Updated May 9, 2023
Introduction to Threading Interview Questions and Answers
THREAD is known as a lightweight process. A thread can also be understood as a path that executes within a process. The concept behind Multi-threading is to achieve parallelism, which helps in being multi-process oriented. A very fine line definition that separates threading and multi-threading is in the way of handling the associated process. The below-mentioned scenario will help us to think similarly.
Imagine, while working on any browser, you need to collect data related to the Indian IT industry; when collecting the details, you try to open a new tab window (in the same browser) but unfortunately can’t. This is one way to explain what threading is precisely and how multi-threading can be a blessing for the user. So, in a browser, multiple tabs can be different threads. Another example will clarify the thinking more precisely; the MS Word application uses various threads while working, one thread for formatting purposes, another for processing the inputs, and so on.
Now, if you are looking for a job related to threading, you need to prepare for the 2023 Threading Interview Questions. Every interview is indeed different as per the various job profiles. Here, we have prepared the critical Threading Interview Questions and Answers to help you succeed in your interview.
This 2023 Threading Interview Questions article will present the ten most essential and frequently used Threading interview questions. These questions are divided into two parts as follows:
Part 1 – Threading Interview Questions (Basic)
This first part covers basic Interview Questions and Answers.
Q1. What is the difference between multi-thread programming and single-thread programming?
Answer:
In a Multi-threading process, multiple threads work at the same time. There is no event loop while pooling in a multi-threading model. The CPU time is utilized in a better way with no time wastage. The Idle time is the least. A more efficient program is the outcome of a multi-threading process. A special behavior of multi-threading programming is that when one thread is paused, the other run as usual.
A single thread runs simultaneously in a Single thread programming; this model uses a process event loop during pooling. The CPU time is not appropriately capitalized, as it has more idle time. The effectiveness of single-thread programming is less because when one thread is paused, the system waits until the thread is resumed, which results in less effective programs.
Q2. What is a process, and how is it different from a thread?
Answer:
This is the basic Threading Interview Question asked in an interview. The primary difference between the two lies in their working behavior. The threads of a related process run in a shared memory location, whereas memory spaces are different in a process. This thread behavior makes it more efficient in terms of responsiveness to its counterpart. Threads share code, data, and OS details due to their association with each other. Another thing about the thread is that they have their Program counter (PC), register sets, and stack space.
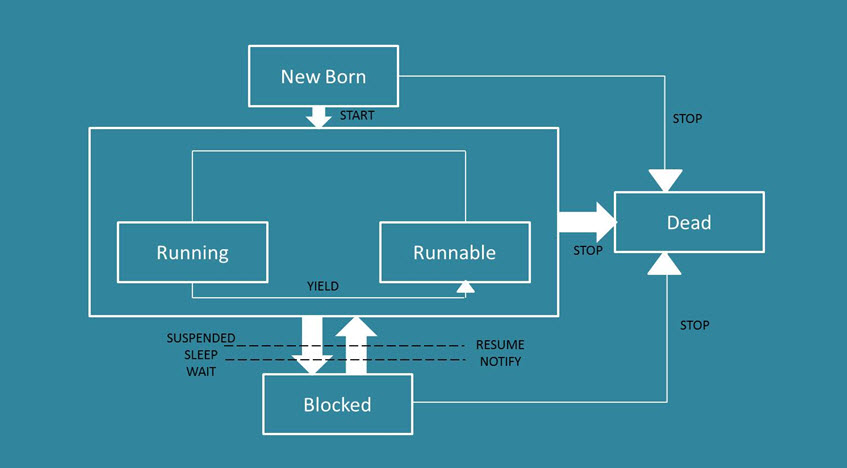
Q3. Elaborate on the life cycle of a thread.
Answer:
Whenever a thread is created, it is in the “New Born” state. After this, the thread can be in 2 states, namely.
- Running
- Runnable
The thread will call the start method to navigate or move to a run or runnable state from the newborn state. Runnable means your thread is ready to execute but waiting for the processor’s availability. Allocating a processor changes the state from “runnable” to “running.” But, to change the state from running to runnable, there are reliable methods (like in JAVA, there is the YIELD method). There are three methods to block a thread from either of the two states (i.e., running or runnable).
- Suspend
- Sleep
- Wait
Also, to run an already blocked thread, there are different methods like
- Resume
- Notify
Lastly, the STOP method changes the thread’s state from newborn, running, runnable, or blocked to DEAD state.
Q4. What is a ThreadLocal class?
Answer:
ThreadLocal class in Java enables you to create variables. These variables can be read and written by the same methods. If two threads are executing the same code, but the codes have a ThreadLocal variable, the chances are that the two threads cannot see each other ThreadLocal variables.
Q5. What is a daemon thread in Java?
Answer:
User threads are the front performer, and demon threads are like assistants. The assistant helps in completing a task. Once the task is completed, the performer is not needed, and in return, the assistant also quits the place. JVM mainly creates these. These threads (demons) are primarily designed for background tasks like garbage collection.
Part 2 – Threading Interview Questions (Advanced)
Let us now have a look at the advanced Interview Questions.
Q6. How to create threads in Java?
Answer:
By extending Thread Class, a thread can be created.
Public class MyThreadClass extends Thread {
Public void run () {
System.out.println (“Thread name is :”+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
Q7. Provide the names of all the sections or details a thread contains in a TCB(Thread control block).
Answer:
Thread Identifier
- Stack Pointer
- Program Counter
- Thread State
- Thread register set
- Parent process pointer
Let us move to the next Threading Interview Questions.
Q8. What is Thread Join() in threading?
Answer:
The thread class contains several methods; join () and sleep()are two of them. The thread.join() method blocks a thread and waits for it to terminate.
Q9. How to debug a thread in C#?
Answer:
These are the most asked Threading Interview Questions in an interview. In visual studio, a shortcut is available for better productivity with limited time.
- CTRL+T+T or snowflakes = This limits the execution to the current thread only and freezes all other threads.
- CTRL+T+J or Next button = allows switching to the next single thread. This only changes the current thread and freezes all the other threads.
Q10. What does the Address of the operator do in the background?
Answer:
The AddressOf operator creates the object in the background process method. A type-safe, object-oriented function pointer is the structure of any delegates in VB.NET. After initializing the thread, code can be executed by calling the Start() method.
Recommended Article
This has been a guide to a list Of Threading Interview Questions and Answers so that the candidate can easily crack down on these Questions. In this post, we have studied the top Threading Interview Questions often asked in interviews. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –