
Introduction to SQL Server Constraints
As the name suggests, SQL Server Constraints are the set of conditions and limitations applied on database, table or column in order to maintain the accuracy, reduced or no redundancy, stability, integrity, etc., of the data in the system. These constraints make sure that the operations applied on the database should pass through only if the conditions or rules established are obeyed, else the operation is stopped or fails by showing the error or exceptional message.
How to Specify Constraints?
We can define constraints at the time of developing the table by using the create table statement. After creating a table, we can also specify the constraints using the ALTER TABLE statement.
Syntax
Create a table by using this syntax
Create TABLE Information_ table
(
Column1 data_type(Size) Constraints_name,
Column2 data_type(Size) Constraints_name,
Column3 data_type(Size) Constraints_name,
);- Information_table: Name of the table which should be created.
- Data_type: Data type that can be stored in the field.
- Constraints_Name: This stands for the name of the Constraints. Therefore the example is NOT NULL, UNIQUE, PRIMARY, etc.
Constraints in SQL
Some Constraints in SQL are as follows:
1. NOT NULL
These NOT NULL Constraints say that we can’t store the null value in the column. This means we can’t store null anymore in this particular column if a column is specified as NOT NULL. You will not be permitted to insert a new row into the table without specifying any value in this field.
Example
We are creating a table name college with the field ID name and Email as NOT NULL. Therefore, without specifying any value in this field, you will not be allowed to insert a new row into the table.
Syntax
Create Table College
(
ID name (10) NOT NULL,
Email (15) NOT NULL,
ADDRESS varchar(50)
);2. UNIQUE
This UNIQUE limitation will help to identify each row in the table as unique. For example Singular column, All the rows must have a different value. In a table, we can have more than one UNIQUE column. SQL uses a special constraint to check whether the sub-query has duplicate tuples in the result.
Points to Remember
- Evaluates on an empty subquery to true.
- Returns true if there are two double rows with at least one attribute as NULL in the subquery.
Syntax
Create Table College
(
ID int (6 ) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
NAME varchar(15),
ADDRESS Varchar(50),
);3. PRIMARY KEY
The primary key is used to identify the unique rows from the table. If the table contains the principle key as a field then, that field cannot contain null values, and because the primary key identifies each row uniquely, all rows should contain unique values. So we can say, in other words, this is a combination of NOT NULL and UNIQUE limitations. A table named Student will be created below, and the field ID is specified as the primary key.
Syntax
Create Table College
(
ID INT(8) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
Address varchar(50),
Email Varchar(20),
Primary Key (ID)
);4. FOREIGN KEY
A foreign key (FK) is a column or column combination that is used in two tables to establish and enforce a data relationship. Here is a sample diagram showing the employee-department table relationship. If you look at it carefully, you will notice that the employees’ table’s dept_id INT column matches the departments’ table’s primary key column. Hence, the employee table’s dept id column is the foreign key to the department table.
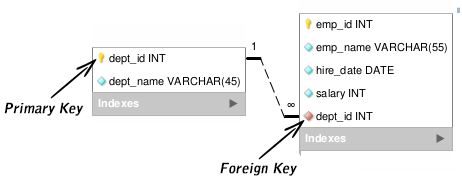
In MySQL, when you create a table that is shown below, you can create a foreign key by setting a FOREIGN KEY restriction. The following statement sets a foreign key on the employee table’s College column that refers to the department table’s College id column.
Syntax
Create table College (
Emp_id Int NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
emp _Name VArchar(20) NOT NULL,
hire_DATE NOT NULL,
salary INT,
Dept_ID INT,
Foreign Key (Dept_id)References Departments (dept_Id)
);5. CHECK CONSTRAINTS
Using the CHECK limit, we can specify a field condition that should be fulfilled when entering values for this field. For instance, the query below creates a Student table and specifies the AGE field condition as (AGE > = 18). In other words, the user is not allowed to enter any records in the AGE < 18 tables.
Syntax
Create table dogs(
ID INT NOT NULL,
Name VARCHAR (25) NOT NULL,
Breed Name Varchar (30) NOT NULL,
AGE OF BREED INT,
GENDER VARCHAR(9),
PRIMARY KEY (ID),
Check (Gender in ('male' , 'female' , 'UNKNOW'))
);NOTE: The check constraint in the above SQL command restricts the GENDER to belong only to the specified categories. If a new tuple is added or an existing tuple in the bond is updated with a GENDER not belonging to any of the three mentioned categories, the corresponding update of the database will be aborted.
Conclusion
Therefore, we learned about the various constraints in SQL in this Constraint SQL tutorial. First, we saw a brief introduction to the SQL constraint. Then we move to SQL Constraint types. We also discussed SQL Foreign Key, SQL Primary Key. We also learned SQL Server Drop Constraint and Integrity Constraint in SQL Server.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Sql server Constraints” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

