Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to Stored Procedure in SQL
If a particular operation you want to perform over and over again then we use the stored procedure. A stored procedure is a SQL code which is saved and can be reused. Once the stored procedure we just need to call the procedure to make use of it. A stored procedure can be parameterized or a normal procedure. In this session, let us learn more about the stored procedure and how it is used and called for execution. Parameterized stored procedure requires the parameters to be passed to it so that the stored procedure will act based on the parameter value passed.
Syntax
Below is the syntax for the stored procedure:
create procedure<procedure_name>
as
/* - - - - SQL statement - - - */
GO;Below is the syntax to execute the stored procedure:
exec<procedure_name>;Below is the syntax for the stored procedure with parameterized:
create procedure<procedure_name> @<parameter_name><datatype>
as
/* - - - - SQL statement - - - */
GO;Below is the syntax to execute the stored procedure with parameterized:
exec<procedure_name>@<parameter_name> = 'parameter_value';How to use a stored procedure in SQL?
Step 1: Now let us consider and create a table and create a stored procedure to get the data from the table:
Code:
create table test_stored_procedure
(
library_id int,
No_of_vistors int,
library_pass varchar(10),
library_opentiming time,
library_closetiming time,
library_location varchar(20),
book_types varchar(40)
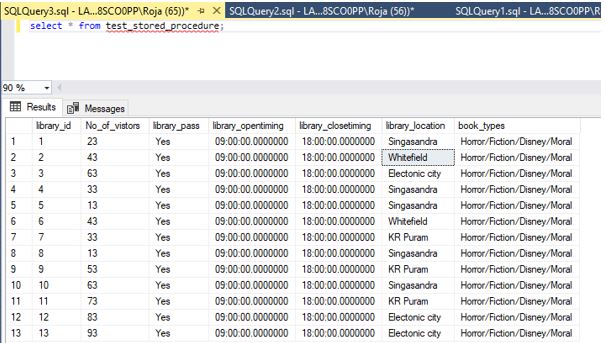
);Step 2: Let us insert data into the table:
Code:
insert into test_stored_procedure values (1, 23,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','Singasandra','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');
insert into test_stored_procedure values (2, 43,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','Whitefield','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');
insert into test_stored_procedure values (3, 63,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','Electonic city','Horrinsert into test_stored_procedure values (5, 13,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','Singasandra','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');
insert into test_stored_procedure values (6, 43,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','Whitefield','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');
insert into test_stored_procedure values (7, 33,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','KR Puram','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');or/Fiction/Disney/Moral');
insert into test_stored_procedure values (4, 33,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','Singasandra','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');
insert into test_stored_procedure values (8, 13,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','Singasandra','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');
insert into test_stored_procedure values (9, 53,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','KR Puram','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');
insert into test_stored_procedure values (10, 63,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','Singasandra','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');
insert into test_stored_procedure values (11, 73,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','KR Puram','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');
insert into test_stored_procedure values (12, 83,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','Electonic city','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');
insert into test_stored_procedure values (13, 93,'Yes','9:00AM','6:00PM','Electonic city','Horror/Fiction/Disney/Moral');Output:
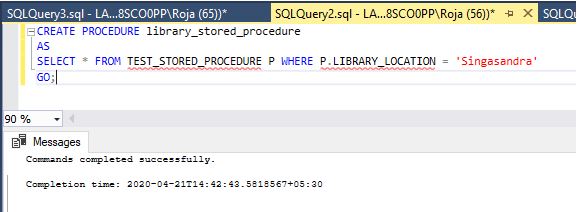
Step 3: Now let us create a stored procedure for the above table to get the data where “library_location” is ‘Singasandra’. Stored Procedure creation without parameters:
Code:
CREATE PROCEDURE library_stored_procedure
AS
SELECT * FROM TEST_STORED_PROCEDURE P WHERE P.LIBRARY_LOCATION ='Singasandra'
GO;Output:
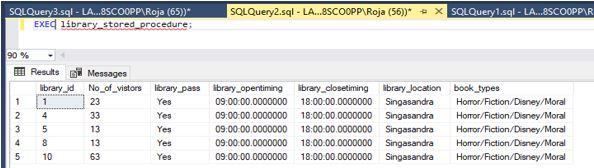
Step 4: Now let us execute the procedure:
Execute command of the stored procedure is below:
Code:
EXEC library_stored_procedure;Output:
Step 5: Stored Procedure creation with parameters:
Code:
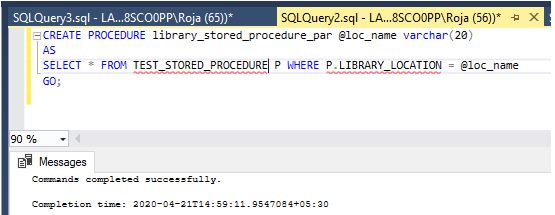
CREATE PROCEDURE library_stored_procedure_par @loc_name varchar(20)
AS
SELECT * FROM TEST_STORED_PROCEDURE P WHERE P.LIBRARY_LOCATION = @loc_name
GO;Output:
Step 6: Execute command of the stored procedure is below:
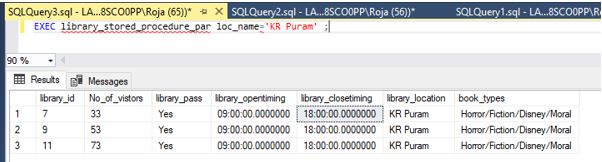
Code:
EXEC library_stored_procedure_par loc_name='KR Puram';Output:
Example to Implement Stored Procedure in SQL
Below is the example mentioned:
Example #1
Step 1: Now let us consider and create a table and create a stored procedure to get the data from the table:
Code:
create table paying_guest_pg
(
pg_id int,
pg_name varchar(20),
no_of_people int,
rent int
);Step 2: Now let us insert data into the table:
Code:
insert into paying_guest_pg values (12 ,'Sri Laxshmi PG',100 ,6000);
insert into paying_guest_pg values (13 ,'Sai Ram PG',120 ,5400);
insert into paying_guest_pg values (14 ,'Sri Maha PG',100 ,6000);
insert into paying_guest_pg values (15 ,'Venkateshwara PG',200 ,5000);
insert into paying_guest_pg values (16 ,'Govinda PG',300 ,4500);
insert into paying_guest_pg values (17 ,'Zen stay PG',120 ,6000);
insert into paying_guest_pg values (18 ,'Radha PG',130 ,6000);
insert into paying_guest_pg values (19 ,'Krishna pg',140 ,6000);
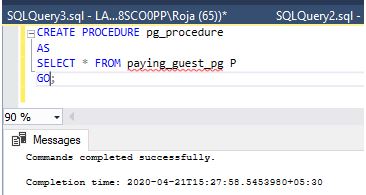
Stored Procedure creation without parameters: -
CREATE PROCEDURE pg_procedure
AS
SELECT * FROM paying_guest_pg P
GO;Output:
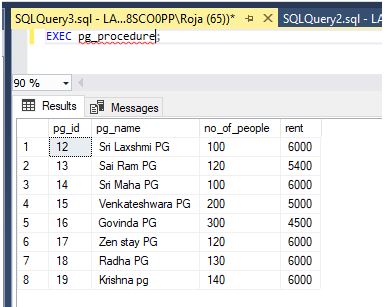
Step 3: Execute command of the stored procedure is below:
Code:
EXEC pg_procedure;Output:
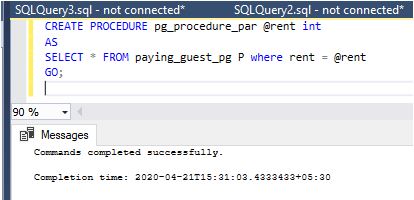
Step 4: Stored Procedure creation with parameters:
Code:
CREATE PROCEDURE pg_procedure_par @rent int
AS
SELECT * FROM paying_guest_pg P where rent = @rent
GO;Output:
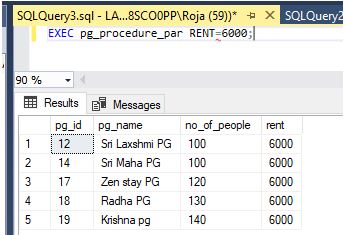
Step 5:
Code:
EXEC pg_procedure_par RENT=6000;Output:
Conclusion
Things to remember in the above session are: If a particular operation you want to perform over and over again then we use the stored procedure. A stored procedure is a SQL code which is saved and can be reused. Once the stored procedure we just need to call the procedure to make use of it. A stored procedure can be parameterized or a normal procedure.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Stored Procedure in SQL ” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.