Updated May 2, 2023
Introduction to RDBMS Interview Questions and Answers
So if you are preparing for a job interview in RDBMS, I am sure you want to know the most common 2023 RDBMS Interview Questions and answers that will help you quickly crack the RDBMS Interview. Below is the list of top RDBMS Interview Questions and answers at your rescue.
Top 11 RDBMS Interview Questions and Answers
We have added the top 2023 RDBMS interview questions commonly asked in interviews.
Q1. What are the different features of an RDBMS?
Answer:
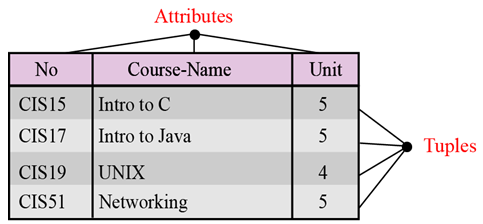
- Name. Every relation in a relational database should have a unique name among all other relations.
- Attributes. We call each column in relation to an attribute.
- Tuples. Every row in a relation is called a tuple. A tuple defines a collection of attribute values.
Q2. Explain the E-R Model.
Answer:
The e-R model is an Entity-Relationship model. The ER model represents a real-world scenario consisting of entities and related objects. A set of attributes illustrates entities in a database.
Q3. Define the object-oriented model.
Answer:
The object-oriented model is based on collections of objects. Values stored in instance variables inside an object define its state. Classes group together objects that have the same type of values and methods.
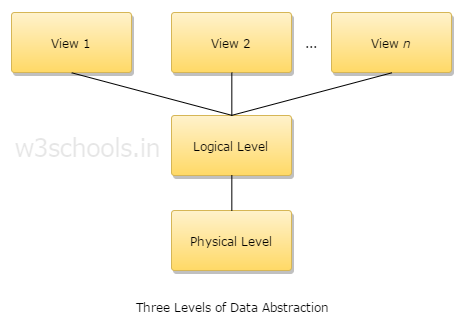
Q4. Explain three levels of data abstraction.
Answer:
- Physical level: This is the lowest level of abstraction, describing how data is stored.
- Logical level: The next level of abstraction is logical; it describes what type of data is stored in a database and the relationship between these data.
- View level: The highest level of abstraction describes only the entire database.
Q5. What are different Codd’s 12 rules for Relational Databases?
Answer:
Codd’s 12 rules are a set of thirteen rules (numbered zero to twelve) proposed by Edgar F. Codd.
Codd’s rules:
Rule 0: The system has to qualify as Relational, as a Database, and also as a Management System.
Rule 1: The information rule: Every information in the database must be represented uniquely, typically as name-value pairs in column positions within different table rows.
Rule 2: The guaranteed access rule: All data must be ingressive. It says every scalar value in the database must be correctly/logically addressable.
Rule 3: Systematic treatment of null values: The DBMS must allow each tuple to remain null.
Rule 4: Active online catalog (database’s structure) based on the relational model: The system must support an online, relational design that allows users to use their regular query.
Rule 5: The comprehensive data sublanguage: The system has to assist a minimum of one relational language that:
- Has a linear syntax.
- Which can be used both interactively and within application programs.
- It supports data definition operations(DDL), data manipulation operations(DML), security and integrity constraints, and transaction management operations (begin, commit, and rollback).
Rule 6: The view updating rule: All views that theoretically improve must be upgradeable by the system.
Rule 7: High-level insert, update, and delete: The system must support insert, update, and delete operators.
Rule 8: Physical data independence: Modifying the physical level, such as changing how data is stored using arrays or linked lists, should not require any changes to an application.
Rule 9: Logical data independence: Modifying the logical level (tables, columns, rows, etc.) must not require a modification to an application.
Rule 10: Integrity independence: Application programs must identify and store integrity constraints in the catalog.
Rule 11: Distribution independence: The distribution of database portions to different locations should not be visible to database users.
Rule 12: The nonsubversion rule: If the interface of a system only allows low-level interactions with its records, it is less likely that someone can use the interface to subvert the system.
Q6. What is normalization? And what explains different normalization forms?
Answer:
Database normalization is a process of organizing data to minimize data redundancy. Which in turn ensures data consistency. Data redundancy can lead to several issues, including wastage of disk space, data inconsistency, and slow DML (Data Manipulation Language) queries.
There are different normalisation forms: – 1NF, 2NF, 3NF, BCNF, 4NF,5NF, ONF, DKNF.
- 1NF: Each column’s data should be atomic, meaning it should not contain multiple values separated by a comma. The table does not contain any repeating column groups. Identity each record uniquely using the primary key.
- 2NF: The table should match all the conditions of 1NF and move redundant data to a separate table. Moreover, it creates a relationship between these tables using foreign keys.
- 3NF: For a 3NF table should fulfill all the conditions of 1NF and 2NF. 3NF doesn’t contain attributes that are partially dependent upon the primary key.
Q7. Define primary key, foreign key, candidate key, and super key.
Answer:
- Primary key: The primary key is the key that doesn’t allow duplicate values and null values. You can define a primary key at the column or table levels. A table can have only one primary key.
- Foreign key: Foreign key only allows the values in the referenced column. It will enable duplicate or null values. It can be defined as a column level or table level. It can reference a column of a unique/primary key.
- Candidate Key: A Candidate key is the minimum super key; there is no proper subgroup of Candidate key attributes that can be a super key.
- Super Key: A superkey is a set of attributes of a relation schema on which all schema attributes are partially dependent. No two rows can have the same value of super key attributes.
Q8. What is a different type of index?
Answer:
Indexes are:
- Clustered index: It is the index at which data is physically stored on the disk. Therefore, only one clustered index can be created in a database table.
- Non-clustered index: It does not define physical data but represents a logical ordering. Typically, B-Tree or B+Tree data structures are created for this purpose.
Q9. What are the advantages of RDBMS?
Answer:
- Controlling Redundancy.
- It is possible to enforce integrity.
- It is possible to avoid inconsistency.
- It is possible to share data.
- It is possible to enforce a standard.
Q10. Name some subsystems of RDBMS.
Answer:
Input-output, Security, Language Processing, Storage Management, Logging and Recovery, Distribution Control, Transaction Control, and Memory Management.
Q11. What is Buffer Manager?
Answer:
Buffer Manager collects data from disk storage to the main memory and decides what data to be in cache memory for faster processing.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the List of RDBMS Interview Questions. Here we have listed the most beneficial 11 interview sets of questions so the jobseeker can easily crack the interview. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –