Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to SQL Administration
Administration in structured query language (SQL) covers database server administration activities. It is a commonly used term for performing tasks such as defining roles for users and groups in the server and their respective privileges or rights. It involves activities related to restoring, recovering and backup databases. It includes other functions such as tablespace and VM (Virtual Machine) creation, control and maintenance.
In this article, we will be discussing creating and managing users and groups in SQL server databases, particularly PostgreSQL. Then, we will focus on other SQL administration activities such as database restoration and backup creation. Finally, we will learn about tablespace management.
SQL Roles for Access Management
We have roles for managing access permissions to databases.
The roles can be of two types :
- user roles: User is someone who will be using the database.
- group roles: whereas a group of users is called a Group.
For example, if we want to give access to a student database to students and teachers in a school. Each student and teacher will be considered as a user. They each can have a separate set of privileges or rights, i.e. what they can view, create or delete? But we don’t want to keep so many student users, then we can create a student group and give them similar permissions.
To create a ROLE in pgSQL, we can use the following syntax.
CREATE ROLE role_name/user_name WITH
List_privileges{LOGIN,SUPERUSER,CREATEDB, CREATEROLE, INHERIT, REPLICATION etc.}
CONNECTION LIMIT numeral;Parameters
The parameters used in the above syntax are as follows :
- Role_name or user_name: It is the name of the user who will be given access to the database.
- List_privileges: It is the section where we mention the list of things that this new user can perform. For example, he can create a database, then simply write CREATEDB, but he can not create any new role, then write NOCREATEROLE.
- CONNECTION LIMIT numeral: Number of times he can access the database. It is by default set to -1.
Of the above-mentioned parameters, role_name is necessary while other parameters can be set to default.
Examples to Implement SQL Administration
Below are examples mentioned:
1. Creating a new login/user using SQL
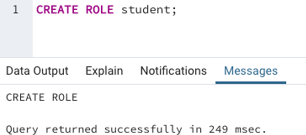
We can create a student role as mentioned below:
Code:
CREATE ROLE student;Output:
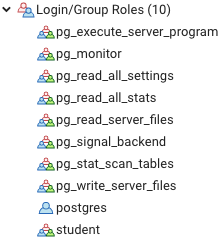
We can check from the browser if the new role has been created or not.
Yay! We can see that we have successfully created the student login.
2. Creating a new login/user using a browser
In the browser, we can successfully create a new login for a group or user in the following ways.
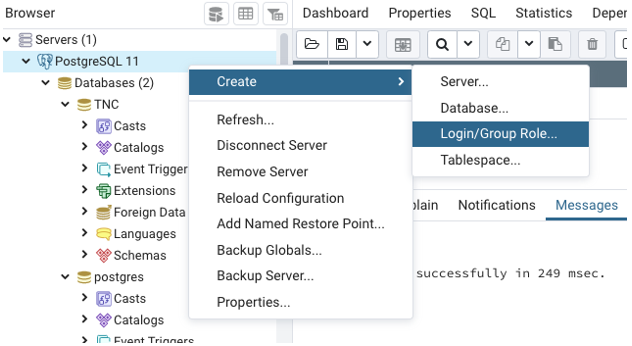
Step 1: Right-click on the database server, you want to use, select CREATE from the menu and finally select LOGIN/GROUP ROLE.
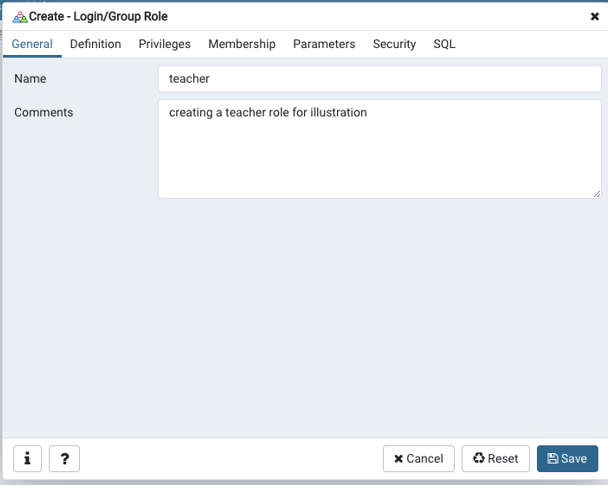
Step 2: Give a user_name or role_name in the dialog box, which appears.
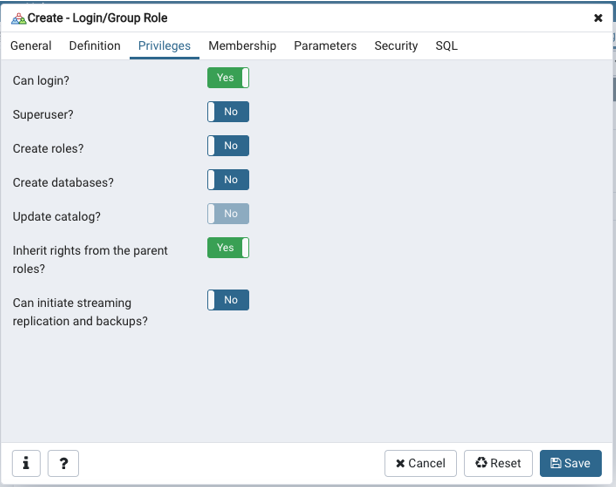
Step 3: Go ahead and check the privileges and edit them as per your choice and finally save the changes.
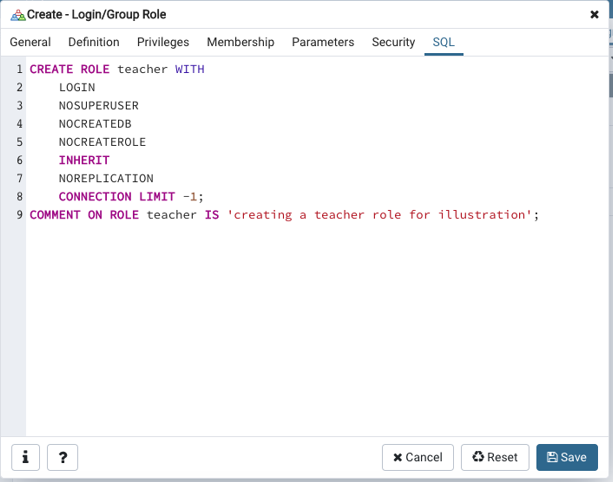
You can even check the equivalent SQL for login creation in the dialog box, as shown below.
Tablespace Management
A tablespace in a relational SQL database is a logical storage unit or file system that collectively stores all the database’s data. A SQL admin can control and manage how the data will be stored in tablespaces.
We can create a tablespace using the following command :
CREATE TABLESPACE tablespace_name;OR
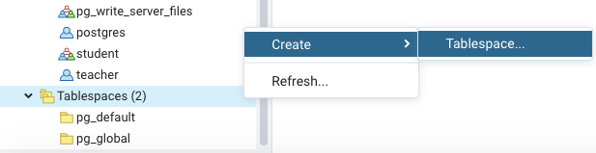
We can directly create a tablespace from the browser, using the shown steps.
We can alter a tablespace using the following statement:
ALTER TABLESPACE tablespace_name
OWNER TO login/user_name;We can even delete a tablespace using a DROP statement :
DROP TABLESPACE tablespace_name;Backup and Restore in SQL Databases
SQL administration involves some very critical tasks such as data backup creation and restoring of a backup file system in the SQL database. Every database management server has some designated functions to perform backup and restore functions. In PostgreSQL, we have functions like pg_dump, pg_dumpall, etc. to create a backup. We will be discussing the above-mentioned functions in great detail in this section.
Steps to create a backup using the browser.
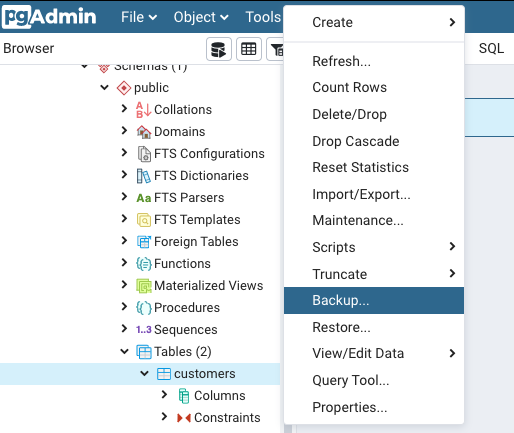
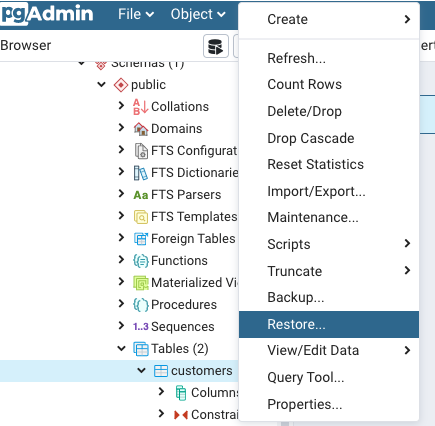
Step 1: Right-click on the desired database or data table for which you want to create a backup.
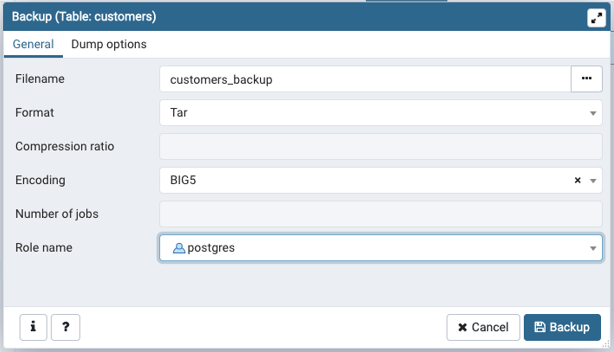
Step 2: In the dialog box so opened, mention the file_name, format, encoding, and user for creating a backup file.
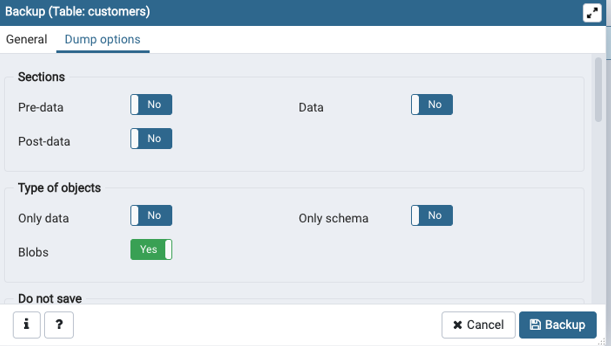
Step 3: Before clicking on the Backup option make sure and correct if required the dump options.
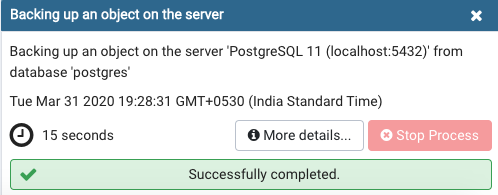
Step 4: Your backup has been successfully created. In this case, a backup for the customers’ table has been created from the ‘Postgres’ username.
Finally, Let’s move on to learn how to restore a backup file in the SQL database management server.
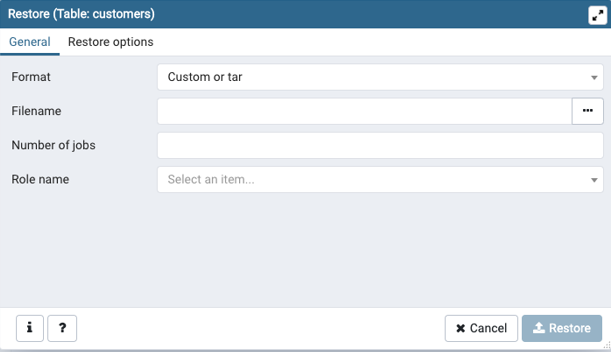
Steps to restore a backup file in the database using the browser.
Step 1: Right-click on the desired database or data table for which you want to restore a backup file.
Step 2: In the dialog box that appeared on the screen mention the file name and type, specify the user.
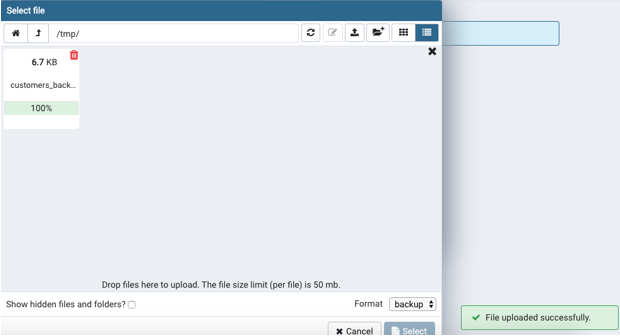
Step 3: In the filename, if the file is not already present in the mentioned folders, upload the backup file as shown below.
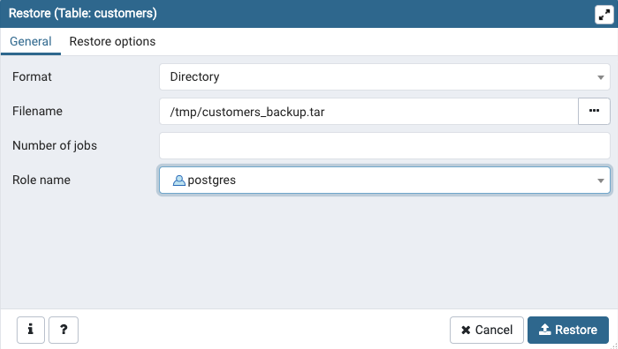
Step 4: Now search for the backup file, which you have just uploaded and click on the restore button. And we are done restoring the backup file.
Conclusion – SQL Administration
SQL administration is a collective term used for database administration activities such as creating backup files and restoring backup files in the database, creating new user logins and user groups and creating and maintaining tablespaces in the database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Administration” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.