Updated April 5, 2023
Introduction to TypeScript Inheritance
Inheritance is the basic concept which comes from the object-oriented programming language. Inheritance in TypeScript works in the same way like any other programming language because TypeScript is also an object-oriented language. In Inheritance, we have two concepts which is known as parent class and child class. In Inheritance, we inherit the properties of the super class, which termed as parent class and the one which is inheriting the super class called a child class; this is the basic concept of inheritance in any programming language.
Types of Inheritance in TypeScript
Inheritance in TypeScript comes up with two different types, but in other programming languages, we have so many different types of inheritance which can be used according to the requirement. But TypeScript supports basically two types which are single and multilevel inheritance. We have different types such as hybrid, multiple which typescript does not support.
We basically have two types of inherits in TypeScript, which is as follows:
- Single Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
1. Single Inheritance
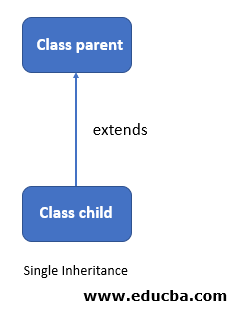
In this type of inheritance, we can extend only one class or a single class. This is why it is called as single inheritance. This inheritance is also achieved by using the ‘extends’ keyword we already have. We will see one image to demonstrate the flow of single inheritance in TypeScript to know it better.
Flowchart:
In the above image, we have two class available called as parent and child class. Here we are trying to extend the parent class using the child class. After this, we can use all its methods and filed inside the child object to perform our logic. Thus in this way, it also provides us usability of the code. We will also see one practice example of single inheritance in TypeScript.
Below is a sample example of how to use this in programming.
Example:
Code:
class Flower {
color():void {
console.log("This is a method in parent class");
}
}
class Rose extends Flower {
color():void {
console.log("This is a method in child class");
console.log("color of rose is red !!!");
}
}
console.log("Demo to show single inheritence in Typescript");
let myobject = new Rose();
myobject.color();Output:
2. Multilevel Inheritance
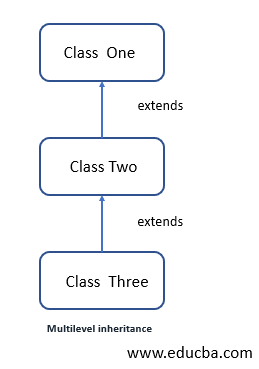
In this type of inheritance, we can derive a new class which is already being derived by another parent class; this type of relationship between parent and child is known as a multilevel inheritance in TypeScript. This inheritance is proceed in levels one, two, three and so on. Below we can see its flow chart of how it actually looks like and also the internally working of it to get more idea about this.
Flowchart:
In the above image or flowchart, we are creating three classes which follow multilevel inheritance in typescript. Here we have classes named as one, two and three. Class ‘one’ is the parent class for class ‘two’, which means it can use its property and behavior in its own class. But as you can see, we have one more class named class ‘three’, which again extends the class ‘two’ here. That means now this class can access the methods and fields of both classes. In this way, we can achieve multilevel inheritance in TypeScript. It is also very easy to use and hence provide the usability of the code.
Now we will see one sample example to implement this in TypeScript.
Example:
Code:
class Flower {
color():void {
console.log("This is a method in parent class");
}
}
class Rose extends Flower {
color():void {
console.log("This is a method in child class");
console.log("color of rose is red !!!");
}
}
class Lotus extends Flower {
color():void {
console.log("This is a method in child class");
console.log("color of Lotus is pink !!!");
}
}
console.log("Demo to show multiplevel inheritence in Typescript");
let myobject1 = new Rose();
myobject1.color();
let myobject2 = new Lotus();
myobject2.color();Output:
As we have already seen, the types of inheritance available in TypeScript or it supports. In the above lines of code, as you can see, we are creating one class calls as parent class ‘Flower’. We have a different variety of flowers, different color and so on. In this example, we are creating flower as the base class, which contain all the common methods inside it. After creating the parent class, we are certain different types of flower classes named ‘rose’ and ‘lotus’ in the above sample example. After this, we can use the parent class methods named as ‘color’ to define the color of each flower. So here we are providing implementation of methods asked on the child class; also, it allows us to remove the duplicate code from the application. If we do not have inheritance, then unnecessary, we have to create this method in every class. In this way, it has so many benefits also to use. This is the most basic concept of object-oriented programming language.
Basic Details and Components Available in Inheritance
Inheritance comes up with two things which are really very common in all its type. It supports the parent-child relationship in any programming language.
Let’s see the parent-child relationship in detail:
1. Parent class/ super class/ base class
The parent class is also known as the base class, super class in TypeScript inheritance. A class which is used to get the property and behavior is called the parent class. All the methods, variable and other stuff of the parent class will be used by the child class.
2. Child class/ sub class/ derived class
The child class is also known as the sub class, derived class in inheritance. When a class which inherits the property and behavior of the parent class, it is known as the child class or derived class in TypeScript inheritance. This class is now able to use the methods, constructors and other stuff of the class.
Now we will see how to achieve inheritance in programming in detail:
- extends: We can use the ‘extends’ keyword like any other programming language; we achieve inheritance in typescript as well. We have to use this keyword in between the two class names while programming. After this, only we will be able to access the properties of the parent class inside the child class. Let’s see one sample syntax to understand how to use this while programming.
Example:
Code:
class one 'extends' class secondConclusion
TypeScript does not support all the types of inheritance; it supports only two types. Inheritance is very easy to use and implement in TypeScript. As we mentioned above, we just have to use extends keyword before and after the parent and child class. Thus provide the reusability of the code, make it readable and easier to understand.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “TypeScript Inheritance” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.