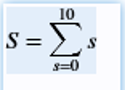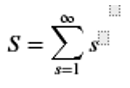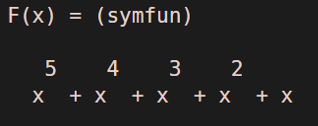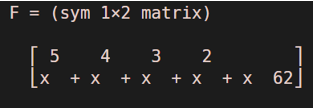Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to Summation Function in Matlab
MATLAB provides its users with a variety of functions with great utilities. This article is focussed on understanding a powerful function called ‘Summation function’. In this topic, we are going to learn about Summation in Matlab.
Mathematical formulae often require the addition of a number of variables. Summation, also called sigma is a simple and convenient notation used to represent an expression for sum of the values of the given variable.
Let a1, a2, a3, …an are denoting a set of n random numbers. a1 is the 1st number of the set. ‘ai’ represents the ‘ith’ number of this set.
Summation Notation
The notation consists of:
1. The summation/sigma sign: This is defined by the symbol S. The symbol of summation is a Greek letter, S, in the upper case. This summation sign signifies that we need to add the elements of the sequence. The element of the given sequence which we are summing appears at the right side of this summation sign.
2. The variables of summation or the variables which are being added: The variables of summation are represented using an index. This index is placed beneath our summation sign. Often, the index is represented by i. (Other commonly used representations of the index are j & t). This index is represented by an expression i = 1. This index takes values that start with the value that is on the RHS of the equation and ends with the value that is above the sign of summation.
3. The starting point of the summation also called the lower limit for the summation
4. The stopping point of the summation also called the upper limit for the summation
Now that we have understood summation function, let’s see how it works in MATLAB
Syntax of Summation Function:
S = symsum(s, i, a, b)
Now let us understand the syntax with the help of various examples
Description of SymSum in Matlab
1. S = symsum(s, i, a, b)
- Here s is a series, i is summation index and a and b are lower and upper bound values, the function S will result in sum of s series for index i from lower and upper bound values.
- The syntax can be alternatively written as symsum(s, i, [a b]) or symsum(s, i, [a;b])
Here is a simple example where we calculate the sum of a series using summation function:
Example
S = symsum(s, s, 0, 10)
Here s is a series which starts at 0 and end at 10
X=10
S=∑s
x=0
the function will return:
S = 55 (which is the sum of 0 + 1 + 2 + 3 +………+ 10)
This is how are input and output will look like in MATLAB console:
Code:
syms s
S = symsum(s, s, 0, 10)
Let’s take a more complex example:
Code:
S = symsum(s^2 , s, 0, 10)
Here s is a series which starts at 0 and end at 10 and is raised to the power 2 in the function.
The function will return:
S= 385 ((0 x 0) + (1 X 1) + (2 x 2) + (3 x 3) + …… + (10 x 10))
This is how are input and output will look like in MATLAB console:
Code:
syms s
S = symsum(s^2 , s, 0, 10)
We can also have sum till infinity, as explained in the below example:
Code:
S = symsum(s, s, 0, inf)
Here s is a series that starts with 0 and ends at infinity.
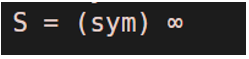
The function will return infinity as the sum
S= ∞
This is how are input and output will look like in MATLAB console:
S = symsum(s, s, 0, inf)
Here is an alternative syntax for Summation:
Syntax:
S = symsum(s, s, [0, 10])
the function will return:
S = 55
Let’s now understand how to find the summation of a given polynomial series:
K=5
F(x) = ∑ x^k , let this be our polynomial.
K=1
To calculate the sum of this polynomial, let us assume the value of x as 2
Code:
syms x k
F(x) = symsum (x^k, k, 1, 5)
This is how the output function will look like in MATLAB:
Let us now put the value of x as 2
Below is how our input and output will look like in MATLAB:
syms x k
F(2) = symsum (2^k, k, 1, 5)
So, the summation function in MATLAB can be used to find sum of a series. This series can be a simple series of numbers or a polynomial function.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Summation in Matlab. Here we discuss the Description of SymSum in Matlab along with the examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –