Updated May 15, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Commands
MySQL is an open-source, widely used relational database management system that helps deliver high-performance and scalable web-based and embedded database applications to customers. It is widely used as a database component of the software stack for a web application. MySQL Commands are very powerful, and we will look into MySQL commands which are very helpful and consequential for every developer to know and use these queries to interact with the system and MySQL database. It is based on a structured query language (SQL) and will support and run on Linux, UNIX, and Windows.
Basic MySQL Commands
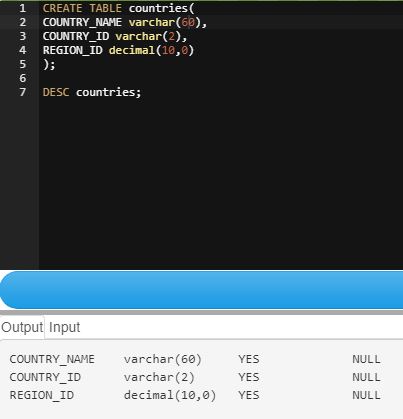
1. Write a query to create a table country with column names, country names, country IDs, and region IDs?
Creating a table country in MySQL is done by using the below query, and the output is as follows:
Query:
CREATE TABLE countries(
COUNTRY_NAME varchar(60),
COUNTRY_ID varchar(2),
REGION_ID decimal(10,0));Output:
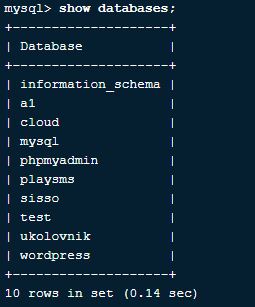
2. How to get a list of all databases present?
We can get a list of all running databases in MySQL using the below query
Query:
Show databases;Output:
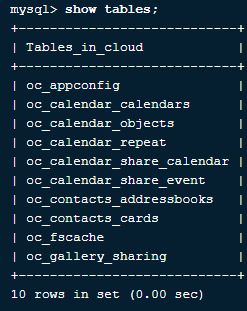
3. How to get all tables in a database using MySQL?
We can get all the tables present in a database in MySQL using the below query:
Query:
Show tables;Output:
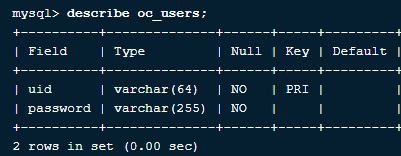
4. How to know all the filed names and types of tables in MySQL?
Using the query below, we can get all the filed names and types of a table in MySQL Command.
Query
describe os_users;Here os_users is a table with filed names u_id and password, and the output is as below:
Output:
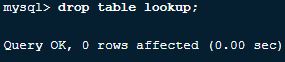
5. How to delete a table and a database in MySQL?
We can delete a table using the below MySql Command query
Drop table lookup;Where lookup is a table name, we can delete a database using the below query.
Drop database users;Where a user is a database
Output for deleting tables is:
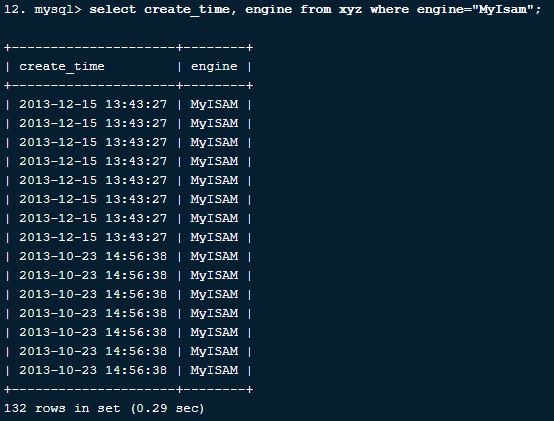
6. How to get data from a table where a particular field is filled with data “MyIsam”. We need to get the creation time and engine field for where the engine field is filled with “MyIsam”.
We can write a MySQL Command query for the above requirement as below: Let us say we have a table XYZ with fields creation_time and engine, and the engine field is filled with string data, and the creation_time field is filled with date and time.
Query:
Select create_time, engine from xyz where engine="MyIsam";The above query will give creation_time and engine where the engine field is filled with “MyIsam”
Output:
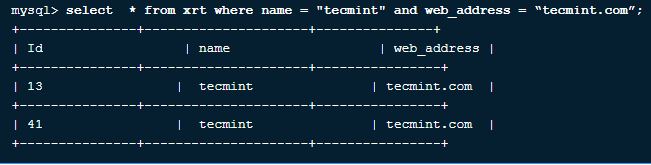
7. Query to get all fields from a table with the name ‘tecmint’ and the web address ‘tecmint.com’.
Let us consider a table as XYZ with the field’s id, name, and web address.
We will get the fields of a table where the name is matched as “tecmint,” and the web address is matched as “tecmint.com”
Query:
Select * from xrt where name="tecmint" and web_address="tecmint.com";The above query will display all the fields where the field name is matched with tecmint and the web address is matched with tecmint.com
Output:
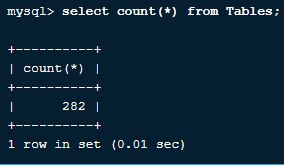
8. How to know the total number of rows in a table?
We can see the number of rows in a table using the query below:
Query:
Select count(*) from Tables;Output:
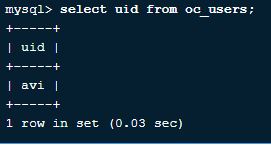
9. How to select particular filed rows in a table?
We can select a particular field let us say uid from a table called os_users is
Query:
Select uid from os_users;Output:
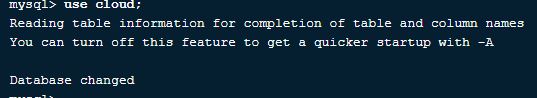
10. How to use a particular database in MySQL?
We can switch to using a particular database using the below query
Query:
use cloud;Output:
Intermediate MySQL Commands
The PHP developer also uses several other popular MySQL commands, which are not very basic but work with MySQL more. Some of the following types of intermediate MySQL commands:
1. Query to get a specific field from a table where a constraint is matched(emp_id=100).
Query:
Select emp_id, emp_name from table employee where emp_id=100;2. Query to order the results from a table based on specific constraints and using ‘order by’.
Using orderby for sorting the results from a table is
Query:
Select emp_id, emp_name from employee where city="Hyderabad" order by emp_id;3. Query to sort the results from a table based on some constraint and using “Group by”.
Using “Group By” to sort the results from a table is as below:
Query:
Select name, age from patients where age > 45 group by age order by name;4. Query to get the total number of customers from a customer’s table.
Query to get all the customers from a customer table is:
Query:
Select count(customer_id), country from customers group by country;5. Query to calculate the total sum of the salary given to each employee in a company.
Query:
Select sum(salary) from employee where emp_age > 30;6. Query to list all the views available in the schema.
Query:
Select * from myschema.views;7. How to create a view from a table?
The query to create a view is as below:
Query:
Create view A_students as select student_name, student_id from student where GPA > 80;8. How to update a view?
The query to update the existing view is as below:
Query:
Create or replace view product_list As select product_id, Product name, category from products where discount=no;9. Query to display primary keys from a table.
The following displays all the fields in a table’s primary key:
Query:
Select * from Sys. objects where type='PK';10. Query to display all the user tables in a system?
Query:
Select * from Sys. objects where type='u';Advanced MySQL commands
1. Why IFNULL() statement is used in MySQL?
The IFNULL() statement will check its first argument and return if it is not a null or second argument.
Query:
Select name, IFNULL(id,'unknown') As 'id' from the taxpayer;2. Query to show only five rows from the result of a query in MySQL?
To achieve this, we need to use LIMIT in the query as below:
Query:
Select * from students limit 53. Query to select all users except one using the not operator?
Query using not operator is:
Query:
Select * from users where user_name !=SAM;4. Query to get the current date in MySQL.
The following query will give the current date
Query:
Select current_date();5. How to export all tables to an XML file in MySQL?
We need to use the –e option to export all the tables to an XML file as below query:
Query:
Mysql –u user_name -xml -e 'select * from table_name' > tables.xmlTips and Tricks to Use MySQL Commands
Some common users who frequently use MySQL commands normally use some tips and tricks to correctly use MySQL commands output. These tricks usually solve user-specific queries and display the execution output to understand it correctly. Some of the key tricks most commonly used are:
- Add Explain statement before the select queries as it better explains what the query is exactly doing.
- We need to enable query cache as it improves the performance of the execution of queries, and it is one of the best methods for database performance.
- Use stack_trace in MySQL, which will help you to differentiate between bugs, track, and fix them.
- We can take the database backup using a mysqldump command in MySQL which will help you to keep track and backup.
Conclusion
It’s an overview of MySQL commands of different levels and tips and tricks to use them. After reading this article, I hope you will have a good understanding and knowledge of MySQL commands and how to use them.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Commands” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.