Updated June 7, 2023
SUM Cells in Excel (Table of Contents)
Introduction to SUM Cells in Excel
Excel provides various ways to sum the numeric contents in cells. The sum operation is commonly used when performing data operations in any context, such as research, business, academic projects, etc. Excel stores a number in an individual cell, and while performing the sum operation across the cells, the entire range(s) must be considered.
Syntax:
The syntax of the SUM function is SUM(number1, number2… number n).
Examples of SUM Cells in Excel
Let’s go through the examples as described in the following section.
Example #1
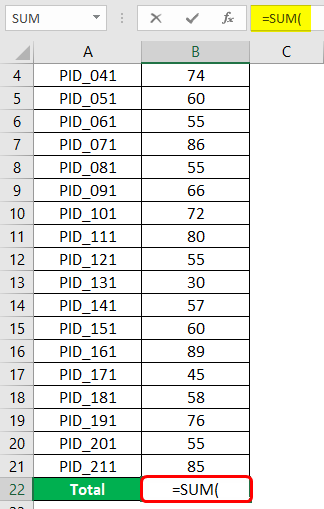
We have Sales data for various products for a particular period. The dataset is shown in the following screenshot. Their product IDs represented the products.
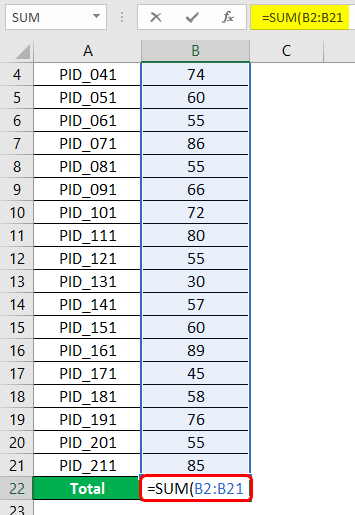
Now, we intend to obtain total sales. This will be sales obtained after adding sales for all the products. So, at the bottom, we will have “Total”. Using the SUM function, we will obtain total sales. The SUM function will be implemented as shown below. Note that we selected all those cells containing sales figures for respective products. In the SUM function, we can pass individual numbers separated by commas or pass range(s). Once done, complete the bracket and press Enter Key.
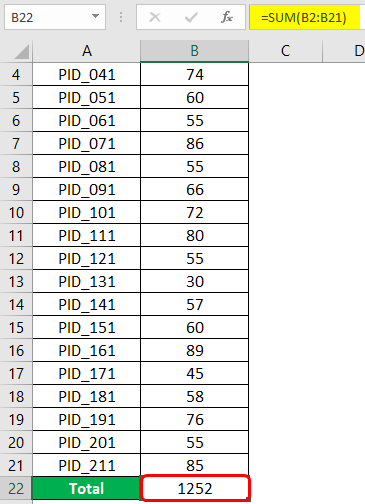
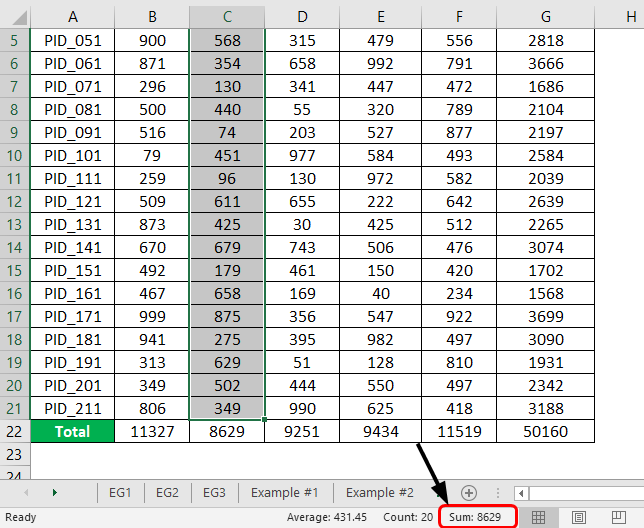
We get the correct result if we properly pass the argument (range of cells containing numeric values) into the SUM function. In the cell, we got the total sales as a number, and in the formula bar, we can see the formula that sums up the numeric contents in the mentioned range. The following screenshot shows the cells summed up using the SUM function.
