Updated April 18, 2023
Introduction to TypeScript Module
TypeScript Modules is a file that contains functions, variables, or classes. These typescript modules are executed within their own scope and not in the global space. Starting with ECMAScript 2015, TypeScript has shared this concept of modules from JavaScript. Variables, classes, functions, etc. are declared in a modular way and are not visible outside the module unless and until these are explicitly exported using one of the available export forms. In the same way, consume any variable, class, function, or interface, etc. are exported from another module, hence these are to be imported using one of the available import forms.
Modules are decorative and relationships among modules are specified based on imports and exports at the file level. The module loader is responsible for locating the dependencies and executing dependencies of a module before executing at runtime. Some of the modern loaders used in JavaScript are NodeJS loaders for RequireJS loader and CommonJS modules for AM modules in web applications.
Modules are designed in such a manner so that code is organized, and these are divided into 2 modules,
- Internal Module
- External Module
These modules help to segment the applications, allow users to create small and independent reusable code. Also, modules know their own dependencies so that users can load modules when required in order.
Syntax:
Here is the Syntax for TypeScript Module, which are of two types; Import-Module and Export Module
Internal Module Statement:
Importing an exported declaration is done using one of the below import statements.
import { sample_file } from "./sample_file";Import statements can also be renamed as below,
import { sample_file as sf } from "./sample_file";This import module can also be used to import the entire module into a single variable as below,
import * as sample_file from "./sample_file";External Module Statement:
Any particular declaration such as variables, functions, class, interfaces, or type aliases can be exported using the export keyword.
export interface sample_file {
}For NodeJS applications, Modules are default and developers recommend modules over namespaces.
Examples of TypeScript module
Let us see how TypeScript Module work with few examples
Example #1 – Simple TypeScript Module example
In script.ts
export function multiple(x: number, y: number): number {
log(`${x} * ${y}`);
return x + y;
}
function log(message: string): void {
console.log("Numbers", message);
}In index.ts
import { multiple } from "./script";
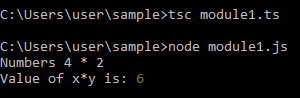
console.log('Value of x*y is:', multiple(4, 2));Output:
We need to run the index.ts module as script.ts is imported into the index file.
Command to be used: tsc index.ts (this will create a .js file of itself, and then by using node command, we need to run the js file to see the output.
Example #2 – TypeScript Module Employee program
In Employee.ts
export interface Employee {
total();
}In Company.ts
import employee = require("./Employee");
import employer = require("./Employer");
function drawAllShapes(shapeToDraw: employee.Employee) {
shapeToDraw.total();
}
drawAllShapes(new employer.Employer())In Employer.ts
import employee = require("./Employee");
export class Employer implements employee.Employee {
public total() {
console.log("There are total of 500 employees in our Company");
}
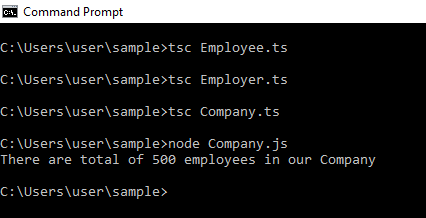
}Compilation Output:
On compiling the below commands,
tsc Employee.ts
tsc Employer.ts
tsc Company.tsWith these commands, .js files are created with the same names.
Employee.js, Employer.js, and Company.js files are created, as below
Employee.js
"use strict";
exports.__esModule = true;Employer.js
"use strict";
exports.__esModule = true;
exports.Employer = void 0;
var Employer = /** @class */ (function () {
function Employer() {
}
Employer.prototype.total = function () {
console.log("There are total of 500 employees in our Company");
};
return Employer;
}());
exports.Employer = Employer;Company.js
"use strict";
exports.__esModule = true;
var employer = require("./Employer");
function drawAllShapes(shapeToDraw) {
shapeToDraw.total();
}
drawAllShapes(new employer.Employer());Output:
In TypeScript, as import and exports are available in Modules, re-exports also serve an important role i.e. exports other modules and expose the properties. Re-export is not importing locally or introducing a local variable. In such cases, re-exporting such cases either use original or rename it.
Example #3 – Student Details using TypeScript Module
In Student.ts
export class Student {
stuCode: number;
stuName: string;
constructor(name: string, code: number) {
this.stuName = name;
this.stuCode = code;
}
displayStudent() {
console.log ("Student Code: " + this.stuCode + ", Student Name: " + this.stuName );
}
}In StudentDetails.ts
import { Student } from "./Student";
let empObj = new Student("Karthik", 101);
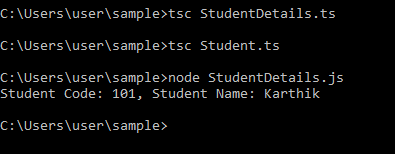
empObj.displayStudent();Compilation Output:
On Compiling .ts files, JavaScript files are created as below
In Student.js
"use strict";
exports.__esModule = true;
exports.Student = void 0;
var Student = /** @class */ (function () {
function Student(name, code) {
this.stuName = name;
this.stuCode = code;
}
Student.prototype.displayStudent = function () {
console.log("Student Code: " + this.stuCode + ", Student Name: " + this.stuName);
};
return Student;
}());
exports.Student = Student;In StudentDetails.js
"use strict";
exports.__esModule = true;
var Student_1 = require("./Student");
var empObj = new Student_1.Student("Karthik", 101);
empObj.displayStudent();Output:
Conclusion
With this, we conclude our topic ‘TypeScript Module’. We have seen what the TypeScript module is and how it works. Syntactically checked both the various version of Modules, be it Internal or import syntax; External or export syntax. It is a very simple way to use modules in TypeScript; be it in understanding the dependencies between the components. While these native modules are not supported, users can simply use modules with SystemJS or RequireJS and migrate to Native form. As modules import one another using a module loader, at runtime, the module loader is responsible for locating and executing all the dependencies of modules before execution.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “TypeScript module” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.