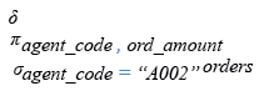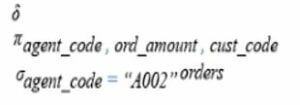Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQL SELECT DISTINCT Multiple Columns
Sql select distinct multiple columns are used to retrieve specific records from multiple columns on which we have used distinct clauses. We can also add multiple table columns with sql select distinct clause, as we know that sql select distinct eliminates rows where all the fields are identical, which we have selected. By using it, we can filter the data from multiple columns.
SQL select distinct on multiple columns is more useful in an RDBMS system to fetch unique records from various columns in a single table. We can use SQL to select distinct keywords on multiple columns from the specified table defined in the query. It will remove duplicate records from the column. It will work on various columns to find unique records. It retrieves the count of all unique records from the multiple columns. Therefore, it will eliminate all duplicate records.
How to Use SQL SELECT DISTINCT Multiple Columns?
SQL select distinct will work on multiple columns; we can use the same on single and multiple columns on the table from which we are retrieving the unique records.
Below is the syntax of sql select distinct multiple column statements as follows:
Syntax:
Select DISTINCT name_of_column1, name_of_column2, …., name_of_columnN
From name_of_table;Select DISTINCT name_of_column1, name_of_column2, …., name_of_columnN
From name_of_table where condition;Select DISTINCT name_of_column1, name_of_column2, …., name_of_columnN from name_of_table where condition order by name_of_column;Below is the description syntax of SQL select distinct multiple columns statement:
- Select: Using select, we can select the data as per the condition given in the query. For example, we can choose a distinct statement to retrieve unique records from the table.
- Name of the table: This is nothing but the table’s name from which we have retrieved the unique records from multiple columns.
- Name of a column: This is the column name used with a distinct keyword to retrieve data from multiple columns.
- Order by: This condition is used with sql select distinct multiple columns statement to fetch the records as per column, which we have used with an order by condition.
- Where condition: The where condition in any statement of SQL will be used to select or retrieve a specified row we defined in the where condition.
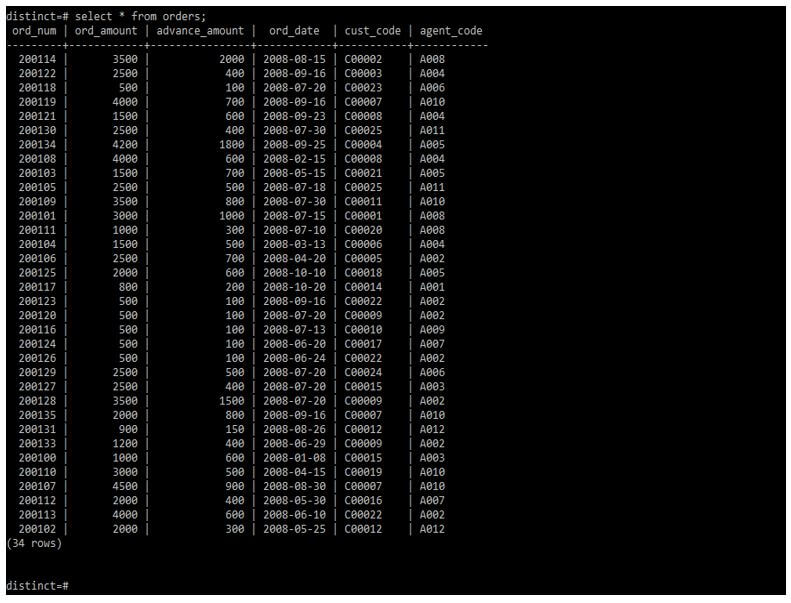
For defining how to use SQL select distinct multiple columns, we are using the orders table. In addition, we are using the Postgres database to execute queries that define how we are using it.
Code:
Select * from orders;Output:
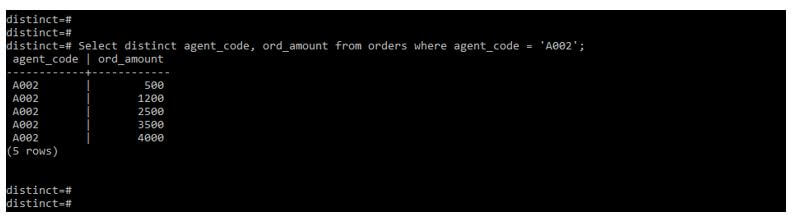
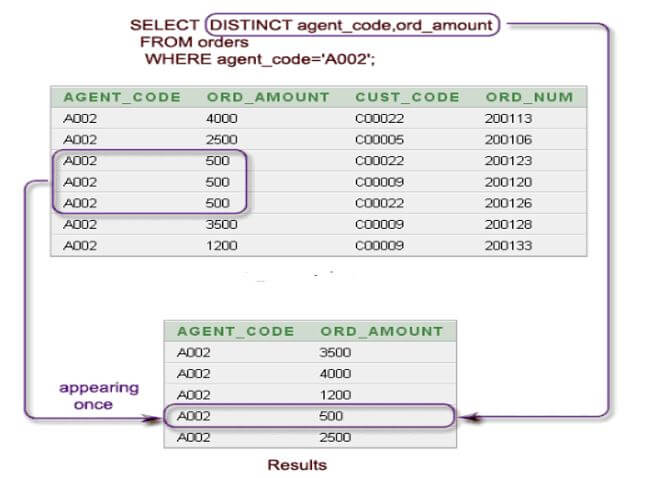
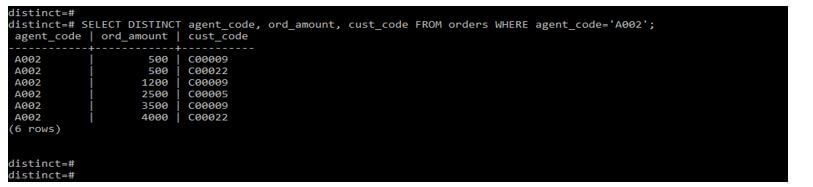
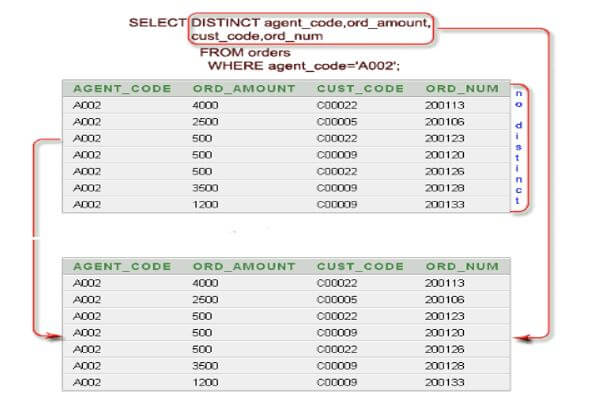
In the below query, we use two columns with sql select distinct clause. After using two columns, we can see the output retrieving the unique values from both columns.
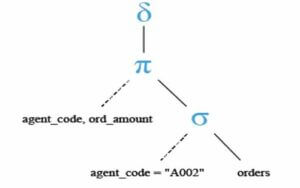
Below are the relational algebra expressions of the above query.
Below is the relational algebra tree of the above query.
Below is the pictorial representation of the above output.
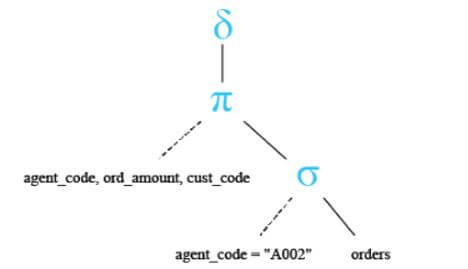
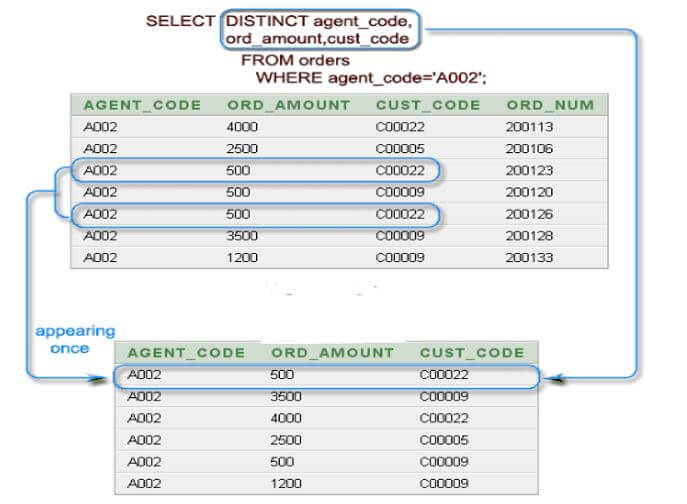
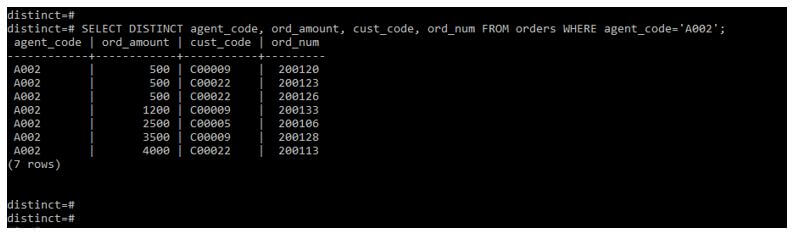
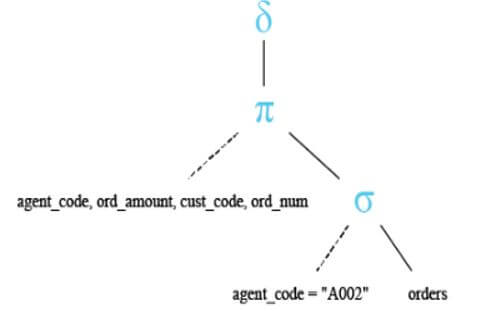
In the below query, we are retrieving data from three columns. After using a distinct clause on three columns, it will retrieve the unique values from both the rows.
Below are the relational algebra expressions of the above query.
Below is the relational algebra tree of the above query.
Below is the pictorial representation of the above output.
In the below query, we are retrieving data from all columns. After using a distinct clause on all columns will retrieve the unique values from all the columns.
Below are the relational algebra expressions of the above query.
Below is the relational algebra tree of the above query.
Below is the pictorial representation of the above output.
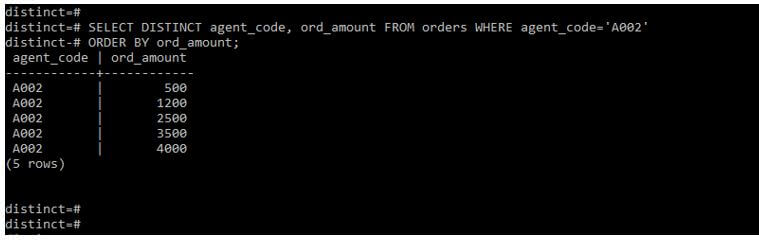
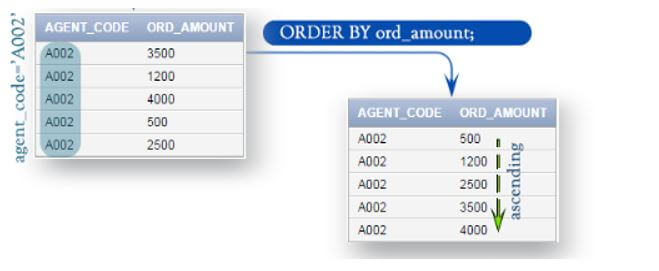
In the below query, we retrieve data from two columns in order by clause.
Below are the relational algebra expressions of the above query.
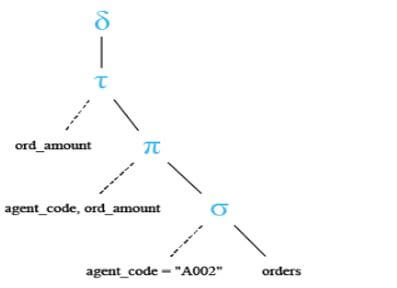
Below is the relational algebra tree of the above query.
Below is the pictorial representation of the above output.
Examples of SQL SELECT DISTINCT Multiple Columns
Different examples are mentioned below:
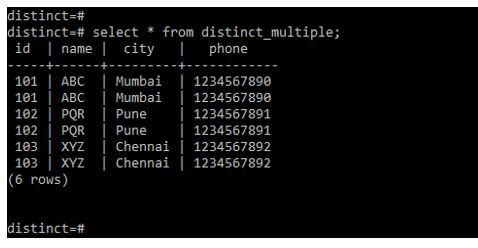
We are using distinct_multiple tables to define examples.
Code:
Select * from distinct_multiple;Output:
Example #1
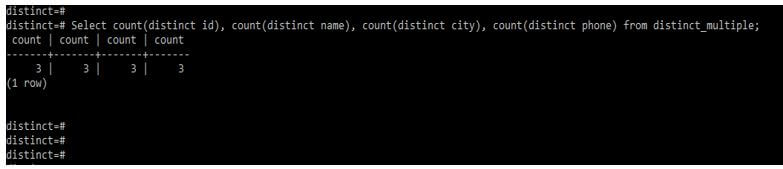
In the below example, we retrieve the count of unique records from multiple columns by using distinct clauses.
Code:
Select count(distinct id), count(distinct name), count(distinct city), count(distinct phone) from distinct_multiple;Output:
Example #2
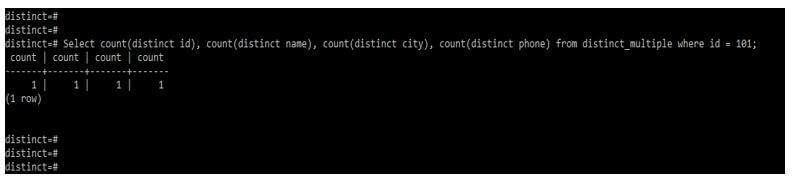
The below example shows the distinct count of all columns by using it with where conditions are as follows.
Code:
Select count(distinct id), count(distinct name), count(distinct city), count(distinct phone) from distinct_multiple where id = 101;Output:
Example #3
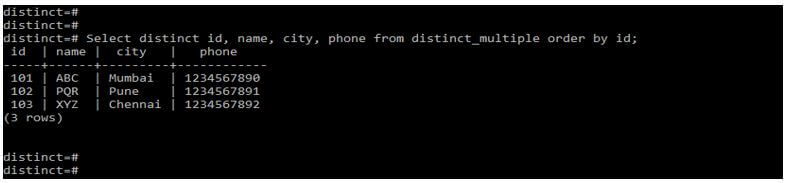
In the below example, we retrieve unique records from all the table columns by using order by condition as follows. We are using order by condition on the id column as follows.
Code:
Select distinct id, name, city, phone from distinct_multiple order by id;Output:
Example #4
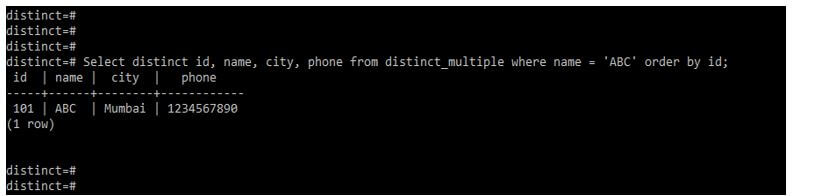
In the example below, we use where condition and order by clause in the same query. In addition, we use where condition on the name column and order by condition on the id column. Also, we are using all the columns with distinct clauses.
Code:
Select distinct id, name, city, phone from distinct_multiple where name = ‘ABC’ order by id;Output:
Example #5
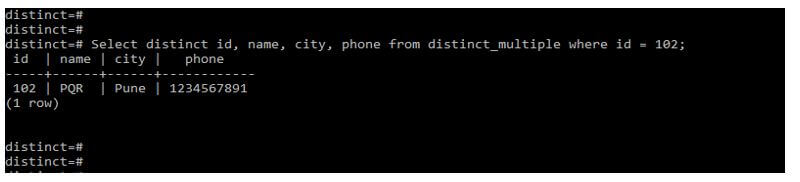
In the below example, we retrieve data from all columns with where condition. We use the id, name, city, and phone column to retrieve the data. After using a distinct clause on all columns with the where condition, it will retrieve the unique values from the rows we defined in the where condition.
Code:
Select distinct id, name, city, phone from distinct_multiple where id = 102;Output:
Conclusion
Selecting distinct counts on multiple columns retrieves all unique records from the multiple columns. It will eliminate all duplicate records. It retrieves distinct records from multiple columns on which we have used distinct clauses.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQL SELECT DISTINCT Multiple Columns. Here we discuss the introduction, how to use and examples, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –