Updated July 25, 2023
Definition of Beta
Beta is a statistical measure of a company’s stock price variability in relation to the stock market overall. It is calculated by regressing the percentage change in a stock or portfolio against the percentage change in the market (usually as defined by an index like the SENSEX/NIFTY).
Risk-Free Rate
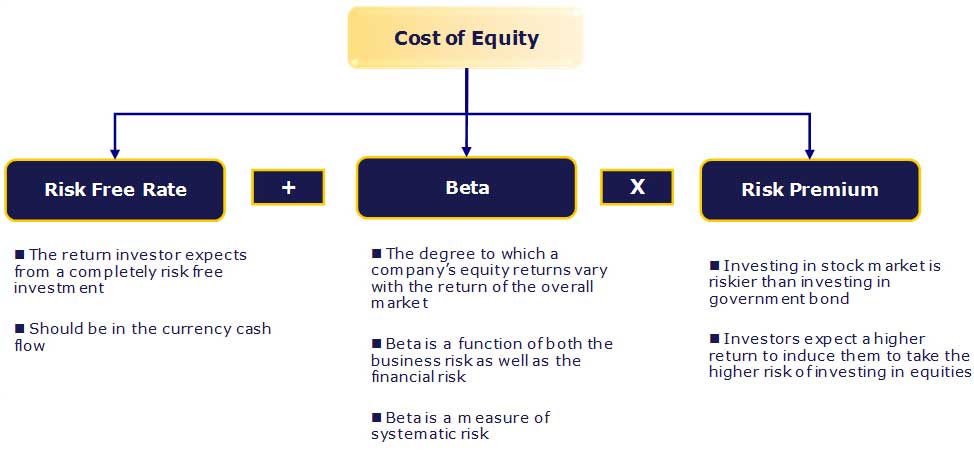
Risk-free security has no default risk, no volatility, and a beta of zero. Practically such a security does not exist; hence, we use securities issued by a political and stable government. Selecting the bond depends on the forecast horizon – short term or long term?
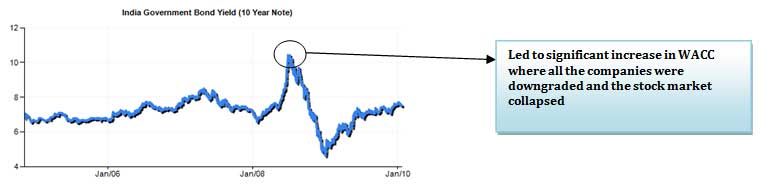
The closest approximation to the risk-free rate is the yield on government bonds. Most analysts use long-term government bond yield. Ideally, the calculation of bond yield should match the forecast’s length with the bond’s tenure. For example, if a company has been forecast-ed for 10 years, we should use a 10-year bond yield as the risk-free rate.
What is Beta?
Beta is a statistical measure of a company’s stock price variability in relation to the stock market overall. It is calculated by regressing the percentage change in a stock or portfolio against the percentage change in the market (usually as defined by an index like the SENSEX/NIFTY).
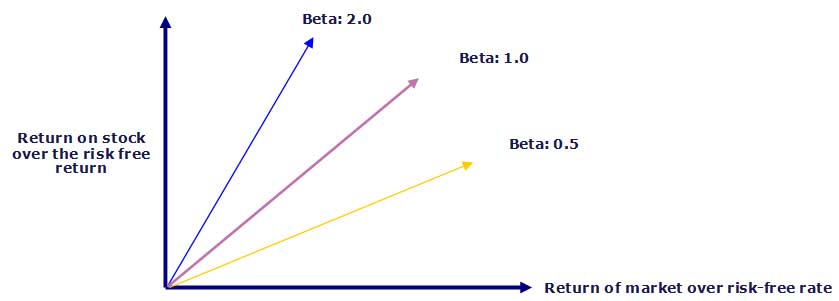
Thus, a beta of one (1) implies a stock that moves exactly with the market. Applying a beta of one (1) to CAPM would result in a premium over the risk-free rate equal to the average equity premium. A higher/lower beta means the stock is riskier/less risky, resulting in a greater/lesser required return. Most betas fall between 0.1 and 2.0 though negative and higher numbers are possible.
The sensitivity of Beta is because of two components: the risk inherent in the assets of the business and the risk associated with the leverage applied to those assets.
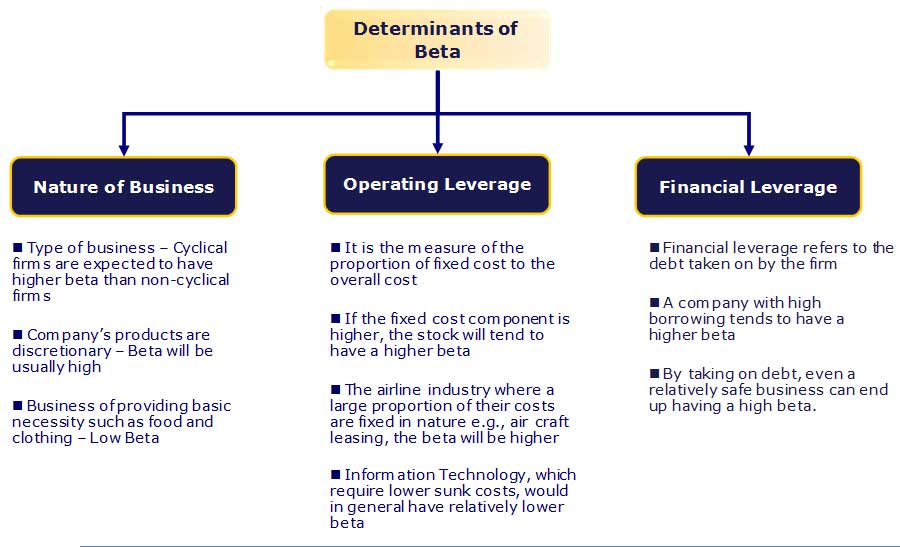
Determinants of Beta
- Product or service: The beta value for a firm depends upon the sensitivity of the demand for its products and services and its costs to macroeconomic factors that affect the overall market.
- Cyclical companies with higher than non-cyclical firms that sell more discretionary products will have higher betas than firms with fewer discretionary products.
- Operating leverage: The greater the proportion of fixed costs in the business’s cost structure, the higher the beta.
- Financial leverage: The more debt a firm takes on, the higher the beta of the equity in that business will be. Debt creates a fixed cost, interest expenses, that increase exposure to market risks.
Unlevering and Relevering Beta:
It is a statistical measure of a company’s stock price variability in relation to the stock market overall. However, if we value a non-listed private company, we cannot find the beta as suggested above.
Beta Calculation
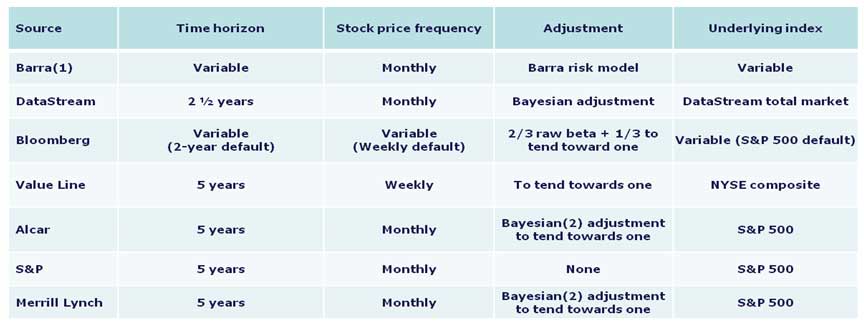
Below are the methodologies utilized by various sources in calculating:
The preferred beta methodology policy in India is that you should use Bloomberg provided Beta unless there is a good reason not to. However, the fundamentals of how beta is calculated are set out below.
1. Time Horizon – Five Years
Studies have demonstrated that longer horizons give more accurate betas. Five years is an appropriate time to capture a stock’s movement while reflecting current market dynamics. Shorter periods can reflect market or company aberrations more readily. Most major sources utilize this horizon.
2. Frequency – Monthly
More history is available for monthly stock prices, allowing generally more in-depth studies. Weekly results can suffer from distortions from the day of the week selected for closing prices. The Fisher effect can distort daily results, as the last trade is recorded as the closing price, not necessarily the trade at the end of the day, thus not matching with end of day market movements.
3. Adjustment – To Tend Toward One
It has been observed that as an industry/company matures, it acts more like the overall economy/market in general. Consequently, betas move more with the market over time. The raw beta will need adjustments better to reflect the tendency of betas over longer periods.
4. Underlying Index
Use the index of the country in which your company is located. In India, SENSEX 30 should be used.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned about the estimation of the cost of equity, which we will find for private companies…Till then, Happy Learning!
Recommended Articles
Here are some articles that will help you get more details about the CAPM Formula, so just go through the link.