What are Python Variables?
Python Variables are memory spaces that hold information, such as numbers or text, that the Python Code can later use to perform tasks.
Here is an example of a variable in Python:
Year = 2023In the above code, the variable Year holds the assigned value 2023.
To understand Python variables better, imagine there is an empty shelf where you want to store a few items. But, before placing anything on the shelf, you add a label to each item so that you can search for anything easily by looking at the label.
In the same way, in Python programming, variables are like those labels. Here, we can say that the memory space is like an empty shelf. There you can store different types of values (items) like numbers, decimals, letters, and sentences. However, to store that data, we need to use variables (labels) so that Python can access the data using the variables.
So, when we create a variable and assign it a value, Python stores that value (item) in the memory (shelf) and remember the variable name (label). If you lack time, you can get help with Python homework on variables from programming experts. Nevertheless, this article will help you to understand better how variables work.
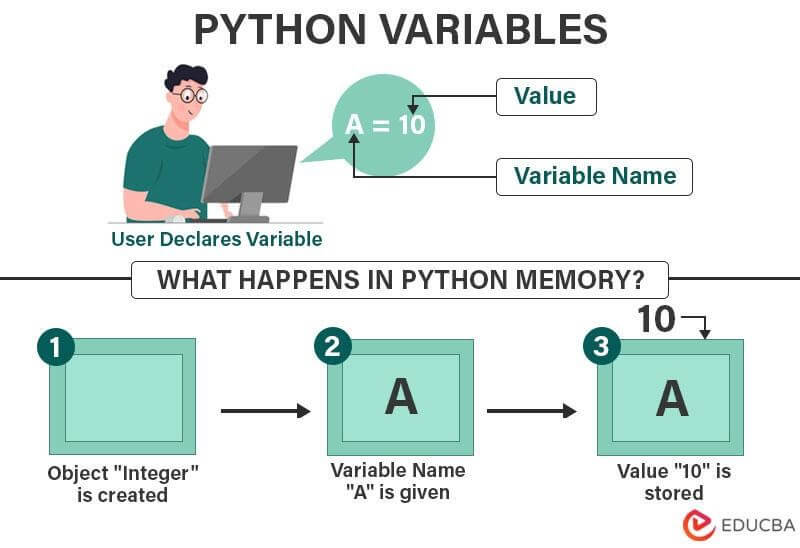
Table of Contents
Python Variable Naming Convention
Before we start writing or declaring variables in Python, it is important to understand the rules for naming variables. Below are the 5 most important Python variables rules you must know:
1. The variable name should start with an underscore or letter.
Example: _educba, xyz, ABC
2. Using a number at the start of a variable name is not allowed.
Examples of incorrect variable names: 1variable, 23alpha, 390say
3. The variable name can only include alphanumeric characters and underscore.
Example: learn_educba, c5, A777_21
4. Variable names in Python are case-sensitive.
Examples of different variable names: educba, Educba, EDUCBA
5. Reserved words in Python cannot be a variable name.
Example: while, if, print, while
Apart from this, it is also possible to create variable names with more than one word. There are 3 types of cases you can use to write multi-word variable names.
| Case Types | Description | Variable Name Example |
| 1. Camel Case |
|
|
| 2. Pascal Case |
|
|
| 3. Snake Case |
|
|
Python Variable Types
Python variable types, also known as variable data types, show the type of data stored in the variable.
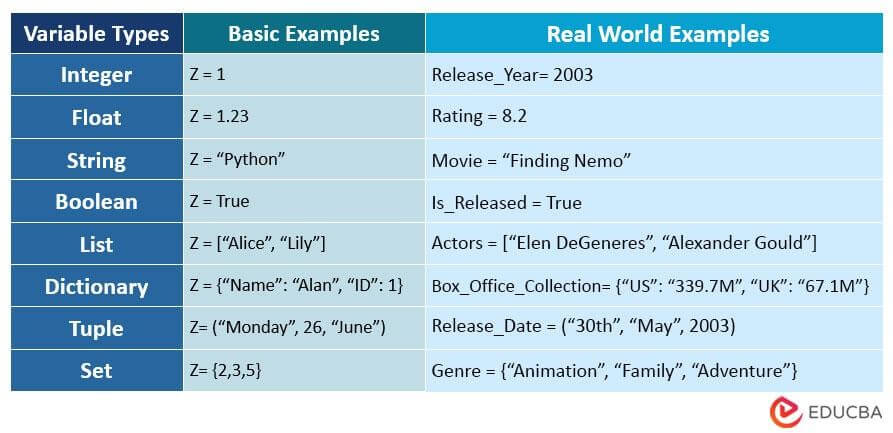
The above image provides a brief overview of the different types of Python variables with examples. However, you should read the detailed explanation below to better understand each variable type.
1. Integer
A Python integer or int refers to whole numbers that can be either positive or negative.
Example of Integer Variables:
a = 1
b = -200
c = 30000
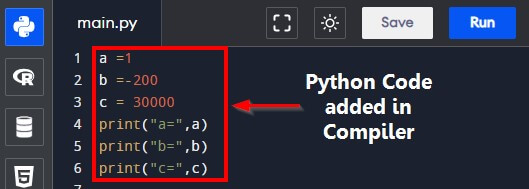
Code for Printing Integer Variables:
a = 1
b = -200
c = 30000
print("a =",a)
print("b =",b)
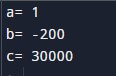
print("c =",c)To print the above code, you must add it to a Python compiler, as shown below. Note that we have explained the print() function in the later section in great detail.
Output:
2. Float
A Python float variable allows you to store decimals or floating-point values.
Example of Float Variables:
a = 1.23
b = 4.567
c = 5.8976
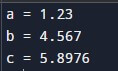
Code for Printing Float Variables:
a = 1.23
b = 4.567
c = 5.8976
print("a =",a)
print("b =",b)
print("c =",c)Output:
3. String
A string variable in Python allows us to store letters, words, or sentences. To declare a string variable, you must write the letter, word, or sentence in double quotes.
Example of String Variables:
a = “A”
b = “Python”
c = “A Python Code”
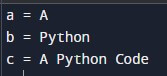
Code for Printing String Variables:
a = "A"
b = "Python"
c = "A Python Code"
print("a =",a)
print("b =",b)
print("c =",c)Output:
4. Boolean
A boolean variable stores only two values, True or False. We use them for logical operations, like checking if a condition is true or false. We don’t enter the true or false in quotes for declaring a boolean as we do for strings.
Example of Boolean Variables:
a = True
b = False
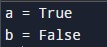
Code for Printing Boolean Variables:
a = True
b = False
print("a =",a)
print("b =",b)Output:
5. List
A Python list is a variable that can store a group of values. To declare a list variable, write each word within square brackets, separated by commas.
Example of a List Variable:
a = [“John”,”Sam”,”Michele”]
Code for Printing a List Variable:
a = ["John","Sam","Michele"]
print("a =",a)Output:
![]()
6. Dictionary
A Python dictionary is a variable that can store any number of pairs of data (Eg, “Item”:”Jam”, “Fruit”:”Apple”). We can use a dictionary when we want to store numerous values for a single variable.
Example of a Dictionary Variable:
Employee1 = {“Name”:”Alan”,”ID”:1234,”Role”:”Analyst”}
Code for Printing a Dictionary Variable:
Employee1 = {"Name":"Alan","ID":1234,"Role":"Analyst"}
print(Employee1)Output:
![]()
7. Tuple
Tuples are variables that can store a collection of different data types in order. Moreover, after creating the variable, the programmer cannot make any changes to the values.
Example of a Tuple Variable:
Today_Date = (“Monday”,”19th”,”June”,2023)
Code for Printing a Tuple Variable:
Today_Date = ("Monday","19th","June",2023)
print("Today_Date =", Today_Date)Output:
![]()
8. Set
A set variable in Python is very similar to a tuple variable (where we store a list of data). However, unlike a tuple, a set variable allows us to modify its elements when necessary.
Example:
Prime_nums = {2,3,5,7}
Code for Printing a Set Variable:
Prime_nums = {2,3,5,7}
print("Prime_nums =",Prime_nums)Output:
![]()
Working with Python Variables
There are 5 ways in which we can work with Python variables, from declaration to deletion.
- Python Variable Declaration: Giving a value to a new variable
- Variable Assignment: Giving a new value to an already declared variable
- Variable Manipulation: Manipulating a variable for a specific result
- Printing the Variable: Displaying the result value of a variable
- Variable Deletion: Removing a variable from memory
Let us explore each stage in detail using the following code as an example.
# Variable Declaration
Location = "Switzerland"
Location, Flight_Number = "Switzerland", "GEN300"
Location = Destination = "Switzerland"
# Variable Assignment
Location = "New York"
# Variable Manipulation
Tourist_spot = Location + " Empire State Building"
# Printing the Variable
print("Destination is",Location)
print("I am going to",Location,"to visit",Tourist_spot)
# Deleting the Variable
del Location
print("Location variable is deleted")
print(Location)Let us understand how you can use the above code. We will see how the above code works by analyzing each section of the code. We have also added outputs wherever necessary.
1. Python Variable Declaration
In the above example code, we first declare the variable by assigning it a value. To declare a variable, you must use the equal sign (=) after the variable name and then assign a value to it.
In Python, you have the option to either declare a single variable at a time or declare multiple variables simultaneously.
Single Variable Example:
Location = "Switzerland"In this case, the variable Location will store the value of Switzerland. You can then use the variable throughout your code.
Python also allows you to assign values to multiple variables in a single line, known as multiple assignments.
Multiple Variables Example:
Location, Flight_Number = "Switzerland", "GEN300"We can also assign the same value to multiple variables:
Location = Destination = "Switzerland"2. Assigning a New Value
After declaring a variable, you can assign a new value to it at any point in your code. This allows you to update the value stored in the variable.
Example:
Location = "New York"Here we are changing the value that Location holds from Switzerland to New York.
3. Variable Manipulation
After declaring a variable and assigning a value to it, you can perform various operations on it. This includes mathematical calculations, string manipulation, or any other relevant operations based on the variable’s data type.
For Example:
Location = "New York"
Tourist_spot = Location + " Empire State Building"Here, we are assigning the value of Location (New York) plus the words Empire State Building to the variable Tourist_spot. Thus, the variable Tourist_spot will store the words: New York Empire State Building. Remember to add a space before the second word Empire State Building to ensure proper spacing in the new variable. Otherwise, the resulting word will be New YorkEmpire State Building.
4. Print Python Variables
To see the value stored in a variable, you can use the print() function. This allows you to display the variable’s value in the output. To print a single variable, just mention the name of the variable inside the brackets of the print() function.
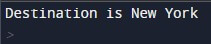
Example:
print("Destination is",Location)This will print the value stored in the variable Location.
Output:
To print multiple variables, just mention all variables in the print function.
Example:
print("I am going to",Location,"to visit",Tourist_spot)Output:
![]()
5. Deleting the Variable
In Python, you can also delete a variable when it is no longer needed. This frees up memory resources. You can use the del keyword followed by the variable name to delete it.
Example:
Location = "New York"
print(Location)
del Location
print("Location variable is deleted")
print(Location)Enter the above Code in Python Compiler as shown below:
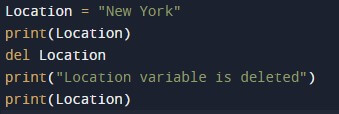
Output:
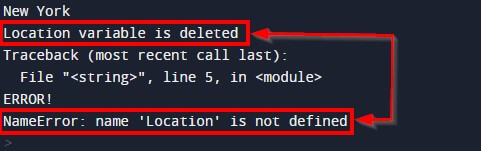
Here, Python deletes the variable ‘Location’ that we created at the beginning. Now the Python compiler holds no memory of Location or its value.
Thus, it prints the value New York in the beginning, but after deleting the variable, it shows a NameError.
Python Variables Example (With Code and Output)
Let’s say you wish to print a movie name and its rating in Python. Hence, you must first declare two variables for each value and then use the print() function.
Code:
# Declaration
movie = "Inception"
rating = 8.8
# Printing the movie
print("Movie:", movie)
# Printing the rating
print("Rating:", rating)Output:
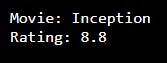
Let us now delete the rating variable and try printing the variable again.
Code:
# Continuing the Code
# Deleting the variable
del rating
# Printing the movie
print("Movie:", movie)
# Trying to print the rating after deletion
print("Rating:", rating)Output:
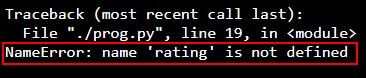
As we have deleted the variable, Python shows the NameError stating that the variable is not defined.
Type Conversion in Python
Apart from declaration, printing, and deletion, we can perform various other operations on variables. One of the most common is type conversion.
It means changing a variable’s current data type to another data type. For example, changing an integer to a string. The programmer can do this manually, or the Python compiler will do it automatically. Let us see each method in detail.
1) Implicit Type Conversion
When Python automatically changes the data type of a variable without the programmer’s instructions, it is known as Type Conversion.
Example:
num = 10
result = num + 5.5
print(result)Output:
![]()
Here, we were trying to add an integer and a decimal number. However, both are different types, so Python automatically converts the integer (10) into decimal (10.0) and gives us a decimal number 15.5 (10.0 + 5.5) as the answer.
2) Explicit Type Conversion
When a programmer specifically tells Python to change the data type of a variable, it is known as explicit type conversion or typecasting.
Example:
# Adding an integer and a string
num = 10
message = "The number is: "
result = message + str(num)
print(result)Output:
![]()
In the above example, we asked Python to add a string (message) and an integer (num). To make sure there are no errors, we also instructed the program to change the data type of the integer (num) to a string using str(num).
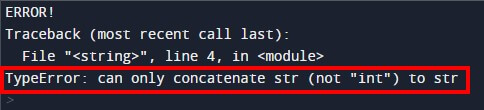
What is Object Reference?
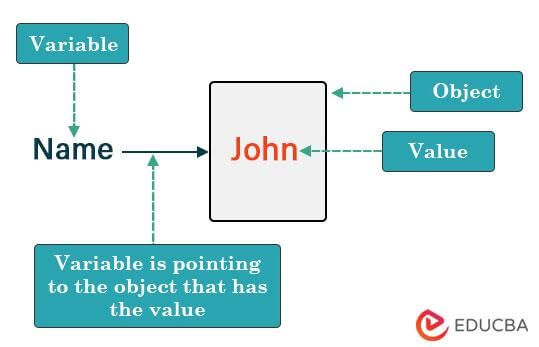
An object reference explains how Python creates and uses a variable.
For instance, when we declare a variable: Num = 10, Python will execute the following steps.
- Python first creates an object of the required data type. (Eg, Python creates an object with the integer data type)
- Python then stores the value we assign within that object. (Eg, Python stores the value 10 in the integer object)
- Finally, it creates a pointer, where the variable name we gave points to the object. (Eg, the variable Num will point to the integer object)
Therefore, Python uses the variable as a reference point for the object. So, when it wants to use the value stored in the variable, it will simply look where that variable is pointing.
For example, let us understand how Python creates a variable for the following declaration using a simple image:
Name = "John"Snapshot:
Moreover, if you want to check what type of object Python has created for your variable, you can use the type() function.
Example:
Name = "John"
print(Name)
print(type(Name))Output:
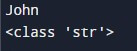
The output indicates that our variable Name belongs to the <class ‘str’> category, which signifies that the variable is of the string data type.
Python Object Identity
We just saw how Python creates an object to store a value, and we know Python accesses the object to use the value. Therefore, every object must have a unique location, right?
So, in Python, every object has a special number called an identifier, which is like a unique fingerprint for each object. The identifier tells Python the object’s location.
If you want to know the Python object id, you can use the id() function.
Example:
name = "John"
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
print(id(name))
print(id(my_list))Output:
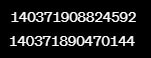
In this example, we defined two variables: name and my_list. We then requested Python to display the identifier numbers of both variables using the id() function. As a result, Python displays each variable’s identifier number (numerical memory address).
Python Variable Scope
After understanding the different Python variables and data types and the different operations, we can perform using them, let us dive a little into the scope of variables.
The scope of a variable tells the Python compiler which parts of the code can access and use the variable. There are two types of scopes: Local and Global.
To understand the concept of scope, let us see the local and global variables in Python.
1. Local Variable & Scope
When we declare a variable within a function, only that function can access the variable. It means we cannot use that particular variable anywhere outside the function. This is called local scope.
For instance, if you buy Adobe Photoshop, you can only use the Photoshop features and not the other Adobe features.
Example of Using a Variable Within Scope:
To use a variable within scope, we will first create a function called appreciate() that declares and prints a variable called text. Afterward, we will call the function to see how the local scope works.
def appreciate():
text = "Good job!"
print(text)
appreciate()Output:
![]()
Example of Using a Variable Outside Scope:
Now let us see what happens if we try accessing the text variable without calling the appreciate() function.
def appreciate():
text = "Good job!"
print(text)Output:
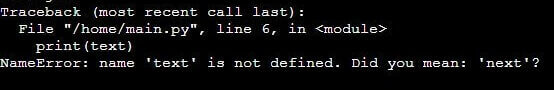
Here, as text is a local variable declared inside the appreciate() function, we can only use it inside that function. So, when we try accessing the text outside the function, the output shows an error.
2. Global Variable & Scope
Unlike local variables, we can use global variables in any part of the program. They are available for use throughout the program until the code finishes running or the variable is intentionally deleted. It is necessary to declare global variables at the start of the program outside any functions or classes.
For instance, if you purchase a subscription to the Adobe Creative Cloud, you can freely use any Adobe software included in the subscription till the subscription ends or you voluntarily cancel the subscription.
Example:
In this example, we begin by declaring the global variable text at the beginning of the program. We then use this variable both inside and outside of a function called appreciate().
text = "Good job!"
def appreciate():
print(text)
appreciate()
print(text)Output:
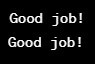
This shows we can access and modify the text variable from anywhere in the code.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Are Python variables case-sensitive?
Answer: Yes, variables in Python are case-sensitive. The upper and lower case letters get different priorities. For example, Python treats X and x differently.
Also, use of the same variable for different values is not possible. Python will just ignore the first value and only focus on the latest value provided to that variable.
For example, you assign the value Soccer to a variable named Sports. But later, if you want to change it to Cricket, you can simply write the code as:
Sports = CricketBy doing this, Python will automatically ignore the Soccer value and only use Cricket.
Q2. Define the empty variable in Python.
Answer: In Python, defining an empty variable is an easy task. Developers can directly assign a null value to any variable using the None keyword. For example, let’s say the variable name is var, so to assign a null value developer can write it as:
var = NoneThe above declaration means that there is no value assigned to var.
Q3. How to add two Python variables?
Answer: It is convenient to add two Python variables using a Python + operator. You can add both numbers and strings in Python.
Example:
a = 5
b = 10
print(a + b)
c = "EDU"
d = "CBA"
print(c + d)Output:

Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA article on Python variables and Python variable types was helpful for a deep understanding of the concept of variables in Python. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


