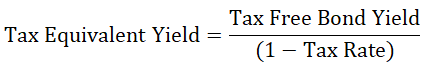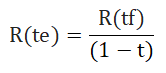Updated November 21, 2023
Tax Equivalent Yield Formula
The minimum pretax yield a particular bond should possess so that it makes equal to the return on tax-exempt investment. The taxable equivalent is vastly used during the calculation of bond yield.
Investors extensively use this calculation to compare the field of a tax-free Bond with a taxable Bond and determine which one offers a higher yield. They refer to this calculation as the after-tax yield.
This yield return is calculated before investing in a Bond, whether Corporate or Municipal. Thus as per the risk-taking ability, the investors decide the particular bond scheme.
The tax Equivalent Yield Formula is:
Where:
- R (te) = taxable equivalent yield for the investor
- R (tf) = return on tax-free investment (usually a municipal bond)
- t = investor’s marginal tax rate
Investors widely use the tax-equivalent yield formula to determine if an investment in a municipal bond is equivalent to its corresponding investment in a taxable bond. On the other hand, in the case of different tax brackets of a particular investor, this calculation is very helpful in making wise investment decisions.
Examples of Tax Equivalent Yield Formula
Let us assume there are two investors – Investor A and Investor B.
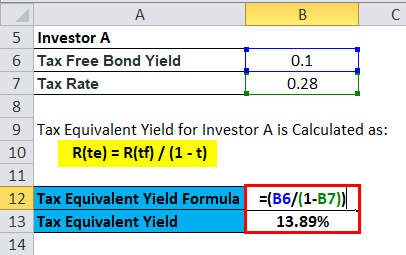
Investor A falls in the 28 percent tax bracket, whereas invested B uses the tax-equivalent yield formula, like a tax bracket of 20. We can make sure whether a municipal bond with an interest rate of 10% per annum would benefit investor A or investor B.
Tax Equivalent Yield for Investor A is Calculated as:
- R(te) = R(tf) / (1 – t)
- R (te) = 0.10 / (1 – 0.28)
- R (te) = 0.10 / 0.72
- R (te) = 0.1389 or 13.89%
Thus, the taxable bond in the case of Investor A must contain a yield greater than 13.89%, which would eventually be more profitable after deducting his 28% tax bracket. In other words, if the yield rate is 13.89%, the investor would gain nothing from the yield because of the 28% tax slab.
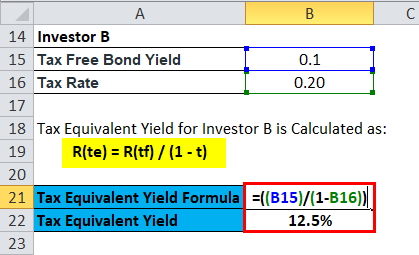
Tax Equivalent Yield for Investor B is Calculated as:
- R(te) = R(tf) / (1 – t)
- R (te) = 0.10 / (1 – 0.20)
- R (te) = 0.10 / 0.8
- R (te) = 0.125 or 12.5%
Investor B gets a yield of 12.5% per annum with a tax bracket of 20%
Explanation
Thus, the taxable bond in the case of Investor B must contain a yield greater than 12.5%, which would eventually be more profitable after deducting his 20% tax bracket.
In the case of Investor A, a taxable bond would give a return of more than +13.89% to become more favorable than the 10% municipal bond. On the other hand, as Investor B has a lower tax bracket, he would get higher than +12.5% from the taxable municipal bond, which tends to be more favorable than the same 10% municipal bond.
Significance and Use of Tax Equivalent Yield Formula
The major benefits of tax-free yields are as follows:
- A profitable yield higher than the tax rate ensures a reliable stream of regular income through interest payments from municipal bonds.
- A properly tax equivalent yield adjusts inflation and stables the entire portfolio’s value without taking any market risk.
- In between corporate bonds and municipal bonds, there are some differences.
- Unlike corporate bonds, the interest income from municipal bonds is always exempted from taxes. Thus to determine interest income exempted from taxes, that is, income from municipal bonds, and the taxable interest income, that is, income from corporate bonds, we have to calculate with the help of tax equivalent yield calculation.
- Thus, with the help of this formula app, one can identify the most suitable element for his portfolio.
Different financial instruments can issue capital, such as corporate and municipal bonds.
Business entities generally issue corporate bonds, whereas municipal bonds are public projects for public services.
The public generally offers capital required for business and public services through debt instruments.
Unlike corporate bonds, municipal bonds give lower returns than corporate bonds but have tax exemptions.
Thus an investor with low-risk bearing capacity and a high tax bracket wood considers municipal bonds over corporate bonds.
However, the choice may vary from investor to investor depending on the requirement and their risk-taking abilities.
Several heels are available per the coupon rate and the current market scenario in a liquid fund or debt market.
An investor should be aware of the tax rate and the rate of return he is getting out of his investments in bonds. So, in an investment decision, one has to consider several points, such as tax rate, bond yield, and interest rate.
Certain exemptions on specific bonds allow investors to save money after investing a lump sum in that particular Bond.
Tax Equivalent Yield Formula Calculator
You can use the following Tax Equivalent Yield Calculator
| Tax Free Bond Yield | |
| Tax Rate | |
| Tax Equivalent Yield = | |
| Tax Equivalent Yield = |
| |||||||||
|
Tax Equivalent Yield Formula in Excel (With Excel Template)
Here, we will do the same example of the Tax Equivalent Yield formula in Excel. It is very easy and simple. You need to provide the two inputs, i.e, Tax-Free Bond Yield and Tax Rate
You can easily calculate the Tax Equivalent Yield using the Formula in the template provided.
Tax Equivalent Yield for Investor A is Calculated Using Formula
Tax Equivalent Yield for Investor B is Calculated Using Formula
Conclusion – Tax Equivalent Yield Formula
Investors carefully evaluate various factors when considering taxable bonds for investment, including their ratings, purpose, and credit measures. These factors help determine the level of risk associated with the bond. It would be unwise to assume that a bond with a higher coupon rate is automatically less risky. Instead, investors must consider multiple aspects such as coupon, discount, tenure, and tax rates to assess whether the bond suits their investment needs.
The tax equivalent yield formula determines whether the interest income from a bond is profitable after accounting for the investor’s specific tax percentage. Both individual investors and corporations use this formula to calculate their net income from the bond over the coming years.
This procedure plays a crucial role in calculating the investment’s systematic risk and risk-free return, both for individual investors and in the context of business orders.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to a Tax Equivalent Yield formula. Here we discuss its uses along with practical examples. We also provide you with Tax Equivalent Yield Calculator with a downloadable excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –