Updated March 1, 2023
Differences Between Splunk vs Spark
Splunk is used for searching, monitoring and analyzing the big data generated by machine using web interfaces. It is used to turn machine data into our answers. Splunk gives real-time answers that meet the customer or business requirements and Splunk is trusted by the 85 of the Fortune 100 companies. Apache Spark is very fast and can be used for large-scale data processing which is evolving great nowadays. It has become an alternative for many existing large-scale data processing tools in the area of big data technologies. Apache Spark can be used to run programs 100 times faster than Map Reduce jobs in the Hadoop environment making this more preferable.
Head to Head Comparison Between Splunk and Spark (Infographics)
Below is the Top 8 comparison between Splunk and Spark:
Key Differences Between Splunk and Spark
The key difference between Splunk and Spark are listed below:
Splunk is a big data analytics tool developed by an American multinational corporation Splunk based in California, USA. Splunk has also collaborated with Horton works vendor which is a Hadoop environment provider. Spark is an open-source cluster computing framework developed by Apache Software Foundation which was originally developed by the University of California Berkeley and was donated to Apache Foundation later to make it open source.
Below are the lists of points, describe the key Differences Between Splunk vs Spark
1. Splunk can be used to search for a large amount of data using SP (Splunk Search Processing Language). Spark is a set of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) out of all the existing Hadoop related projects more than 30. Spark can be run on Hadoop or Amazon AWS cloud by creating Amazon EC2 (Elastic Cloud Compute) instance or standalone cluster mode and can also access different databases such as Cassandra, Amazon DynamoDB, etc.,
2. Splunk concepts include Events, Metrics, Fields, Host, Source and Source Types, index-time, search-time, and indexes. Spark provides high-level APIs in different programming languages such as Java, Python, Scala and R Programming.
3. The core features of Splunk include Search, Report, Dashboard and Alerts whereas Spark has core features such as Spark Core, Spark SQL, M Lib (Machine Library), Graph X (for Graph processing) and Spark Streaming.
4. Splunk is used to deploy and use, search, scale and analyze the extracted large-scale data from the source. Spark cluster mode can be used to stream and process the data on different clusters for large-scale data in order to process fast and parallel.
5. Splunk maintenance mode can be used to manage and maintain the indexes and index clusters whereas Spark Cluster mode will have applications running as individual processes in the cluster.
6. The maintenance mode in Splunk can be enabled using the Command Line Interface option available after making the cluster up. The components of the Spark cluster are Driver Manager, Driver Program, and Worker Nodes.
7. The cluster management in Splunk can be done by using a single master node and multiple nodes exist to search and index the data for searching. Spark has different types of cluster managers available such as HADOOP Yarn cluster manager, standalone mode (already discussed above), Apache Mesos (a general cluster manager) and Kubernetes (experimental which is an open source system for automation deployment).
8. The cluster functions of Splunk can be studied by different concepts called Search factor, replication factor and Buckets. Spark cluster component functions have Tasks, Cache, and Executors inside a worker node where a cluster manager can have multiple worker nodes.
9. Splunk provides API, view and search manager to interact with data. Spark Cluster computing framework provides a shell to analyze the data interactively and efficiently.
10. Splunk Products are different types like Splunk Enterprise, Splunk Cloud, Splunk light and Splunk Universal Forwarder Enterprise Security, Service Intelligence etc., Spark provides configuration, monitoring, tuning guide, security, job scheduling and building Spark etc.,
11. Splunk Web Framework provides search manager, Splunk view, Simple XML wrapper and Splunk JS Stack view. Spark provides Spark SQL, Datasets and Data Frames. Spark Session in Spark can be used to create Data Frames from an existing Resilient Distributed Dataset (RDD) which is a fundamental data structure of Spark.
12. Splunk has also a cloud-based service to process jobs or processes as needed by the business requirement. Spark is lazily loaded in terms of job triggering where it will not trigger action until and unless a job is triggered.
13. Splunk Cloud has several features to send data from various sources and to cloud deployment. Spark streaming has a fault tolerance mechanism where it recovers the lost work and state out of the box without any extra configurations or setup.
14. Splunk Cloud has capabilities of Ingestion, Storage, Data Collection, searching and connectivity with Splunk Cloud. Spark Streaming is available through maven central repository and the dependency can be added to the project to run the Spark Streaming program.
Splunk and Spark Comparison Table
Below is the comparison table between Splunk and Spark.
| BASIS FOR
COMPARISON |
Splunk | Spark |
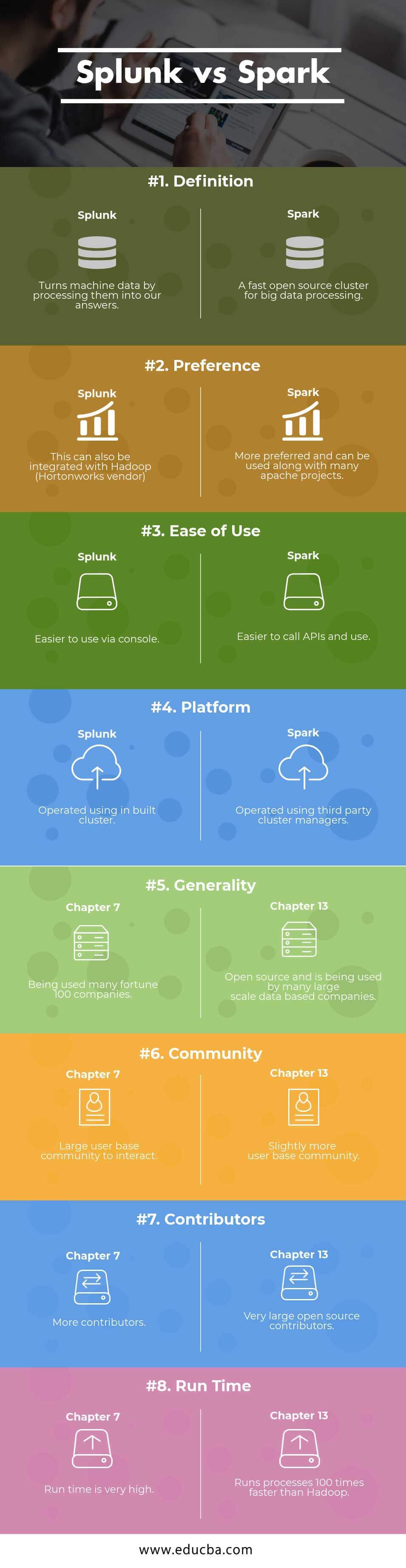
| Definition | Turns machine data by processing them into our answers | A fast open-source cluster for big data processing |
| Preference | This can also be integrated with Hadoop (Horton works vendor) | More preferred and can be used along with many Apache projects |
| Ease of use | Easier to use via console | Easier to call APIs and use |
| Platform | Operated using inbuilt cluster | Operated using third-party cluster managers |
| Generality | Being used by many fortune 100 companies | Open source and is being used by many large-scale data-based companies |
| Community | Large user base community to interact | Slightly more user base community |
| Contributors | More contributors | Very large open-source contributors |
| Run Time | Runtime is very high | Runs processes 100 times faster than Hadoop |
Conclusion
Splunk can be used to integrate with companies having large customer base data such as transportation, banking, and financial institutions whereas Spark has different types of core frameworks and a group of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) where it can be used to integrate with many Hadoop based technologies or projects.
Spark can be preferred for lightning-fast clustering operations and whereas Splunk has some limited base of APIs with fewer integration facilities but which can also be integrated with the Hadoop framework provided by Horton works vendor. Spark can be better preferred that is having a large community user base and having more integration options with many databases and platforms or software applications.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Splunk vs Spark. Here we have discussed Splunk vs Spark head to head comparison, key difference along with infographics and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –
- Hadoop vs Splunk – Find Out The Best 7 Differences
- Spark SQL vs Presto – Find Out The 7 Useful Comparison
- Apache Hive vs Apache Spark SQL – 13 Amazing Differences
- Splunk vs Nagios
- 5 Importants And Benefits of Big Data Analytics
- Top Differences of Graylog vs Splunk
- Zabbix vs Nagios | Top Differences
- Difference between Datadog vs Splunk