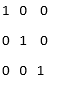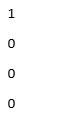Updated March 24, 2023
Introduction to Identity Matrix in Matlab
Matrix is defined as the arrangement of the numbers in rows and columns. They can be accessed with the help of row number and column number. If a matrix has 3 rows and 5 columns, then it is called a 3*5 matrix. There are different types of matrices, one of them is Identity Matrix. Identity Matrix is defined as the matrix where all the diagonal elements are ones and the rest of the elements are zeroes. It is also known as the elementary matrix or unit matrix. There are different operations that can be performed with identity matrix-like multiplication, addition, subtraction, etc.
Working of Identity Matrix in Matlab
In Matlab, the identity matrix is used for several purposes. It is denoted by I, E or U. The most important property of the identity matrix is, if a normal matrix is multiplied with the identity matrix then the resultant will always be the original matrix. Identity matrix can be of any dimension i.e. it can have any number of rows and columns. There are different operations that can be done with the help of the identity matrix in Matlab. In Matlab, the identity matrix can be created by using the” eye” keyword. We can define the dimension of the identity matrix by mentioning it in the brackets.
Below are the syntaxes which are used in Matlab to denote Identity Matrix:
- U = eye: This syntax returns 1 of type scalar.
- U= eye(a): This syntax returns identity matrix with a number of rows and a number of columns where all the diagonal elements are 1 and the remaining elements are zero.
- U= eye (a, b): This syntax returns identity matrix with a number of rows and b number of columns where all the diagonal elements are 1 and the remaining elements are zero.
- U = eye (size of array): This syntax is defined to return an array containing ones as the diagonal elements and zeroes elsewhere. The size of the array is defined as the size of an identity matrix. For example eye ([1,2]) will create an array of 1 by 2 where all the diagonal elements are one.
- U = eye (__, name of the type): This returns the data type of the identity matrix. For example eye(2,’int4’): This returns a 2 by 2 matrix where the elements have 4-bit integers.
- U = eye (__,’ like’, a): This syntax means that identity matrix has the same type containing diagonal elements as 1 and rest other elements as 0 which has the same type as that of a.
Examples to Implement Identity Matrix in Matlab
Below are the examples of identity matrix in Matlab:
Example #1
The below example always return scalar type value.
Code:
U = eye (3)
Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we have just created a simple identity matrix in Matlab, by defining the dimension inside the brackets. Here the dimension is 3 which means that identity is created with 3 number of rows and 3 number of columns where all the diagonal elements are 1 and rest other elements are zero. The diagonal elements are (1,1), (2,2), (3,3) in the above example. If the dimension is mentioned as 0 in the above example, then it will create an empty matrix and if the dimension is given as any negative value, then it will result in 0. The data types that can be accepted are int8, int32, int16, single, double, etc.
Example #2
To create an identity matrix with a number of rows and b number of columns.
Code:
U = eye (4,4)
Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we have given two dimensions to create an identity matrix which means it will create an identity matrix with a number of rows as 4 and number columns as 4 where all the diagonal elements are one and rest other elements as zero. The diagonal elements can be accessed by its row number and column number that are (1,1), (2,2), (3,3), (4,4). If the second part of the dimension is given as 0, then it will create an empty matrix and if the second part of the dimension is negative then it is always treated as zero. The data types that can be accepted are int8, int32, int16, single, double, etc.
Example #3
To create an identity matrix by mentioning the size of an array.
Code:
sze = [4,1];
U = eye(sze)
Output:
Explanation: In the above example, size is defined which will help in creating the identity matrix in Matlab. As the size is given as 4 by 1 array which means it will create an identity matrix with 4 numbers of rows and number of columns as 1. Size can have only two values and not more than that. If the size of the given element is mentioned as 0, then it will create an empty matrix and if the size of the given element is mentioned or declared as negative integer then it is always treated as 0. If the size is [4,5] then it will create a 4 by 5 matrix having a number of rows like 4 and the number of columns as 5.
The data types that can be accepted are int8, int32, int16, single, double, etc. The class or the type name can be int8, int32, int16, logical, single, double, etc. If we mention the output class of some prototype, then it also supports complex numbers. One of the most important properties of an identity matrix is that if we multiply a normal matrix with an identity matrix having the same dimension then the resultant matrix will always be the original matrix without any change in the elements. Please find the below example which will give you a better idea in understanding the concept behind it.
Example #4
This is the other example that shows how to perform matrix multiplication using syntaxes.
| A= | 5 | 2 |
| 3 | 4 | |
| B= | 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 |
Output:
| A*B= | 5*1+2*0 | 5*0+2*1 |
| 3*1+4*0 | 3*0+4*1 | |
| 5 | 2 | |
| 3 | 4 |
Explanation: In the above example, if a normal matrix is multiplied with the identity matrix then the resultant is the normal matrix with no change in the values having the same dimension.
Conclusion
There are various types of matrices that are used in Matlab for various purposes. Identity Matrix has also a wide number of applications like it is used in the field of engineering, statistics and more.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Identity Matrix in Matlab. Here we discuss the working of identity matrix in Matlab along with examples and code implementation. You can also go through our suggested articles to learn more–