Updated June 16, 2023
Introduction to SQL Backup
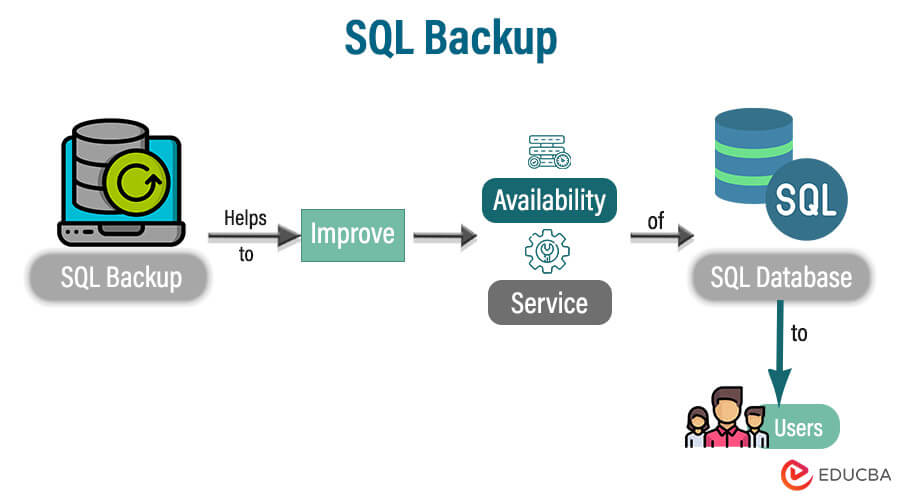
SQL Backup helps us continuously improve the availability and service of the SQL database to the users. If you use the SQL database in the production environment for your clients, you must ensure that your database is always working fine and available 24 * 7. For the availability of the database, you must often keep a backup of your client. In the event of database corruption, crash, or loss, it is essential to have the capability to restore the data in the database.
For this reason, SQL provides us with a facility to back up the database using the SQL backup utility. To utilize this utility, you must have access to the database and possess the select privilege assigned to its tables. Additionally, the database must be running. This utility is designed to create a logical backup consisting of SQL statements that can be executed to restore the database to its state when the backup file is created. It supports both single and multiple database backup scenarios.
You must backup your database frequently to have the updated backup of your database available to you. Restoring the backup file using SQL backup will revert the database to its state at the time of backup creation. In this article, we will learn about the types of backups available in SQL and also study some of them in detail.
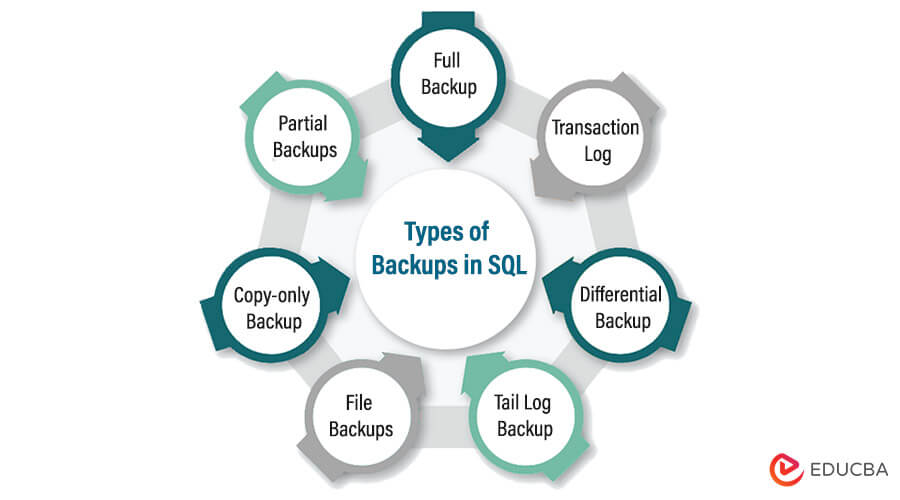
Types of Backups in SQL
Many types of backup are available in SQL, and all differ in strategy, content, scope, and methodology of the backup and restore process.
The types of backups in SQL are specified below.
Out of them, some are commonly used.
1. Full backup
In this backup strategy, the query backs up all the database data to the specified disk or memory location. As the backup process involves backing up the entire database data, it may take some time, especially when dealing with a large amount of data. Also, the restoration process becomes time-consuming.
But once the backup is created using a full backup strategy, at the time of necessity, the database can be restored to the state when it was being backed up. In SQL, we use the BACKUP DATABASE command to create a full backup of the database, with which we also have to mention the name of the database that we wish to back up and the disk location where the backup needs to be created.
2. Differential backup: BACKUP DATABASE
Backing up the whole database every time can be very time-consuming and unnecessary. In cases where the old data undergoes minimal modifications, we can back up only the recently added and modified data in the database since the last backup was created. This approach effectively saves significant resources and time that would have otherwise been consumed and required for backing up the previously backed-up old data. The system performs a differential backup by actively backing up only a small amount of data that has changed between the time interval of the last backup and the current one, assuming that the number of transactions made during that time duration is significantly low.
If a significant amount of data is generated daily, even incremental backups can become time-consuming. It’s important to note that the restoration process remains unaffected and still requires the same amount of time as when restoring a full backup. This is because the entire database is restored in both cases. The command used to perform the differential backup in SQL is the same BACKUP DATABASE along with an extra clause of the specification that is DIFFERENTIAL, along with the name of the database and disk location must be specified.
3. Transaction log Backup
We can use transactional log backups when utilizing the bulk-logged or full recovery models in the SQL database. This type of backup allows us to capture all the transaction logs generated on the database. As a result, we can recover the data to a specific point in time of our choice since the transactional log backups store the complete history of modifications on the database.
This type of backup consists of all the logs not backed up in the previous transactional log backup. The nature of the backup of the transaction log is incremental. In the event of a data loss accident, when you intend to restore the database to a specific point in time just before the occurrence of the accident, you need to restore the latest differential backup data and all the transaction logs that contain the modifications you want to recover.
In SQL, to perform the transaction log, we will have to use the BACKUP LOG command along with the TRANSACTION LOG clause in the query statement, along with the name of the database and the device location where we want to backup the logs.
Examples to Implement SQL Backup
Here are the examples:
Example #1 – Full Backup
Code:
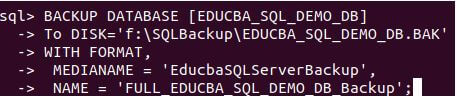
BACKUP DATABASE [EDUCBA_SQL_DEMO_DB]
To DISK='f:\SQLBackup\EDUCBA_SQL_DEMO_DB.BAK'
WITH FORMAT,
MEDIANAME = 'EducbaSQLServerBackup',
NAME = 'FULL_EDUCBA_SQL_DEMO_DB_Backup';Output:
Example #2 – Differential backup –BACKUP DATABASE
Code:
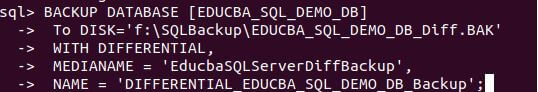
BACKUP DATABASE [EDUCBA_SQL_DEMO_DB]
To DISK='f:\SQLBackup\EDUCBA_SQL_DEMO_DB_Diff.BAK'
WITH DIFFERENTIAL,
MEDIANAME = 'EducbaSQLServerDiffBackup',
NAME = 'DIFFERENTIAL_EDUCBA_SQL_DEMO_DB_Backup';Output:
Example #3 – Transaction log Backup
Code:
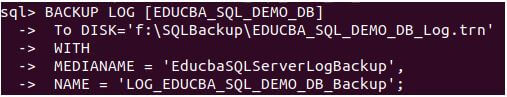
BACKUP LOG [EDUCBA_SQL_DEMO_DB]
To DISK='f:\SQLBackup\EDUCBA_SQL_DEMO_DB_Log.trn'
WITH
MEDIANAME = 'EducbaSQLServerLogBackup',
NAME = 'LOG_EDUCBA_SQL_DEMO_DB_Backup';
GOOutput:
Conclusion
The backup and restore facility in SQL provides users with continuous access to data and services of the SQL database. This feature ensures that data is available for as long as needed. In the event of accidents like server crashes or data corruption, the backed-up data can be restored to return the SQL database to a previous state when the backup was performed. Users can safeguard their data and recover from unexpected issues by utilizing backup and restore. We can use various ways to back up the data, and the type we choose for backup depends upon the requirement and amount of data and the strategy we want to back up the data in SQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Backup” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.