Example #2
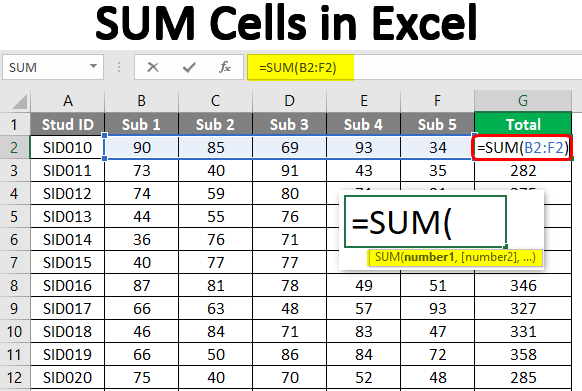
Here, we have marks for five different subjects for a certain number of students. Now, our task is to obtain total marks for each student. We will do this by adding the marks for five using the SUM function. Once implemented in the first cell, the function must be copied across all the requisite cells. The following screenshot shows the marks of data for students. In the Total columns, we want five subjects for each student.
We implemented the SUM function to sum cells across the range containing marks of five subjects, as shown in the following screenshot. Observe how the function has been implemented. Once the requisite range is passed as an argument, close the function and press Enter Key. If implemented correctly, we shall obtain the right results.
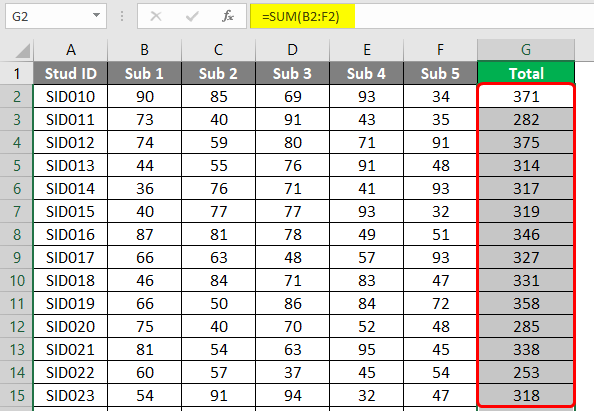
As the following screenshot shows, we obtained the total marks for each student using the SUM function, following the above procedure properly. Note that to verify that the correct right totals have been obtained, select the range we had used for addition and see the sum in the status bar. If both the figures match, we have successfully managed to sum cells to obtain total marks for each student.
In this example, summing marks for each subject across different students is not meaningful, as a total of marks for all students is never desired.
Example #3
The context governs the summing of cells, and we have seen it with examples. In the first example we discussed, we summed cells across rows, and in the second column, we summed cells across columns. In this example, we must sum across rows and columns because both sums are meaningful.
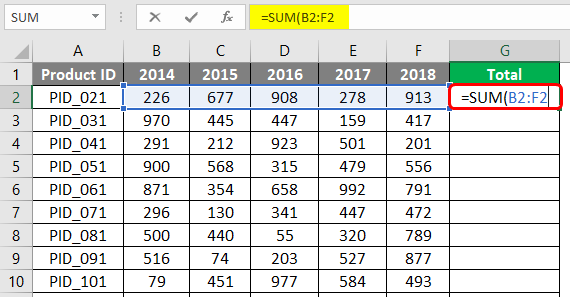
Let’s first understand the data. We have product sales data for five years, from 2014 to 2018. The sales figures for different products for these years are shown in the screenshot below.
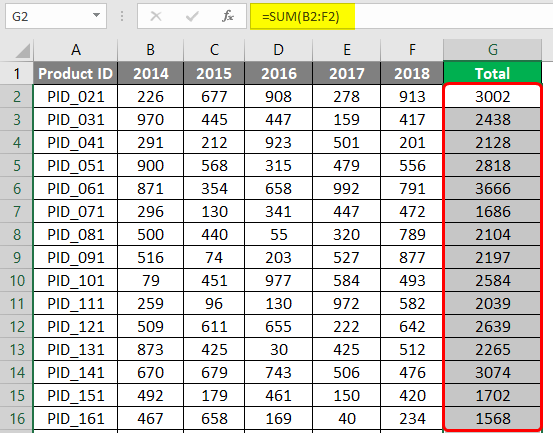
Our task is to obtain total sales figures for each product for all the years and total sales figures for all the products. The former sum task means summing across columns, while the latter sum task means summing across the rows. First, we will perform the sum of cells across columns, i.e., total sales for each product across different years. We can obtain the sum by implementing the SUM function, as shown in the below screenshot. Observe how the function has been implemented and what range it considers. Once done, close the function and press Enter Key.
We obtained the total across all the years in the data, and the total figures can be seen as shown in the below screenshot.
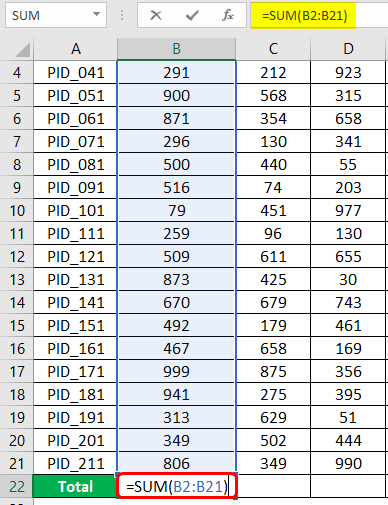
We are just half done, and now we want to obtain the total sales for each year. For this, we implemented the function, as seen in the screenshot below. Here, one fact must be noted carefully. As we can see, the Year label is also a number, so while performing a sum operation for summing across cells in the range, ensure that the cell with a year value is not selected, or else we shall obtain incorrect results. Such scenarios are prone to this common blunder when obtaining sums through shortcuts.
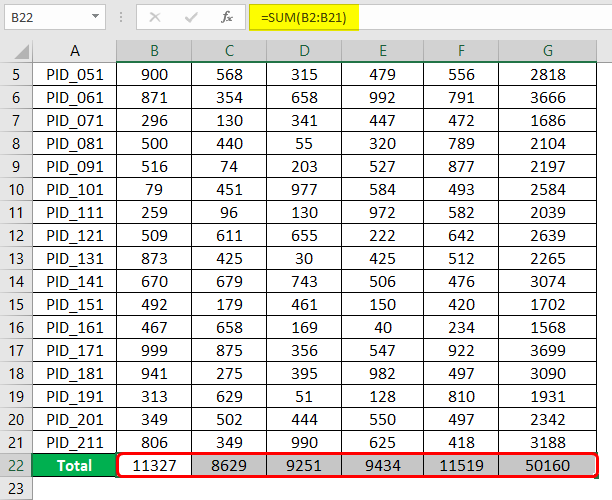
As described in the preceding section, we implemented the SUM function and successfully obtained the results, as seen in the following screenshot.
Once all the totals have been obtained, we should check if the results are correct. One of the ways to do this is to select the range we intend to sum. Excel gives Average, Count, and Sum details for the selected range in the status bar. Validate the requisite figures by cross-checking. As can be seen in the following screenshot, the sum of numbers in the selected cells matches the sum figure in the status bar.
Things to Remember
- In Excel, we can sum across cells using the SUM function; however, based on the context, it must be decided whether summing across rows or columns is feasible.
- Sometimes, SUM may return an error. These errors must be handled appropriately using suitable functionalities provided by Excel.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SUM Cells in Excel. Here we discuss How to SUM Cells in Excel, practical examples, and a downloadable Excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –