Updated July 6, 2023
Introduction to Fourth Normal Form
The fourth normal form is the next level of normalization after BCNF which deals with a more universal type of dependency known as multi-valued dependency. The fourth normal form just like the other normal forms brings in features that organize the data and eliminates anomalies and redundancy. Each normalization has a set of rules that should be followed in creating the database. And in order to Based on the type of normalization that is being wished to the larger tables are divided into smaller ones. That is referred to as the decomposition of tables. A relation should satisfy the below two conditions to be in 4NF. The conditions are:
- It should be in BCNF.
- There should be no Multi-valued Dependency.
A table which is in 4NF will by default satisfy all the conditions of the previous normal forms. The different forms of normalization before 4NF are:
- 1NF
- 2NF
- 3NF
- BCNF
How does Fourth Normal Form Work?
To understand how 4NF works it is necessary to understand multi-valued dependency. Multivalued dependency requires a minimum of three columns in which there should be at least two attributes that depend on the third one. And those two attributes are dependent on each other. Conditions for Multi-valued dependency.
- There should be at least 3 columns in a table.
- For every dependency A-> B, for every value of A multiple values of B exists then the dependency is referred to as a multi-valued dependency.
- In the relation of 3 columns R(XYZ), if there exists a multi-valued dependency between X and Y then Y and Z should be independent of each other.
All the above conditions should be satisfied to establish the fact that multi-valued dependency exists in relation.
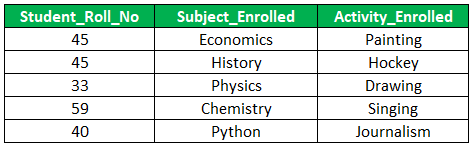
Example #1
Here we have a Students table which has information about the subjects and the activity the students have enrolled in. Subjects_Enrolled and Activty_Enrolled are the two attributes that are independent of each other. The given table is in BCNF which satisfies the first condition of 4NF.
Let’s check further the Multi-valued Dependency.
- The dependencies in this relation are:
Student_Roll_No —> Subject_Enrolled
Student_Roll_No —> Activity Enrolled
- Based on the conditions for Multi-Valued dependency, checking the existing relation.
- There should be at least 3 columns in a table. – – Satisfied
- For every dependency A-> B, for every value of A multiple values of B exists then the dependency is referred to as multi-valued dependency. – – Roll no 45 has enrolled in Economics and History in terms of academics and Painting and Hockey as activities. Thus for a value of Student_Roll_No different values of Activity_Enrolled exist.
- In the relation of 3 columns R(XYZ), if there exists a multi-valued dependency between X and Y then Y and Z should be independent of each other. – – Subject_Enrolled and Activity Enrolled are independent of each other.
As we checked the above conditions it is clear that the relation consists of multi-valued dependency. In order to normalize the table into 4NF, we need to decompose it into smaller tables.
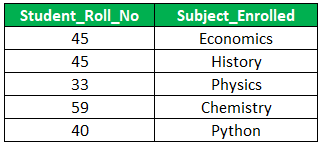
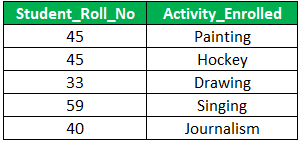
Student relation is now been decomposed into smaller tables S1 and S2 which are in 4NF.
S1:
S2:
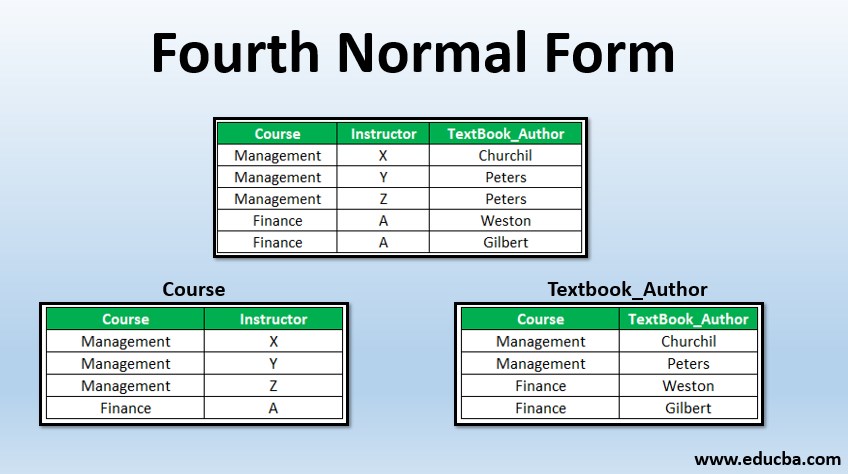
Example #2
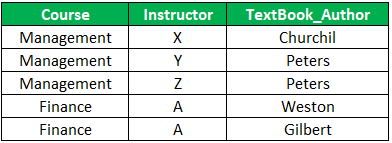
Here Course is a relation with the below dependencies.
Course -> Instructor
Course -> TextBook_Author
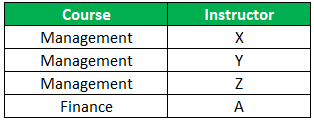
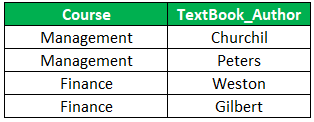
For a certain value, of course, we have a set of values for instructor and a set of values for TextBook_Author. But instructors and textbooks are not related. Thus the table has a multi-valued dependency and does not satisfy 4NF. To solve this, the decomposition of the table is required. The table will be split into two tables where one table will preserve the Course -> Instructor and the second table will preserve Course -> TextBook_Author. This decomposition will result in a table that is in 4NF.
C1:
C2:
Advantages of Fourth Normal Form
Following are the advantages given.
- Helps in removing redundancy and anomalies in the database.
- Data integrity and consistency can be maintained through normalization and restricted constraints.
Conclusion
By default, relation in 4NF will satisfy all the properties of 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, and BCNF. A table needs to be in BCNF and have no multi-valued dependency. It will ensure data integrity and consistency. These particular set of rules which constitutes the basis of normalization is an update, delete and insert anomalies does not occur in databases.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Fourth Normal Form. Here we discuss a brief overview and how does fourth normal form works along with examples and advantages in detail. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –