Updated May 23, 2023
Introduction to Software Testing Life Cycle
The Software Testing Life Cycle, commonly referred to as STLC, is a flow for a testing process performed in serial order on a software application system to verify and validate the application for its correctness against the requirement provided by the business. It comprises six phases, similar to the software development life cycle. Depending on the chosen development methodology, these phases can either run parallel to the development process or be carried out as the final step in the software development life cycle.
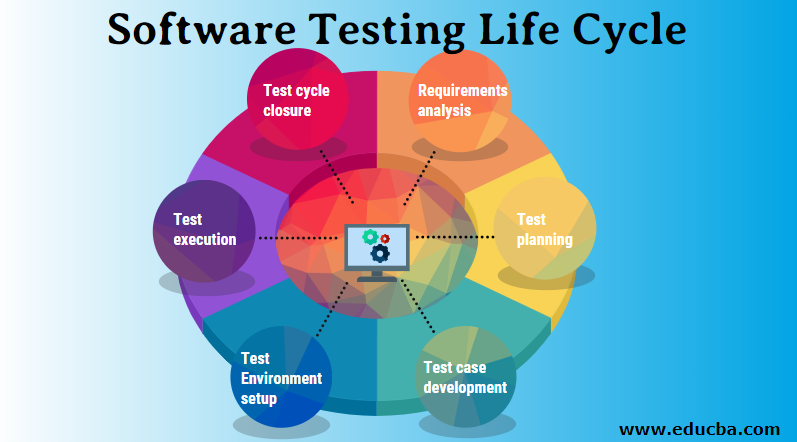
Software Testing Life Cycle
Different phases of the software testing life cycle are as follows:
- Requirements analysis
- Test planning
- Test case development
- Test environment setup
- Test execution
- Test cycle closure
Let us discuss the software mentioned above testing phases in detail for more understanding.
1. Requirement Analysis
This is the first phase of the software testing life cycle. After that, requirements analysis is the most important phase because it is the base phase for all software development; Making a mistake in requirements analysis can result in delivering the wrong software to the client.
In this phase, the quality assurance team initially focuses on understanding the requirements of the software to identify the specific areas or components that need to be tested. Then, for more understanding of the requirement, the QA, i.e.quality assurance team, may meet different organizations like business organizations, stakeholders, development teams, technical teams, design teams, etc. Once the software requirements are fixed, the QA team identifies and tests the components or parts of the software or system.
2. Test Planning
This is the second phase of the software testing life cycle. This phase is known as the test strategy because the test strategy is planned in this phase. The test manager oversees this activity, which involves managing all testing-related aspects. The test manager assesses the effort required, determines the cost of testing the entire project, and identifies the types of testing that need to be performed for each component. Other than this, it also involved following the task.
- Analyzing software
- Define the objective of the test
- Designing a test strategy
- Planning resources for test
- Planning test criteria
- Designing test cases
- Scheduling and executing test
- Planning test environment for execution
- Analyzing test delivery
3. Test Case Development
This is the third phase of the software testing life cycle. After completing the test planning phase, creating test cases commences. In this phase, the testing team designs the test cases for test execution in detail. It also prepares the information, i.e. data for test cases. The peer team or quality control, such as the QA team, examines and reviews the delivered test cases once they have been designed. The test case is good if it identifies errors quickly and solves them immediately under the test.
- The characteristics of a good test case are
- A test case is transparent and simple.
- Generate the same result every time for the same test.
- The test case id contains the name.
- Covers 100% of software requirements.
4. Test Environment Setup
This is the fourth phase of the software testing life cycle. This phase is a vital part of STLC. Test environment setup sets up all the resources like software and hardware for the testing team to execute all the test cases. The customer or the organization does not set up the testing team’s test environment. Instead, the testing team prepares the smoke test for executing the test environment setup.
5. Test Execution
This is the fifth phase. It executed the test with code, compared it with the expected result, and analyzed the report. The testing team executes tests based on test planning and strategies. While the execution of the test, the test analyst marks the test report.
- When the execution of a test case is successful, it is marked as “passed.”
- If the test case is failed, it is marked as failed, and the corresponding defect is reported to the software developer team
- The testing team marks a test case as blocked if it encounters an error. After resolving the defect, the team retests the test cases previously marked as blocked or failed to verify that they have been successfully addressed.
6. Test Cycle Closure
This is the final phase of the software testing life cycle. In this phase, software testers meet to evaluate the test coverage based on the software requirements, test cases, cost, time, and quality assurance. Test cases and bug reports are analyzed to find defect distribution by type. After completing the test cycle, the test cycle closure report is prepared. Finally, the test leader prepares test cycle closure.
The standard format of the test cycle closure is as follows
- Test summary report
- Identifier
- Test summary
- Variances
- Comprehensiveness assessment
- Summary of results
- Evaluation
- Summary of activities
- Approval
Conclusion
This article has seen phases of the software testing life cycle.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Software Testing Life Cycle. Here we discus the basic concept and different phases of the software testing life cycle. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –