Updated May 31, 2023
Excel VBA Environ Function
VBA Environ where Environ stands for Environment is used for getting any information that is there in Operating System. The Excel VBA Environ function returns the value such as path, location, name, extension available in the system. Apart from this Environment (Operating System) also holds the information about User Name, Authorization, Folder name, etc.
VBA Environ considers only expression as an Input. Where that expression can be anything. Below is the syntax of Environ.
How to Use Environ Function in Excel VBA?
Below are the different examples to use the Environ function in Excel VBA.
VBA Environ – Example #1
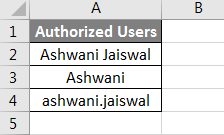
There are different ways to get operating system information through VBA Environ. One of them we will see in this example. Below is the list of possible authorized users of my system which can be TRUE or FALSE. We have mentioned these names in Sheet2.
Follow the below steps to use Environ function in VBA:
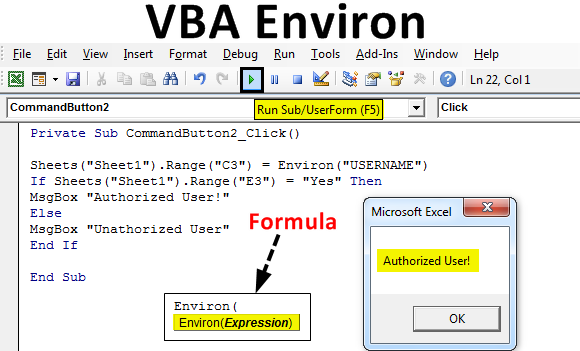
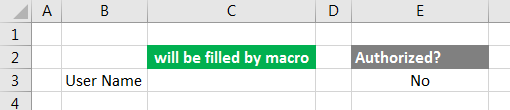
Step 1: Now with the help of VBA Environ, we will find which of these is the correct authorized user name of the current operating system. Sheet1 is the place where we will find the correct user name of the system in cell C3.
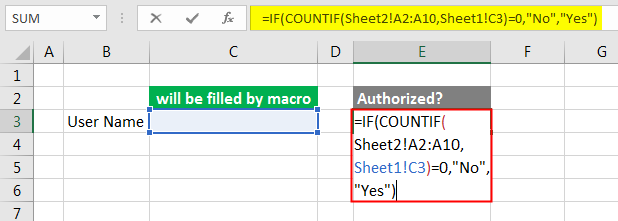
Step 2: Under the header “Authorized?” We will see if the user name is authorized or not with the If and CountIf function as shown below. If the user name is valid and authorized then we will get YES, if valid but not authorized we will get No. For both unauthorized and invalid user name, we will still get No.
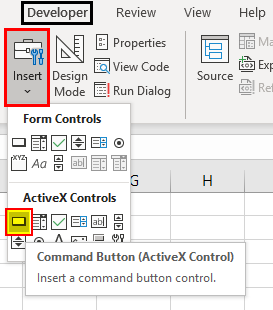
Step 3: Now in excel worksheet, create a Command button that is available in the Developer tab under the Insert menu’s Active X Control as shown below.
Step 4: Now create a command button anywhere in the sheet. We can choose any Shapes over the command button as well.
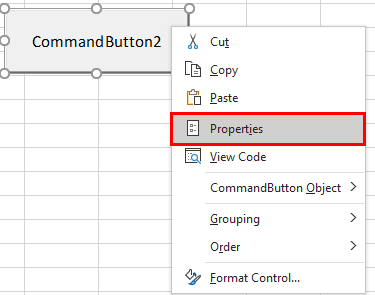
Step 5: Right-click on the created button and go to the Properties option.
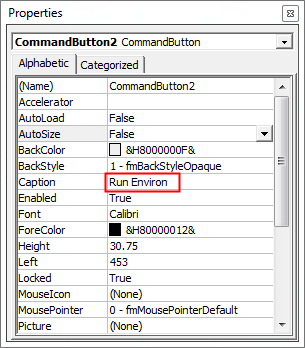
Step 6: Under that, we can change the default name to anything. Here we have chosen Run Environ as shown below.
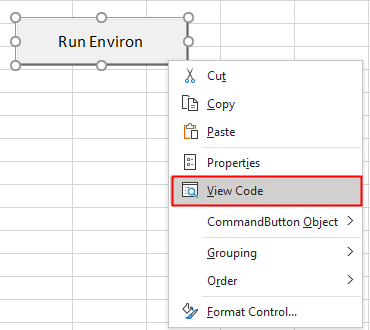
Step 7: Now right-click on the same button and select View Code to go in the VBA window.
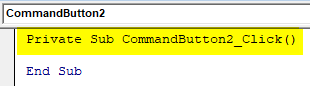
Step 7: In that, we will get the pre-built sub procedure of the command button.
Code:
Private Sub CommandButton2_Click() End Sub
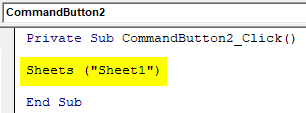
Step 8: Select the sheet where we want to apply the Environ function.
Code:
Private Sub CommandButton2_Click() Sheets("Sheet1") End Sub
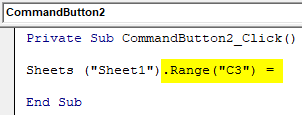
Step 9: Then select the range cells where we want to see the output.
Code:
Private Sub CommandButton2_Click() Sheets("Sheet1").Range("C3") = End Sub
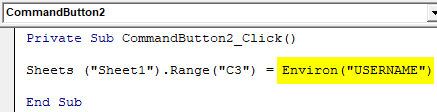
Step 10: Now use Environ function with the field which we want to get. Here we want to see USERNAME.
Code:
Private Sub CommandButton2_Click() Sheets("Sheet1").Range("C3") = Environ("USERNAME") End Sub
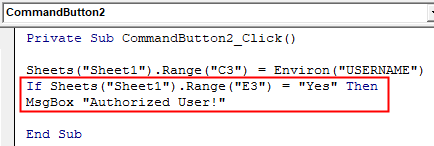
Step 11: Now open an IF-ELSE loop where write the condition if range cell E3 is YES then give me the message as Authorized User.
Code:
Private Sub CommandButton2_Click() Sheets("Sheet1").Range("C3") = Environ("USERNAME") If Sheets("Sheet1").Range("E3") = "Yes" Then MsgBox "Authorized User!" End Sub
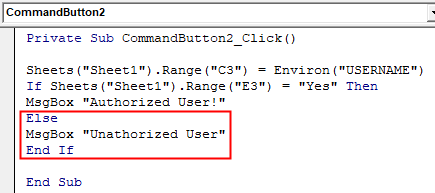
Step 12: In Else give me the message as Unauthorized User as shown below.
Code:
Private Sub CommandButton2_Click() Sheets("Sheet1").Range("C3") = Environ("USERNAME") If Sheets("Sheet1").Range("E3") = "Yes" Then MsgBox "Authorized User!" Else MsgBox "Unathorized User" End If End Sub
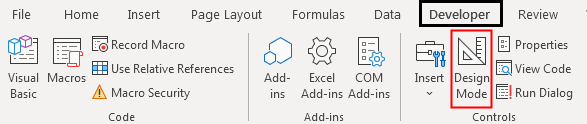
Step 13: Now we will compile our code step by step by pressing the F8 function key to see if there is any error or not. If all is good, then exit from the VBA window and unselect the Design mode from the Developer tab as shown below.
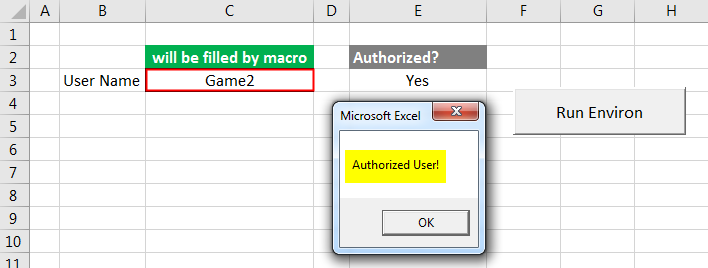
Step 14: Now we will run our macro by clicking on the command button named “Run Environ”. We will see, at C3, the authorized user name is printed as Game2 and then the same is confirmed twice. Once by the message box and other at cell E3.
This means that the user name which is mention at Sheet2 as Game2 is valid and authorized both.
VBA Environ – Example #2
There is another way by which we can get the complete information about the operating system which we have. This works in the same manner as we have seen in example-1. For this, follow the below steps:
Step 1: Open a Module from the Insert menu tab.
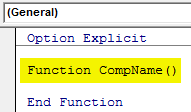
Step 2: Now under Option Explicit, we will define the functions which we want to see.
Code:
Option Explicit Function CompName() End Function
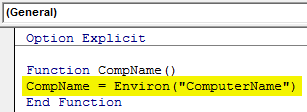
Step 3: Suppose, if you want to see the Computer Name, use any word which defines Computer. Here we have chosen CompName and use Environ function with “Computer Name”.
Code:
Option Explicit Function CompName() CompName = Environ("ComputerName") End Function
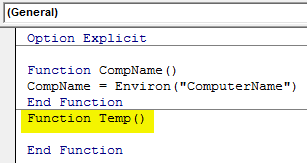
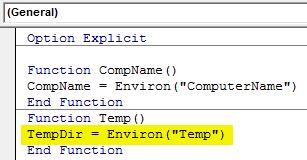
Step 4: Let’s open another function by which we will see the temporary file path as shown below.
Code:
Option Explicit Function CompName() CompName = Environ("ComputerName") End Function Function Temp() End Function
Step 5: Now again use any word which defines the Temp file path, like TempDir and insert Environ function with TEMP.
Code:
Option Explicit Function CompName() CompName = Environ("ComputerName") End Function Function Temp() TempDir = Environ("Temp") End Function
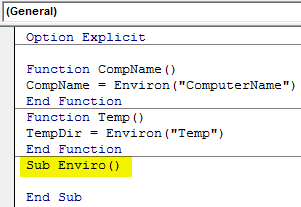
Step 6: After that open the subprocedure in which we will use both functions which we defined above to see their details.
Code:
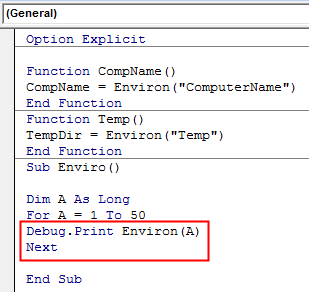
Option Explicit Function CompName() CompName = Environ("ComputerName") End Function Function Temp() TempDir = Environ("Temp") End Function Sub Enviro() End Sub
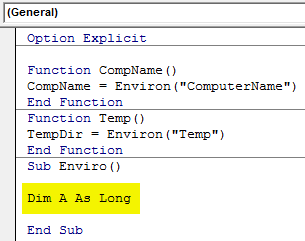
Step 7: Define a variable as Long in which we will see the details.
Code:
Option Explicit Function CompName() CompName = Environ("ComputerName") End Function Function Temp() TempDir = Environ("Temp") End Function Sub Enviro() Dim A As Long End Sub
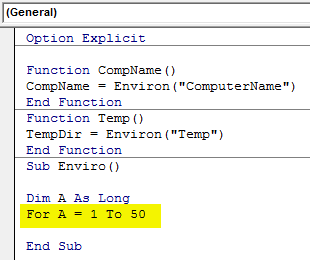
Step 8: Open a For-Next loop and give the length to variable A how long will be the character limit. Here we have set it as 50.
Code:
Option Explicit Function CompName() CompName = Environ("ComputerName") End Function Function Temp() TempDir = Environ("Temp") End Function Sub Enviro() Dim A As Long For A = 1 To 50 End Sub
Step 9: Now use Debug Print for variable A and with Environ function as shown below.
Code:
Option Explicit Function CompName() CompName = Environ("ComputerName") End Function Function Temp() TempDir = Environ("Temp") End Function Sub Enviro() Dim A As Long For A = 1 To 50 Debug.Print Environ(A) Next End Sub
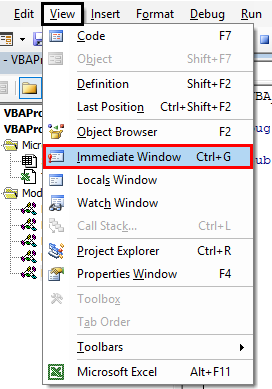
Step 10: Compile each step of the code and open an immediate window from the View menu tab.
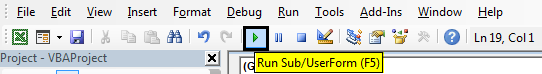
Step 11: Now run the code by clicking on the Play button located below the menu bar.
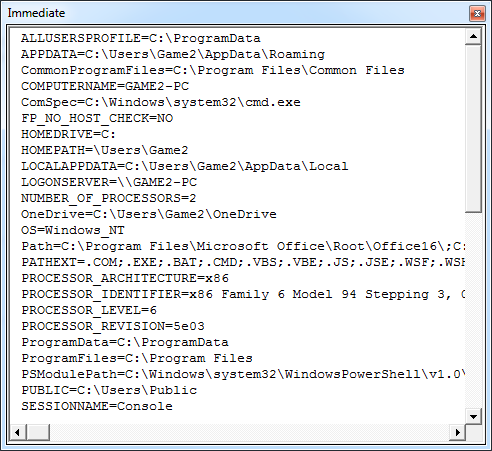
Step 12: We will see, in the immediate window, complete operating system details related to the functions which we have declared are fetched.
Pros of Excel VBA Environ Function
- It seems complex, but it is easy to implement.
- It gives the complete computer and operating system details.
- We can list out any specific detail as well as per our requirements.
- We can also see who are the authorized user to use and edit the system.
Things to Remember
- The VBA Environ is not limited to the process shown in the above examples. We can get many more operating system details such as any path, location, folder or file, even any file size as well with the help of VBA Environ.
- If any value which we input is not an environment string table, then we will end up getting Zero-length string.
- Once we are done with coding, save the file in macro enable excel format to avoid losing the code.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to VBA Environ. Here we discuss how to use Environ Function in Excel VBA along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –