Updated March 27, 2023
Introduction to SQL String Operators
The string operators in SQL are used to perform important operations such as pattern matching, concatenation, etc. where pattern matching is performed by using the wildcard characters such as ‘%’ and ‘_’ in concurrence with the Like operator to search for the specific patterns in strings and by the usage of concatenation operation one or more strings or columns of the tables can be combined together.
Examples of SQL String Operators
The concatenation of strings, as well as pattern matching, can be performed by using the below operators in SQL. Let us look at a few examples.
1. Concatenation Operator
The concatenation operation is used to combine character strings, columns of a table or it can also be used for the combination of column and strings.
In the below example, we can see that the two strings ‘Hello’ and ‘World!’ are combined by using the ‘+’ in between the string values.
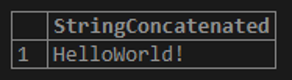
SELECT 'Hello' + 'World!' AS StringConcatenated;The above statement gives the below result where both the strings are combined and the same is displayed in the output.
In the below statement, it can be seen that the two strings are concatenated along with space in between.
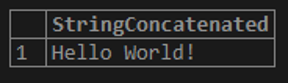
SELECT 'Hello' + ' ' + 'World!' AS StringConcatenated;In the result below, the concatenation is performed where both the strings ‘Hello’ and ‘World!’ are combined along with a space in between them.
In the above examples, we could see that the concatenation operation is performed and ‘+’ is used along with the strings to combine strings as well as space between the strings values. The concatenation can be performed on the columns of the table also.
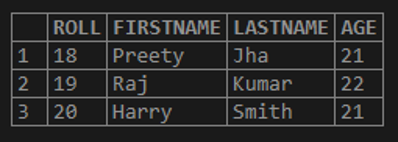
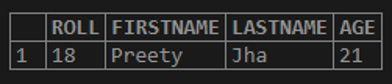
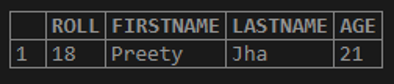
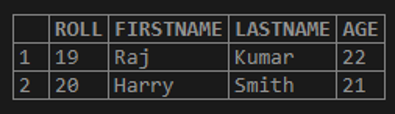
Let us take the example of the table “STUDENTS” as shown below.
select * from STUDENTS;Output:
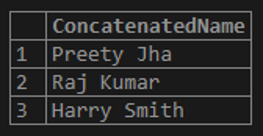
In the below example, the columns FIRSTNAME and LASTNAME of the table “STUDENTS” are combined with space in between the columns.
SELECT FIRSTNAME + ' ' + LASTNAME AS ConcatenatedName FROM STUDENTS;In the below result, we can see that the FIRSTNAME and LASTNAME and the space in between them are concatenated.
2. Like Operator
This operator is used to decide if the specific character string matches the specific pattern where the pattern can be a regular or wildcard character. While pattern matching, the regular characters should match exactly with the specific characters of the string but when we want to match the arbitrary fragments of the string, wildcard characters can be used.
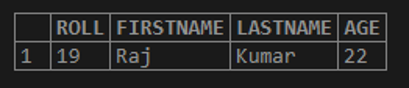
Let us take the example of the below query.
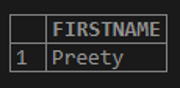
SELECT * FROM STUDENTS WHERE FIRSTNAME='Preety';The result of the above query is as shown below.
Here if we need to retrieve the details of the STUDENT Preeti, we need to remember the complete FIRSTNAME. In some other cases it might occur that it is not possible to remember the FIRSTNAME easily and in such cases the usage of pattern matching is helpful so that the retrieval of the data is possible even with a partial match of the student’s first name. The usage of Like in the below query will check if the data value in the column matches with the specific pattern. Here the pattern may also include the wildcard characters. The wildcard character used in the below query is % and any sequence of zero or more characters are matched by %.
So the previous query is now altered as below with the usage of Like along with the wildcard character.
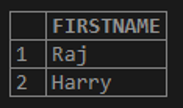
SELECT * FROM STUDENTS WHERE FIRSTNAME LIKE 'p%';In the above query, the FIRSTNAME column is compared with the pattern ‘p%’ and then it finds the Student name which starts with ‘p’ as shown below.
In the below query, it can be seen that the wildcard character % is used before ‘j’ and this will find the values which end with ‘j’.
SELECT * FROM STUDENTS WHERE FIRSTNAME LIKE '%j';The result of the above statement below shows the output of the Student name which ends with ‘j’.
In the below query, any value which starts and ends with a specific character can be found.
SELECT FIRSTNAME FROM STUDENTS WHERE FIRSTNAME LIKE 'p%y';The result of the above statement is shown below.
In the below query, the values which matches the pattern in any position is found.
SELECT * FROM STUDENTS WHERE FIRSTNAME LIKE '%a%';The result of the above statement can be seen below.
The ‘%a%’ finds any value which has ‘a’ in any position of the first name and we can see that ‘a’ is present both in the first name of the students Raj and Harry and the same is displayed in the result.
The other wildcard character ‘_’ is used to match any single character. If we want to find any character at a particular position, we can do so by using the character ‘_’ as shown in the below query.
SELECT FIRSTNAME FROM STUDENTS WHERE FIRSTNAME LIKE '_a%';The above query will display the FIRSTNAME of the students ‘Raj’ and ‘Harry’ as they have ‘a’ at the second position in their first names.
Also, we can see that in the below query, the values of the FIRSTNAME which start with ‘p’ having the character length of at least 2 can be found.
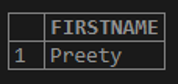
SELECT FIRSTNAME FROM STUDENTS WHERE FIRSTNAME LIKE 'p_%';In a result, it can be seen that the first name ‘Preeti’ starts with ‘p’ and has a length of at least two characters.
Conclusion
The concatenation operation and pattern matching in SQL have an important role. In concatenation operation, the strings and columns can be combined and in pattern matching, the data value in a column is matched with the specific pattern. The developers need to have a better understanding of these operations.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL String Operators” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.