Updated October 30, 2023
Difference Between Stocks vs Bonds
In Stock vs bonds, when someone buys stocks, they invest money to own a small portion of the company, whereas when someone buys bonds, they give the company a loan and receive interest payments in return.
- Stocks help in having ownership in a business enterprise. When a company sells its stocks, it sells a part of the company in exchange for cash. In simple words, stores can also be understood as individual company shares. When a company thinks of expanding but cannot do so with the income it is earning through its operations, it takes the help of financial markets for additional financing.
- The company can split it into shares and sell them in the open market. So basically, a person who buys a stock has an actual share of the company. For this reason, the stock is also known as equity. The company pays dividends to stockholders only if it declares a dividend. The biggest corporations trade their stocks on stock exchanges. Stocks are either publicly or privately issued. If publicly issued, it is sold on stock exchanges like NASDAQ. The small group of individuals holds a substantial percentage of ownership when secretly issuing stocks.
Bonds mean long-term debt. When the government or corporation needs cash, it borrows money from the public market and pays interest on the money raised to the investors. The issuing corporation of bonds promises to pay the principal amount at a specific date. Bond issuers pay interest to bondholders by issuing bonds. According to a fixed contract, bondholders receive a fixed interest payment at specific intervals, usually every six months. More giant corporations may trade their bonds in the bond market. A corporation issues bonds to invest in plant and equipment or acquisition of another business. The government issues bonds generally to raise financing for capital improvement projects or other obligations.
Types of Stocks and Bonds
Below are the different types of stocks and bonds that are as follows:
Stocks
- Common Stock – This kind of stock gives general ownership in the company. The common stockholders can elect and vote, but they come much after bondholders and preferred shareholders in case of liquidation.
- Preferred Stock – Shareholders under this category don’t have voting rights but are eligible to get dividends before common stockholders. They get fixed dividend payments.
- Growth Stock – This stock invests its profits in helping to grow the company. This stock may not pay a dividend or may offer a small dividend.
- Dividend Stock – The company gives much of its profits as dividends to these stockholders. It may offer some capital appreciation, but the main focus is the dividend yield.
- Value Stock – The general investing public takes these stocks out of favor.
Bonds
- Convertible Bonds – These are corporate bonds, but a provision exists to convert them into company stocks.
- High-yield Bonds – Issuers with low credit ratings issue these bonds, also known as junk bonds, which pay higher interest rates.
- Foreign Bonds – Foreign governments and corporations issue these. Investors invest in these since they pay higher interest rates than domestic bonds.
- Municipal Bonds – These types of bonds are issued by states, countries, and municipalities. The interest paid is tax-free.
- S. Government Bonds – These are the debt obligations of the US government and are known as treasuries. These are generally issued for terms of 20 and 30 years.
Head-to-Head Comparisons Between Stocks vs Bonds ( Infographics)
Below is the top 8 Difference between Stocks vs Bonds
Key Differences Between Stocks vs Bonds
let us discuss some of the significant Differences Between Stocks vs Bonds:
- Stocks are financial assets issued by a company and have ownership rights. Issuers issue bonds as long-term debt instruments to raise capital and promise to repay the principal and interest.
- Stocks are equity instruments, and bonds are debt instruments.
- Dividends are paid on stocks, while interest is paid on bonds. Stocks do not guarantee a return, but bonds guarantee a return.
- Stocks are riskier than bonds.
- In the stock market, a centralized trading system operates, whereas in the bond market, trading occurs over the counter.
- Stockholders are owners of the company, while bondholders are lenders to the company.
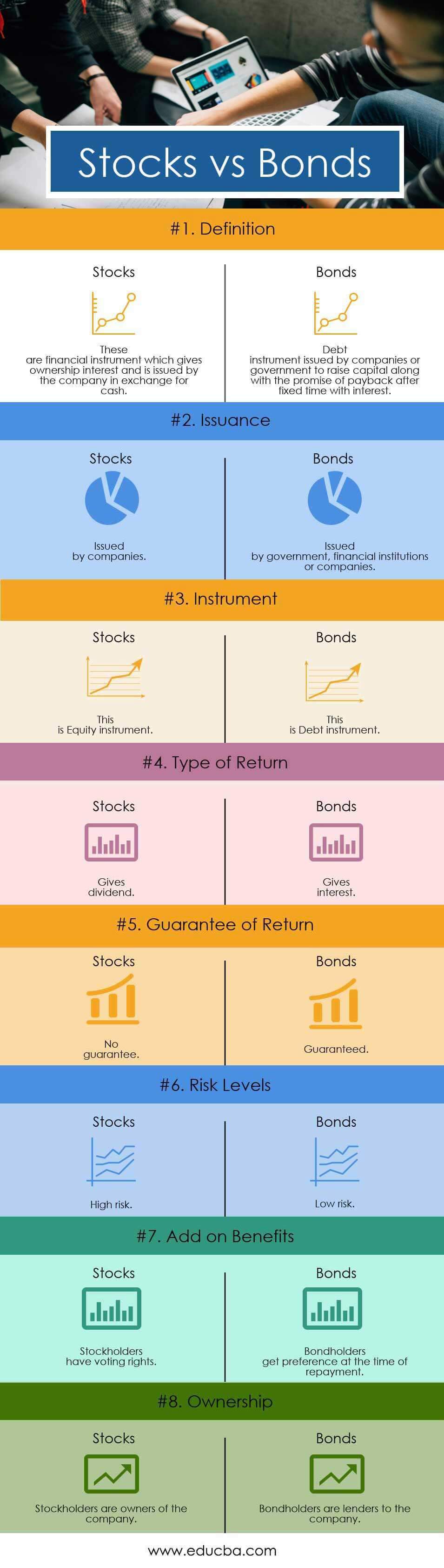
Stocks vs Bonds Comparison Table
Below is the Comparison table between Stocks vs Bonds
| Basis of Comparison |
Stocks |
Bonds |
|
| Definition | These are a financial instrument that gives ownership interest and is issued by the company in exchange for cash. | Companies or governments issue the debt instrument to raise capital and the promise of payback after a fixed time with interest. | |
| Issuance | Issued by companies. | Issued by the government, financial institutions, or companies. | |
| Instrument | This is an Equity instrument. | This is a Debt instrument. | |
| Type of Return | Gives a dividend. | Gives interest. | |
| Guarantee of Return | No guarantee. | Guaranteed. | |
| Risk Levels | High risk. | Low risk. | |
| Add on benefits | Stockholders have voting rights. | Bondholders get preference at the time of repayment. | |
| Ownership | Stockholders are owners of the company. | Bondholders are lenders to the company. | |
Conclusion
Both stocks vs bonds are good ways of raising capital from the market and are beneficial financial instruments. A well-balanced portfolio has bonds and stocks, and proper allocation can help maximize growth and minimize risk.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Stocks vs Bonds. Here, we have discussed the Stocks vs Bonds key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –