}
}
//child class of fourwheeler and parent of maruti
class car extends fourwheeler
{
public void type()
{
System.out.println("I'm a car");
}
}
//child class of car class
class maruti extends car
{
public void comp()
{
System.out.println("I'm maruti");
}
}
public class InheritanceExample
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
maruti fr = new maruti(); //object of child class
fr.wheels();
fr.type();
fr.comp();
}
}Output:
3. Hierarchical Inheritance
If a class has more than one child class (subclasses) and more than one child class has a similar parent class, then such inheritance is called hierarchical inheritance. For example, classes B and C extend the same class A.
public class A { ……………… }
public class B extends A { ……………… }
public class C extends A { ……………… }We are writing a code where class B and C extends class A
In Hierarchical inheritance, a base class has more than one child class, which means different classes acquire the class’s properties.
For example, a class vehicle has subclasses car, bike, and scooter.

Code:
//Java program to demonstrate Hierarchical Inheritance
//parent class
class vehicle {
public void wheels()
{
System.out.println("I have wheels");
}
}
//first child class of vehicle class
class bike extends vehicle
{
public void countwl()
{
System.out.println("I am a bike and has 2 wheels");
}
}
//second child class of vehicle class
class car extends vehicle
{
public void countwlc()
{
System.out.println("I am a car and has 4 wheels");
}
}
//third child class of vehicle class
class scooter extends vehicle
{
public void countwls()
{
System.out.println("I am a scooter and has 2 wheels");
}
}
public class InheritanceExample
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
scooter sc = new scooter(); //object of scooter class
sc.wheels();
sc.countwls();
car c = new car(); //object of car class
c.wheels();
c.countwlc();
bike b= new bike();//object of bike class
b.wheels();
b.countwl();
}
}Output:
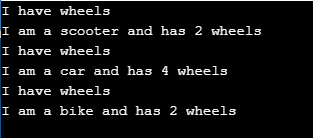
4. Multiple Inheritance
Multiple inheritances in Java is a type of inheritance in which a class has more than one parent class. For example, class C acquires the properties of both class A and class B.
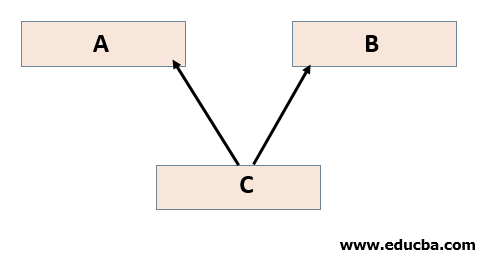
The syntax for Multiple Inheritance
public class A { ……………… }
public class B extends A { ……………… }
public class D extends A, B, C { ……………….. }Java would not support multiple inheritances. This is because various inheritances cause ambiguity, and thus, Java does not use it. Diamond issue assists with comprehension of this scenario.
However, multiple inheritances in Java may be accomplished by using interfaces. Regardless of the many quantities of interfaces in a class with an exact method, there is no indication of ambiguity since methods within an interface are often abstract.
The other way is to use interfaces. Interfaces will start becoming important.
An interface specifies the form of its methods but does not give any implementation details; therefore, you can think of it much like the declaration of a class.
In Java, achieving Multiple Inheritance is possible only through interfaces. You can create the interface with the interface keyword:
interface C
{
…………………………
}
interface b
{
…………………….
}
class a implements b, c
{
………………………
}We can use these two interfaces with the implements keyword:
If multiple inheritances were implemented like other types of inheritance, the system could encounter a compile-time error as follows.
Code:
//Java program to demonstrate multiple Inheritance
//parent class
class A
{
public void hh()
{
System.out.println("A is working");
}
}
class B
{
public void hh()
{
System.out.println("B is working");
}
}
class C extends A,B
{
//code for class c
}
public class InheritanceExample
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
C sc = new C(); //object of C class
C.hh();
}
}The output won’t be displayed here as it contains a compile-time error.
5. Hybrid Inheritance
Hybrid inheritance is mostly a mixture of more than one type of inheritance. When classes A and B extend class C, Plus another class, D, extends class A, this can be a hybrid inheritance since it is a variety of single and hierarchical inheritance.
public class C {
public void display() {
System.out.println("C");
}
}
public class A extends C {
public void display() {
System.out.println("A");
}
}
public class B extends C {
public void display() {
System.out.println("B");
}
}
public class D extends A {
public void display() {
System.out.println("D");
}
public static void main(String args[]){
D obj = new D();
obj.display();
}
}Output:

Stopping Inheritance with the final keyword
You can prevent the class from being a subclass by declaring the entire class final below.
final class animal
{
public void breathe()
{
System.out.println("Breathing...");
}
}
class dog extends animal
{
public void breathe()
{
System.out.println("Barking...");
}
}
public class history
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Creating an animal...");
animal a = new animal();
a.breathe();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Creating an bulldog...");
dog d = new dog();
d.breathe();
}
}If you try to execute this code:
Can’t subclass final classes: class animal class dog extends animal 1 error generated.
Importance of Inheritance in Java
- Code Reusability: Inheritance helps in reducing the rewriting of code. other classes can reuse i.e., Code, and the child class only has to write its unique properties. This reduces the time consumption and complexity of the code.
- For Method Overriding: Multilevel inheritance occurs when a class extends another class, which, in turn, can be extended by yet another class.
Syntax:
final class A
{
. . .
}
Class B extends A
{
. . .
}In this case, an error that says ‘Cannot inherit from the final A’ will be generated.
Creating Constants with final keyword
To prevent method overriding and to prevent subclassing. There is another use for final in Java; you can use it to declare constants.
As per the below code:
public class history
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
final int a = 4;
a = 5;
}
}If you try to execute this code:
Can’t assign a value to a final variable: a one error generated
Advantages
Inheritance, as one of its primary features, reduces the amount of duplicate code in an application by allowing the sharing of common code among multiple subclasses. Refactoring the hierarchy often involves transferring the common code to a shared superclass when two related classes contain identical code. This will result in a superior organization of code and smaller, easier compilation units.
- Inheritance: It can make application code much more adaptable to modify simply because classes inherited from a standard superclass may be used interchangeably. When the return type of a procedure is the superclass.
- Reusability: Ability to manage public methods of a base class without rewriting the similar.
- Extensibility: Extending the base class logic according to the business logic of the derived class.
- Data hiding: The base class wants to keep a few private data, so the derived class never modifies it.
- Overriding: With inheritance, we can override the base class’s methods, so important implementation of the base class method could be completed in the derived class.
Why should we use it?
Inheritance is a practical programming concept, but it may be simple to use inappropriately. Usually, interfaces are effective and more efficient.
Inheritance is the best choice when:
- Your inheritance hierarchy signifies an “is-a” relationship but not a “has-a” relationship.
- You may reuse the code from the base classes.
- You may need to apply similar classes and ways to distinct data types.
- The class hierarchy is relatively shallow, and other developers are not contributing many more phases.
- You wish to modify a base class by creating global variations to derived classes.
Why do we need it?
It is an OOP (object-oriented programming) concept. The primary purpose of inheritance is to create a new part of your project’s code that is reusable, possibly adding or eliminating features. A child class could inherit or override methods chosen from the parent class; it is the methods from without exchanging the parent class. This can include its own new methods, which is usually not found in the child class.
- Encapsulation: When we involve some common attributes, we encapsulate these in a parent class and simply provide particular attributes to child classes.
- Polymorphism: We could utilize Polymorphism with Inheritance in Java. The same class acts differently to ensure according to the form of the Child’s class.
- Code Reusability: Applying Inheritance can help reuse code.
- Efficiency: It can be effective to apply Inheritance while writing code. This could boost the speed of the task.
Like in real life, a child could inherit selected features from his parents and, through selected environmental variations, develop new features or drop features he attained from his parents.
Who is the right audience for learning Java Inheritance technologies?
When thinking about what should be done with it, several developers think of building:
Android Developer
Android is the most effective mobile operating system in today’s competitive market, with more than 1.5 million new devices activated daily. Android training offers you hands-on experience in creating and constructing easy to complex Android apps, ensuring you are proficient in acquiring your dream IT job. You could have an excellent history in programming, but Android training will benefit you and enhance your abilities.
Learning the fundamental principles and features of Android will enhance your skill set, growing it in tandem with the platform’s expansion. Developers can make games and apps for Android users and spread them through an open world. Android training is amongst the most intelligent facts a developer can accomplish, so it has many benefits.
IoT Developer
You can hear much about the Internet of Things (IoT). The IoT is all around, from sensors in enormous industrial machinery to smart-house devices like digital security cameras. Did you know the popular Nest thermostat will depend on a remarkable combination of Java and AI? A few smart vending machines are Java-dependent, working with software to track inventory, temperature, humidity, and region. Furthermore, several wearable technology applications are designed in Java Inheritance.
Big Data Analysis
Nowadays, big data analysis is at the core of one of the most exciting uses of technology. Research studies in several key industries are applying innovative data analysis techniques to learn new patterns in large volumes of data also to figure out complex processes better.
Embedded Systems
Embedded systems, ranging from small chips to specialized computers, comprise components in larger electromechanical devices that perform dedicated tasks. Like SIM cards, many devices, blue-ray disk players, utility meters, and television sets use embedded Java solutions. According to Oracle, 100% of Blu-ray Disc Players and 125 million Television devices utilize Java.
How will this technology help you in career growth?
Java is among the most prominent and essentially used programming languages on the globe of Information Technology. Furthermore, Java is a fundamental programming language that a fresher can quickly learn. As per the report by Oracle, Java runs on over 3 Billion devices..!
Java is an evergreen programming language. Almost all known companies, including IBM, Infosys, CTS, and TCS, apply Java as their ideal Programming Language.
Today the Existing trends Java developers can play with are listed below –
- Java with Selenium Automation Tester
- Java with DevOps
- Java with Hadoop Development
Conclusion – Java Inheritance
It is a powerful weapon of Java that can help to succeed in the most suitable language. It can minimize code duplication and reduce bugs. With the code set in the parent class, you can no longer prefer to write similar code for many child classes with the characteristics. Inheritance in Java executes code reusability.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to What is Java Inheritance? Here we have discussed the basic concept, use, need, career growth, and advantages of Java Inheritance. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –