Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to SQL BETWEEN
The BETWEEN operator chooses values from a predetermined range. For example, the values could be text, integers, or dates. The BETWEEN operator includes both the start and finish variables. Users may quickly determine whether an expression falls inside a certain range of values using the SQL BETWEEN condition (inclusive).
This article will teach how to pick data from a set of values using the SQL BETWEEN operator.
Key Takeaways
- The SQL Between operator is a key component of query language and is used to determine whether an expression falls within a specified range of values. Since this operator is inclusive, it also considers the range’s beginning and ending values. The values may take the form of text, numbers, or dates.
- To choose values that do not fall within the defined range, we may alternatively combine the NOT operator with the BETWEEN operator.
- When used sequentially, the SQL Between operator is almost like the SQL IN operator.
SQL Between Server Operator
In a SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE query, the BETWEEN operator in SQL Server is being used to obtain data that fall inside a predefined range. A record’s placement within the given range is initially verified using the BETWEEN operator. After the records have been validated, only those that fall inside the specified range will be returned.
Syntax
The SQL Server BETWEEN condition’s syntax is as follows:
expression BETWEEN val1 AND val2;Where expression here designates either a calculation or a column.
The inclusive range that is used by the expression for comparison is specified by the values val1 and val2.
Examples
The following demonstrates how to use BETWEEN Operators with Where Condition.
Table Creation:
-- create a table
CREATE TABLE library (
lid INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
lname TEXT NOT NULL,
lauthor TEXT NOT NULL,
book INTEGER NOT NULL
);
-- insert some values
INSERT INTO library VALUES (1, 'AAA', 'RICHARD', 12);
INSERT INTO library VALUES (2, 'Jjjj', 'kevin', 11);
INSERT INTO library VALUES (3, 'programs', 'Simon', 10);
-- fetch some values
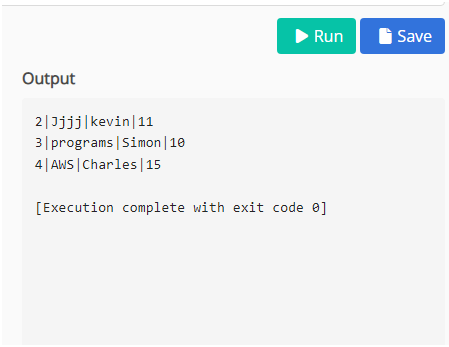
SELECT * FROM library;Output:
Example #1: The following Query shows it selects the number range between 2 and 4.
SELECT *
FROM library
WHERE lid BETWEEN 2 AND 4;Output:
ii) The above statement is replaced by >= operator, and the query looks like this:
SELECT
lname, lauthor
FROM
lib
WHERE
book >= 10 AND book <= 12;Example #2- Using Dates
CREATE TABLE BankEur
(
[Code] nchar(3) NOT NULL,
[CName] nchar(15) NOT NULL,
[Date] datetime NOT NULL
)
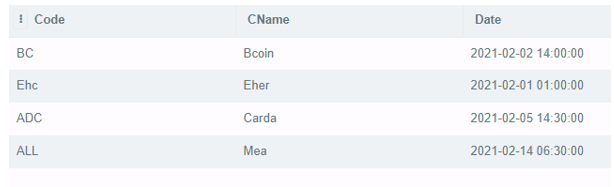
INSERT INTO BankEur
VALUES
('BC','Bcoin', '2021-02-02 14:00:00'),
('Ehc','Eher', '2021-02-01 01:00:00'),
('ADC','Carda', '2021-02-05 14:30:00'),
('PA','Pakistani', '2021-02-17 07:00:00'),
('ALL','Mea', '2021-02-14 06:30:00')
SELECT *
FROM BankEur
WHERE [Date] BETWEEN '2021-02-01' AND '2021-02-17'Output
Example #3- Using Between in the Text values
SELECT * from lib2
WHERE lname BETWEEN 'RICHARD' AND 'Simon'
ORDER BY book;SQL where BETWEEN
We extract the data using SQL Server databases while applying different filters. A particular range of information can usually be extracted from enormous volumes of data using the SQL Between operator. For instance, let’s say we want to know the employee information from January through February 2022. This operator can be applied to a SQL query in this situation.
Within the Where clause, the SQL Between operators is used to pick a range of possible values. For example, the following is the syntax for SQL Between:
SELECT
Col_name
FROM
table name
WHERE
test_expr
BETWEEN min_value(expression) AND max_value;In MySQL, an expression is used as a variable or parameter for the between query. For example, the expression could be a computation or a column. The records will be validated using this phrase with a parameter, and if a record falls inside the acceptable value range, it will be returned.
Parameters explained:
Test Expression is the expression or column that needs a range to be defined.
- Min value(expression): For the between operator, a minimum range is established. It must have the same data type as the Test expression.
- Max value(expression) represents the operator’s widest possible range. Additionally, it must share the same data type as test expression and min value(expression).
SELECT * FROM Products
WHERE Price BETWEEN 18 AND 22;Employ the less than() and larger than(>) operators to express its exclusive range instead.
The BETWEEN operator returns NULL if we supply NULL values, such as expr, lower value, or upper value. The greater than (>) and less than () operators are used in the example that follows, and because these operators are not inclusive, the sample produces one row as opposed to the ten that have been returned in the preceding example.
SELECT lname, lauthor FROM lib WHERE book >= 10 AND book <= 12;Some transactions in SQL must be retrieved depending on the dates and times they were completed. SQL’s DATETIME2 data type is used to carry out these actions in this case.
By using BETWEEN keyword, we will use the two times and dates supplied in the query to distinguish among them. The WHERE phrase comes before this to fulfill the needs set forth by the BETWEEN clause.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How a Data value acts in a SQL Between, and what are their limits?
Date and time have higher precision and need to be entered as Strings. To fetch the values between the current date and the next two dates. The Syntax goes like this:
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE ejoining
BETWEEN CURDATE() AND DATE_ADD(CURDATE(), INTERVAL 2 DAY)2. How to Retrieve the details of the transactions done between 08:00 pm, 20th March 2015 and 11:00 am, 24th November 2018.
SELECT * FROM Barclay WHERE TRANS_TIME
BETWEEN '2015-04-20 20:00:00'
AND '2018-11-24 23:00:00';3. How to use between with the SQL In Operator?
The SQL In operator provides multiple values in a WHERE clause as an alternative to distinct OR criteria.
Conclusion
This post looked at the SQL Between operator and some of its applications. Knowledge of the function to obtain a certain range of data is necessary.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQL BETWEEN. Here we discuss the Introduction, SQL Between Server Operator, SQL Between Selecting Data and Values, and key takeaways. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –