Updated July 6, 2023
What is Third Normal Form?
Third normal form is a form used to normalize the database design to avoid duplication of data. In a Relational Database Management System, a huge amount of data gets stored across multiple tables and the storing as well as the retrieval and manipulation of data becomes easier with the introduction of the concept of the key which establishes the relationship among the tables. As we store a huge amount of data in the tables, there might be cases where duplicate records may get stored in the table which will result in inconsistent data. Also, the redundancy in the data will lead to various issues such as insert, update and delete anomalies.
How does Third Normal Form Work?
The update, insert and delete anomalies are seen because of the redundancy of data. In update anomaly, the data does not get updated correctly and the data becomes inconsistent due to existing redundancy of data. In case of delete anomaly, if the record that is to be deleted is present in more than one rows of a table, deleting one record creates inconsistency. In insert anomaly, a table does not allow the null values to be inserted for a specific column. The data independency is ensured by the normalization of data and the redundant data gets removed. A relation is in Third Normal Form if the relation is in First and Second Normal Form and the non-primary key attributes are not transitively dependent upon the primary key.
A super key can be defined as a group of single or multiple keys which will identify the rows of a table. A candidate key is a column or set of columns in a table that can identify the record uniquely. The Transitive Dependency in a table or relation comes into picture when one non-prime attributes are dependent upon another non-prime attribute instead of it being dependent upon the primary key. So removing the transitive dependency ensures data integrity as well as less duplication of data.
A relation is in Third Normal Form if one of the below conditions are true for every non-trivial functional dependency A -> B.
- A is a super key.
- B is a prime attribute where each element of B is part of any candidate key.
The normalization from Second Normal Form to the Third Normal Form requires the transitive dependencies to be removed. The transitive dependencies are removed by eliminating the transitive attributes from the relation by locating these attributes in a new relation.
The steps for achieving Third Normal Form are as below:
- A table or relation should be in Second Normal Form.
- The table or relation should not contain any transitive partial dependency.
Example of Third Normal Form
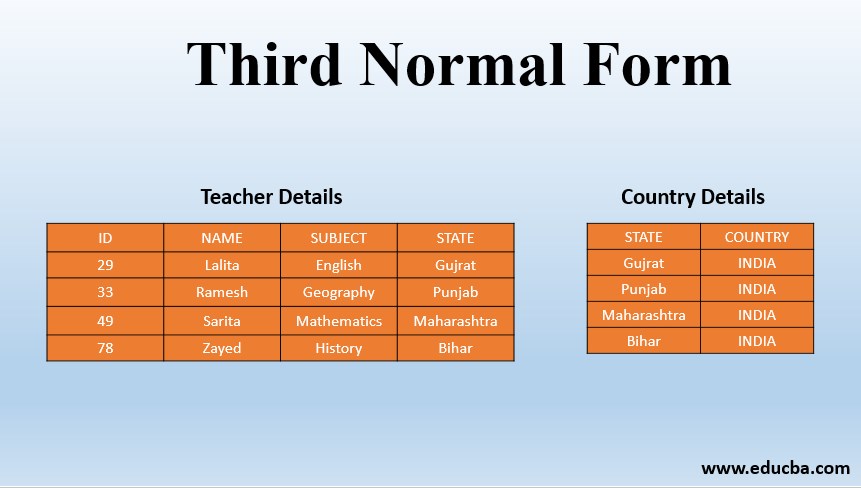
Let us consider the below table ‘TEACHER_DETAILS’ to understand the Third Normal Form better.
| ID | NAME | SUBJECT | STATE | COUNTRY |
| 29 | Lalita | English | Gujrat | INDIA |
| 33 | Ramesh | Geography | Punjab | INDIA |
| 49 | Sarita | Mathematics | Maharashtra | INDIA |
| 78 | Zayed | History | Bihar | INDIA |
The candidate key in the above table is ID. The functional dependency set can be defined as ID->NAME, ID->SUBJECT, ID->STATE, STATE->COUNTRY.
If A->B and B->C are the two functional dependencies, then A->C is called the Transitive Dependency. For the above relation, ID->STATE, STATE->COUNTRY is true. So we deduce that COUNTRY is transitively dependent upon ID. This does not satisfy the conditions of the Third Normal Form. So in order to transform it into Third Normal Form, we need to break the table into two tables in total and we need to create another table for STATE and COUNTRY with STATE as the primary key.
Below are the tables after normalization to the Third Normal Form.
TEACHER_DETAILS:
| ID | NAME | SUBJECT | STATE |
| 29 | Lalita | English | Gujrat |
| 33 | Ramesh | Geography | Punjab |
| 49 | Sarita | Mathematics | Maharashtra |
| 78 | Zayed | History | Bihar |
STATE_COUNTRY:
| STATE | COUNTRY |
| Gujrat | INDIA |
| Punjab | INDIA |
| Maharashtra | INDIA |
| Bihar | INDIA |
Advantages of Third Normal Form
Below are the advantages of Third Normal Form:
- Normalization increases the data quality as the unwanted data is reduced from the database. Even though the redundancy of the Second Normal Form is less as compared to the First Normal Form, it is still possible to have update anomalies. For example, if one tuple is updated only while others remains unchanged, the inconsistency of data will be there in the database.
- The transitive dependency creates the update anomalies and they can be removed by the usage of the Third Normal Form.
- The Third Normal Form is also considered to be the ample requirement to build a database as the tables in the Third Normal Form are devoid of insert, update or delete anomalies.
- The Third Normal Form removes the redundancy effectively so the data becomes consistent as well as maintains the data integrity. As the redundancy is reduced, the database becomes less in size and also the duplication of data is reduced which also improves the performance.
Conclusion
The design of a robust and effective database is crucial. The role of Normalization is also very critical as it ensures both data consistency and integrity. But normalization has certain disadvantages too such as having more tables and joining of the multiple tables taking more time in development. Also, a fully normalized database takes more time in analyzing and understanding critical business logic. So the understanding of the Third Normal Form is very important for the database designer and the usage of this normal form should be done according to the business requirement.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Third Normal Form. Here we discuss how does it Work, and Advantages of Third Normal Form along with its Examples. You can also go through our suggested articles to learn more –