Updated August 1, 2023
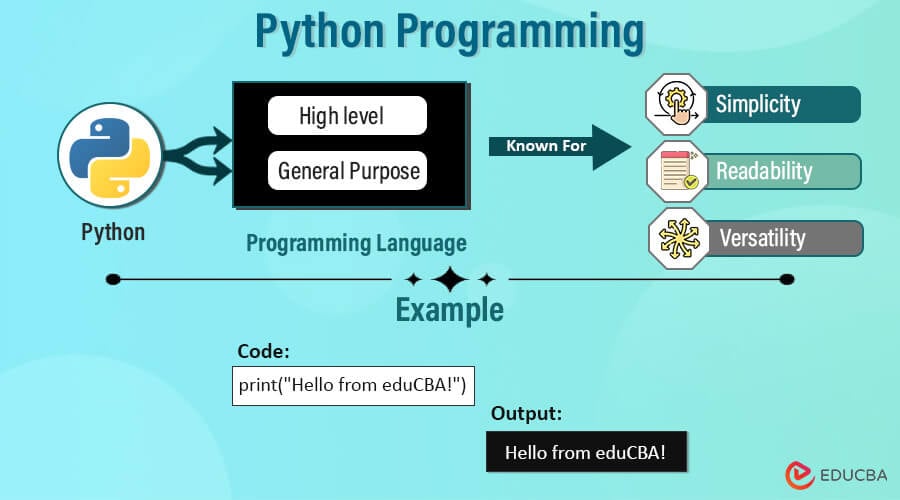
What is Python, and why is it useful?
The adoption of high-level programming languages like Python benefits many applications. Some of the reasons Python is popular are as follows:
- The syntax is straightforward and logical, and Python is an excellent programming language for beginners since its code is clear and simple to develop.
- There is a comprehensive standard library. Python has many modules for tasks like web development, scientific computing, system administration, etc. This means less time writing code from scratch.
- It supports multiple programming styles. Python supports object-oriented, imperative, and functional programming styles. This makes Python adaptable and suitable for complex applications.
- A tremendous ecosystem of collections existed. Several third-party libraries for Python provide flexibility for essentially all requirements. This makes Python very versatile.
- Integration with other languages is possiblePython can be connected to C, C++, Java, and several other computer languages, enabling you to employ the best aspects of several programming languages in a single application.
- Python code can be executed without compilation, which makes the development cycle very fast. This increases developer productivity.
- Being open-source, Python has many contributors and users who help improve the language. This ensures Python stays up to date with current trends.
Table of Content
- What is Python, and why is it useful?
- History of Python
- Python Versions and Distributions
- Setting Up Your Python Environment
- Basic Syntax and Data Types
- Functions and Modules in Python Programming
- Lists, Tuples, and Dictionaries
- Input and Output
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
- Error Handling and Debugging in Python Programming
- Advanced Topics
History of Python
- While working at the Dutch national research institute CWI in the late 1980s and early 1990s, Guido van Rossum created Python and named the programming language after the British comedy group Monty Python.
- The first public version of Python was released in 1991. Initially, it was designed to be an easy-to-learn scripting language. In the early years, Python was mainly used for scripting and connecting other tools and systems.
- 2000 Python 2.0 was released with new features like list comprehension and garbage collection. This release marked the split between Python 2 and Python 3.
- Python 3.0 was released in 2008 with backward incompatible changes such as:
- Print became a function instead of a statement
- Integer division always returns a float
- The range() function returns an iterable instead of a list
- Some library modules were removed
- These changes caused a divide, with some users sticking to Python 2 and others adopting Python 3.
- Python is used for web dev, data science, ML, AI, scripting, and more.
- The latest major release is Python 3.10, released in March 2022. The language continues to evolve by adding new features while maintaining backward compatibility within major versions.
| Year | Version | Notable Features |
| 1991 | 0.9.0 | Initial release |
| 1994 | 1.0 | Introduces lambda, map, filter, and reduce |
| 2000 | 2.0 | List comprehensions, garbage collection |
| 2008 | 3.0 | Print function, integer division, range() returns an iterable |
| 2010 | 3.1 | Improved I/O handling, multiprocessing |
| 2012 | 3.2 | New syntax features, performance improvements |
| 2012 | 3.3 | New library modules, improved performance |
| 2014 | 3.4 | Asyncio, improved metaclasses, statistics module |
| 2015 | 3.5 | Coroutines with async and await type hints |
| 2016 | 3.6 | Formatted string literals, asynchronous generators |
| 2017 | 3.7 | Data classes, context variables, built-in breakpoint |
| 2018 | 3.8 | Assignment expressions, f-strings enhancements |
| 2020 | 3.9 | Dictionary merge operator, improved type hinting |
| 2022 | 3.10 | Parenthesized context managers, pattern matching |
Python Versions and Distributions
Setting up your Python environment involves installing a specific version of Python and, optionally, choosing a distribution that provides additional tools and packages. Here’s a breakdown of Python versions and distributions:
Python Versions:
- Python 2: Python 2.x was the older version of Python and is no longer actively maintained or supported. It reached its end of life in January 2020 and is not recommended for new projects.
- Python 3: Python 3.x is the current and recommended version of Python. The latest Python 3 version is 3.10, released in March 2022. It introduces many improvements and enhancements over Python 2. Python 3 is backward-incompatible with Python 2, which means that code written for Python 2 may require modifications to run on Python 3.
There are different ways to install and use Python, like:
- CPython: Python’s reference implementation is CPython. It is written in C and is the most widely used implementation. When you download and install Python from python.org, you’re using CPython. It provides the official interpreter for executing Python code.
- Anaconda: Anaconda is a popular Python distribution for data science and scientific computing. It has a curated collection of pre-installed packages such as NumPy, Pandas, matplotlib, and Jupyter Notebook. Anaconda simplifies the installation process for data science libraries and provides an environment management system called Conda.
- PyPy: PyPy is a Python implementation designed to enhance performance and serve as an alternative. It includes a Just-in-Time (JIT) compiler that can provide faster execution in some cases. PyPy is compatible with most Python code and supports many packages.
- Miniconda: A lightweight version of Anaconda that includes only the conda package manager and a minimal set of packages. You can manually install additional packages as needed.
Setting Up Your Python Environment
To set up Python, you should:
- Choose a Python Distribution: Several Python distributions are available, but the most popular ones are CPython (the default reference implementation) and Anaconda. CPython is suitable for most users, while Anaconda includes additional packages and tools for scientific computing.
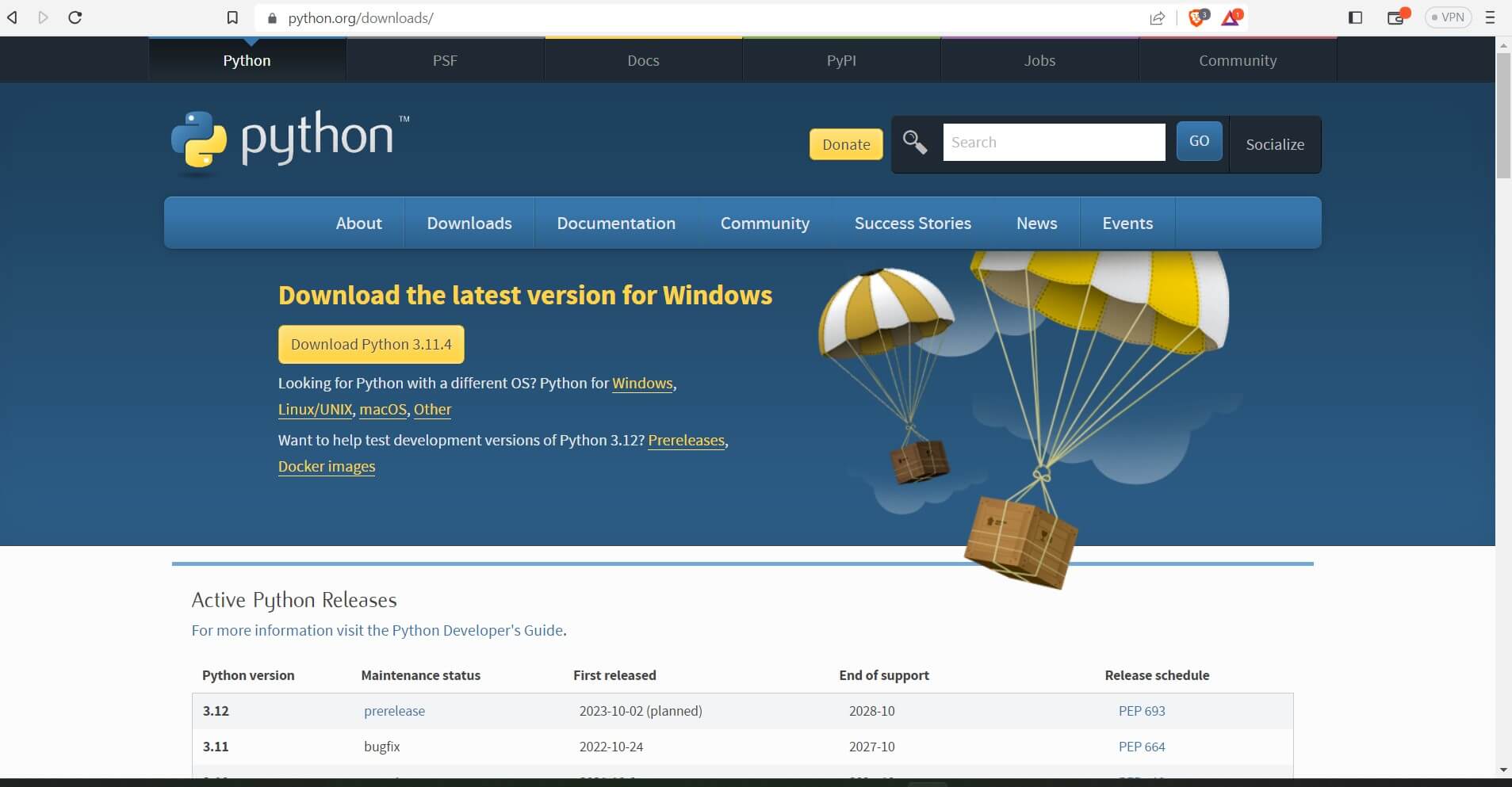
- Download Python: To access Python, visit python.org and select the “Downloads” tab. Choose the appropriate version of Python for your operating system (Windows, macOS, or Linux) and download the installer.
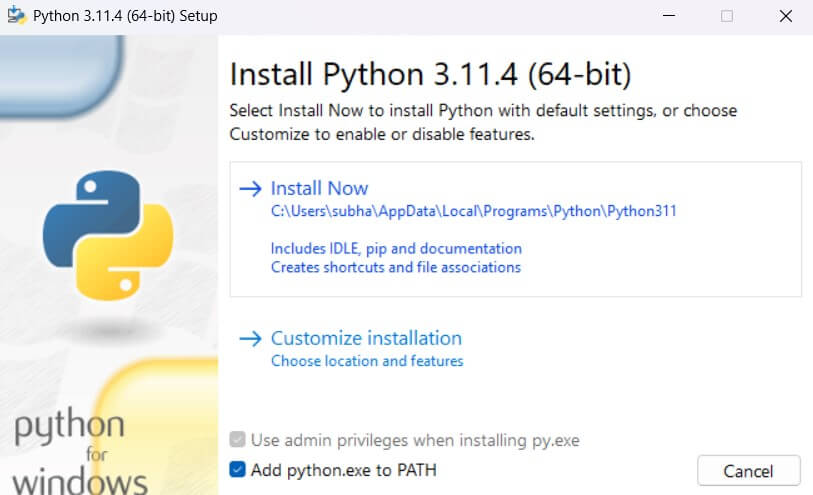
- Run the Installer: After downloading the installer, double-click on it to initiate Python installation. Follow the installation wizard’s instructions to complete the process.
- Add Python to PATH (Windows only): During the installation process on Windows, Please select “Add Python to PATH” when checking the box. This will allow you to use Python from any command prompt or terminal window.
- Verify the Installation: To proceed, open a command prompt and enter the following command:
python --version- To view the current Python version, enter this command. Make sure the version number matches the one you downloaded.
- Install an Integrated Development Environment (IDE) (optional): While you can write Python code in any text editor, using an IDE can significantly enhance your development experience. Some popular Python IDEs include PyCharm, Visual Studio Code (with the Python extension), and IDLE (included with Python).
Installing Python on your computer
Download the Python installer from the official Python website.
LINK: https://www.python.org/downloads/
(The latest stable release, which is recommended.)
The long-term support (LTS) release will receive support for a longer period.
During setup, select the option to add Python to the system PATH. Follow on-screen instructions to complete installation. This makes it easier to run Python from the command line.
Open a command prompt and type the following command to test that Python is installed correctly:
python –versionOutput:
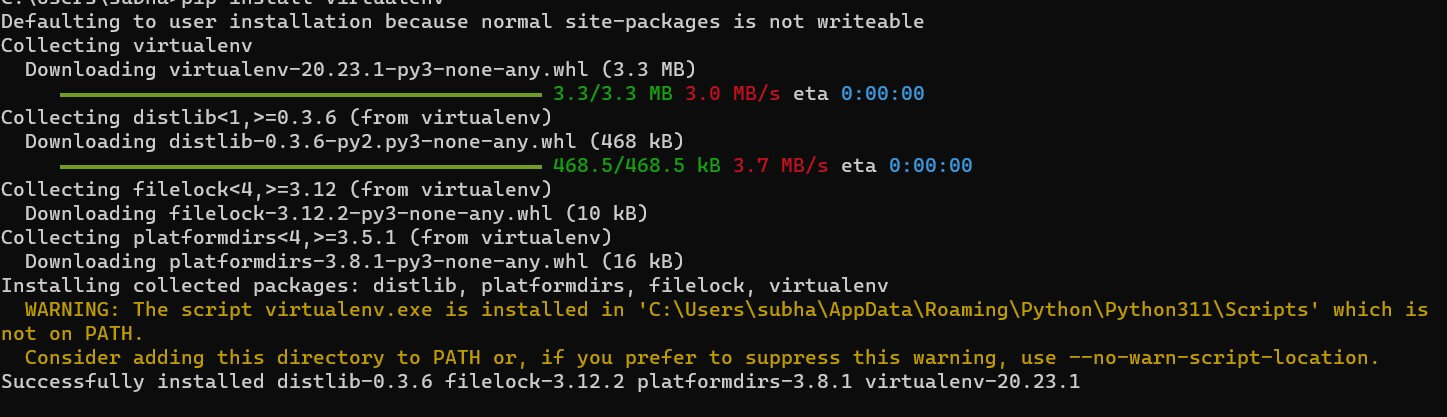
Install pip, the package manager for Python. If it did not install automatically, run this command:
python get-pip.pyInstall virtualenv to create isolated environments for projects:
pip install virtualenvOutput:
Install an integrated development environment (IDE) like Visual Studio Code, PyCharm, or Spyder for code editing.
Install useful Python libraries. Some of the most popular are
- NumPy
- Pandas
- Matplotlib
- Django
We can install libraries using the pip command.
Create a simple Python program to test the installation.
print("Hello from eduCBA!")Output:
Then run the program from the command line:
python hello.pyYou should see the output “Hello from eduCBA!”
Choosing a text editor or integrated development environment (IDE)
There are several options for writing Python code, ranging from basic text editors to full-featured integrated development environments (IDEs).
Text editors are simple programs for writing and editing code. Examples include Notepad++ and Sublime Text.
IDEs provide more features like:
- Syntax highlighting
- Code completion
- Debugging tools
- Version control integration
Examples of popular Python IDEs are:
- Visual Studio Code (link: https://code.visualstudio.com/): Visual Studio Code (VS Code) is a lightweight yet feature-rich text editor developed by Microsoft. It has many extensions, including the Python extension, which provides excellent Python support. VS Code offers debugging capabilities, Git integration, and customizable settings.
- PyCharm (link: https://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/): PyCharm is a powerful IDE developed by JetBrains. It offers advanced features like code completion, debugging, version control integration, and an integrated terminal. PyCharm is free (Community Edition) and paid (Professional Edition) versions.
- Spyder: (link: https://www.spyder-ide.org/): Spyder is an IDE designed specifically for scientific computing and data analysis. It provides a MATLAB-like interface with powerful features such as an interactive console, variable explorer, and debugging capabilities. The Anaconda distribution includes Spyder, a popular tool for scientific Python packages.
- Eclipse (link: https://eclipseide.org/): Eclipse is an IDE primarily focused on Java but supports other languages through plugins.PyDev, an Eclipse plugin, adds Python development support to the IDE.
Basic command line usage
Command Line: The command line provides a text interface to operate your computer. To use Python, you can:
- Open the terminal app on Mac or Command Prompt on Windows.
- Run a Python file:
python hello.py- Use Python as a calculator:
print(1 + 2)Output:
Install packages:
pip install numpyOutput:
Basic Syntax and Data Types
- Use indentation to organize code into blocks.
- Create variables by assigning a value:
my_variable = 5- Create strings with’ or “:
string = "Hello"- Use # for comments:
# This is a commentVariables and data types
Variables allow us to store information in our programs to refer to and manipulate that data. We assign a name to a variable using an equals sign like this:
name = "John"
age = 30Python supports several data types for variables:
- Integers store whole numbers. We can declare an integer variable like this:
age = 30- Floating point numbers represent decimal values using the following:
pi = 3.14- Strings store text, enclosed in either single or double quotes:
name = "John"or
name = 'John'- Boolean variables hold either True or False:
has_certificate = True- Lists store multiple values in a list:
fruits = ["Apple", "Orange", "Cherry"]- Dictionaries store key-value pairs using curly braces:
student = {
"name": "Kellen",
"age": 25,
"grades": [70,80,85]
}Operators
Below are the different operators used in Python programming.
1. Arithmetic Operators:
- + Addition
- – Subtraction
- * Multiplication
- / Division
- % Modulus (Returns remainder)
- ** Exponentiation
- // Floor division (Removes decimal)
Example:
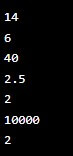
a = 10
b = 4
print(a + b) # Addition -> 14
print(a - b) # Subtraction -> 6
print(a * b) # Multiplication -> 40
print(a / b) # Division -> 2.5
print(a % b) # Modulus -> 2
print(a ** b) # Exponentiation -> 10000
print(a // b) # Floor division -> 2Output:
2. Comparison Operators
- == Equal to
- != Not equal to
- > Greater than
- < Less than
Example:
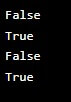
a = 15
b = 60
print(a == b) # False
print(a != b) # True
print(a > b) # False
print(a < b) # TrueOutput:
3. Logical Operators
- and – Returns True if both statements are true
- or – Returns True if one of the statements is true
- not – Reverses the result, True becomes False and vice versa
Example:
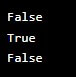
a = True
b = False
print(a and b) # False
print(a or b) # True
print(not a) # FalseOutput:
4. Assignment Operators
- = Assign
- += Add and assign
- -= Subtract and assign
- *= Multiply and assign
- /= Divide and assign
- %= Modulus and assign
- //= Floor division and assign
Example:
a = 15
a += 5 # a is now 20
a *= 2 # a is now 40
print(a)Output:
Control flow Statements
Conditional statements allow a program to choose between different computation paths.
1. If/else statements: If a condition is true, the if block executes. Otherwise, the else block executes.
if condition:
# Executes if the condition is true
else:
# Executes if condition is false2. While loops: Executes a code block if a condition is true.
while condition:
# Executes while the condition is true3. For loops: Iterate over each element in a sequence, executing a code block for each element.
for items in sequence:
#Executes each item in the sequenceFunctions and Modules in Python Programming
Functions: Functions define reusable blocks of code. They take in inputs (arguments) and return an output.
def function_name(arguments):
# Function body
return outputModules: Modules organize Python code into reusable files. Modules have a .py extension. Modules are imported, and their functions are called.
import module_name
module_name.function_name()Defining and calling functions
Defining Functions: Functions are defined using the def keyword followed by the name and parentheses():
def function_name(parameters):
function_bodyThe parameters specify the inputs to the function. An optional docstring can document the function. The function body contains the statements that define what the function does.
Calling Functions: To call a function, use its name followed by parentheses:
function_name()Passing Arguments: You can pass arguments by specifying values for the parameters:
function_name(arg1, arg2, arg3)The number of arguments must match the number of parameters defined. The Arguments are assigned to parameters in the order they are given.
Return Values: To return a value from a function, use the return statement:
return expressionAny expression can be returned.
Example:
def multiply(x, y):
return x * y
result = multiply(2,3)
print(result) # Prints 6Output:
Built-in functions and user-defined functions
Built-in functions: The functions are pre-defined and available in Python. Examples include:
- print() – Displays text on the screen
- len() – Determines the length of an object
- abs() – Computes the absolute value
- max() – Finds the maximum value
- min() – Finds the minimum value
Built-in functions can be called directly in your code.
User-defined functions: User-defined functions are created and defined by the programmer. They allow customization of functionality to meet specific needs.
We can define a user-defined function using the def keyword:
def add_numbers(a, b):
return a + bThen call the function:
result = add_numbers(2,3)The differences include:
| Built-in Functions | User-defined Functions |
| Built-in functions are predefined. | The programmer creates user-defined functions. |
| Built-in functions provide general-purpose functionality. | User-defined functions provide custom functionality. |
| Built-in functions can be called directly. | User-defined functions must be defined first. |
| Built-in functions have broad applications. | User-defined functions focus on specific tasks. |
| Built-in functions are always available; | User-defined functions must be imported or defined. |
Importing and using modules
Modules: Modules organize Python code into reusable files.
To import a module, use:
import module_nameYou can then access its functions using the following:
module_name.function_name()Lists, Tuples, and Dictionaries
Lists: Lists store multiple items in a variable. They are defined using [ ]:
[] # Empty list
[1, 2, 3]
["a", "b", "c"]You can access elements using indexes:
list[0] # First element
list[-1] # Last elementAnd modify element values:
list[1] = 4 # Changes 2 to 4Example
# Empty list
my_list = []
# List of integers
integers = [1, 2, 3]
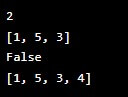
# Access element at index 1
print(integers[1])
# Prints 2
# Change element value
integers[1] = 5
print(integers)
# Prints [1, 5, 3]
# Check if value is in list
print(2 in integers)
# Prints False
# Append value to list
integers.append(4)
print(integers)
# Prints [1, 5, 3, 4]Output:
Tuples: Tuples are like lists but immutable. They are defined using ( ):
() # Empty tuple
(1, 2, 3)
("a", "b", "c")Example:
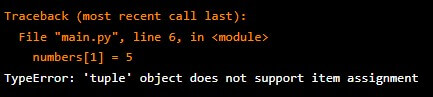
# Empty tuple
my_tuple = ()
# Tuple of integers
numbers = (1, 2, 3)
# Cannot change tuple values
numbers[1] = 5
# Throws an errorOutput:
It will show the Type error because tuples are immutable, which means the elements cannot be changed here. tuples are defined by using ().
Dictionaries: Dictionaries store key-value pairs. They are defined using { }:
{} # Empty dictionary
{
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
}You can access values using the keys:
dict["key1"] # Returns "value1"And modify values:
dict["key1"] ="newValue1" # Updates value for key "key1"Example:
# Empty dictionary
my_dict = {}
# Dictionary with string keys
user = {
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"city": "New York"
}
# Access value using a key
print(user["name"])
# Prints John
# Change value
user["age"] = 31
print(user["age"])
# Prints 31
# Check if key exists
print("address" in user)
# Prints FalseOutput:
Slicing and indexing
Slicing: Slicing allows accessing subsections of sequences. You can omit the start or end index to slice from the beginning or end:
Example:
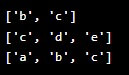
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
print(my_list[1:3]) # ['b', 'c']
print(my_list[2:]) # ['c', 'd', 'e']
print(my_list[:3]) # ['a', 'b', 'c']Output:
Indexing: Indexing uses brackets [ ] with an integer to access a single element at that position. Indexing starts at 0 for the first element.
Example:
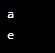
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
print(my_list[0]) # 'a'
print(my_list[4]) # 'e'Output:
Negative indexes count from the end:
my_list = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e']
print(my_list[-1]) # 'e'
print(my_list[-2]) # 'd'Output:
Indexing accesses elements. Slicing accesses subsequences.
List Comprehensions
Comprehensions create lists using an expression followed by a for clause.
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4]
doubles = [n * 2 for n in nums]
print(doubles)Output:
You can filter the list with an if clause:
nums = [1, 2, 3, 4]
evens = [n for n in nums if n % 2 == 0]
print(evens)Output:
Input and Output
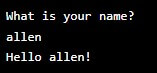
Input(): The input() function prompts the user and returns a string.
name = input("What is your name? ")
print(f"Hello {name}!")Output:
print(): The print() function displays the output.
print("Hello!")Output:
You can print multiple values:
print(1, 2, 3)Output:
And use f-strings to interpolate variables:
name = "John"
print(f"Hello, my name is {name}!")Output:
Reading and writing files
To read a file in Python:
file = open("filename.txt", mode="r")The “r” indicates read mode.
You can read the entire file contents:
contents = file.read()
print(contents)Or read line by line:
line = file.readline()
while line:
print(line)
line = file.readline()To write to a file:
file = open("filename.txt", mode="w")The “w” indicates write mode, overwriting existing content.
You can write strings:
file.write("Hello!")
file.write("This is a test.").write() writes a string.
You can write a list of strings:
lines = ["Line 1", "Line 2"]
file.writelines(lines)It’s essential to close the file:
file.close()This ensures all content is written.
- To read a file, open it in read mode and use read or readline methods.
- To write a file, open in write mode and use write or writelines.
- Always close the file to ensure all content is written.
Basic Input/Output
Python provides built-in functions for basic input and output operations. The print() function outputs data to the standard output device (screen). For
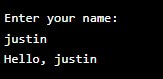
print("Hello, World!")The input() function allows for user input. It reads a line from input (usually the user), converts it into a string, and returns that. For
name = input("Enter your name: ")
print("Hello, " + name)Output:
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
Python is an object-oriented programming language. It allows us to develop applications using an OOP approach.
In Python, we can define classes using the class keyword. A class is a blueprint for the object. Here’s a simple class definition:
class MyClass:
x = 5We can use classes to create objects, which are instances of these classes. For
p1 = MyClass()
print(p1.x)Python also supports inheritance and polymorphism, which are fundamental concepts in OOP. Inheritance allows us to define a class that inherits all the methods and properties from another class. Polymorphism allows us to use a single type entity (method, operator, or object) to represent different types in different scenarios.
Encapsulation is another key concept in OOP. It refers to bundling data with the methods that operate on that data. It hides the values or state of a structured data object inside a class, preventing unauthorized parties’ direct access to them.
Overview of OOP Concepts
Classes define objects – objects are instances of classes. Classes describe objects’ properties (attributes) and behaviors (methods).
Attributes store data about an object. Methods define the actions objects can take.
class Dog:
color = "brown" # Attribute
def bark(self): # Method
print("Woof!")Inheritance allows one class to inherit attributes and methods from another class.
class Animal:
pass
class Dog(Animal):
passHere, the Dog class inherits from the Animal class.
- Polymorphism occurs when methods in child classes have different implementations from parent classes.
- Encapsulation involves hiding data in classes and providing access via methods. This makes classes more modular.
- Abstraction focuses only on the important details of a class, hiding unnecessary information.
Defining and using classes
We define a class using the class keyword. The class body contains attributes and methods.
class ClassName:
# attributes and methodsAttributes store data about an object. Methods define the object’s behaviors.
class Dog:
species = "Canis familiaris" # Attribute
def bark(self):
print("Woof!") # MethodWe create instances of a class using the class name.
sam = Dog()We access attributes and call methods using the dot (.) operator.
sam.bark()
print(sam.species)One class can inherit from another using inheritance.
class Labrador(Dog):
passHere the Labrador class inherits from the Dog class.
In summary, classes define object templates. Instances are created from classes. Attributes store data about instances, and methods define their behaviors. Inheritance allows classes to extend existing classes.
Inheritance and Polymorphism
Inheritance allows a class to extend an existing class, inheriting its attributes and methods. The child class extends the parent class. ε
class Parent:
passclass Child(Parent):
passThe child class inherits from the parent class. The child class can override or extend parent class methods.
Polymorphism occurs when classes implement common interfaces in different ways. In Python, polymorphism is achieved through method overriding in child classes.
Error Handling and Debugging in Python Programming
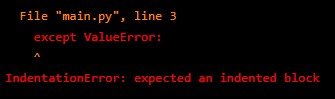
Errors can be caught using try/except blocks:
try:
# code
except ValueError:
print("Invalid input!")Output:
Specific exceptions can be caught:
try:
# code
except ValueError:
print("Invalid input!")Output:
Code can be debugged using print statements, IDE debuggers, and assertions.
In summary, inheritance allows classes to extend existing classes. Polymorphism enables different classes to implement common interfaces in different ways. Try/except blocks catch errors, and various debugging techniques help troubleshoot code.
Common Types of Errors in Python
Here are some common types of errors you may encounter in Python programming:
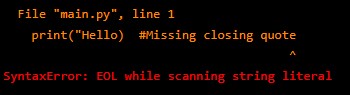
1. SyntaxErrors – These occur when Python encounters incorrect syntax.
For example:
print("Hello) # Missing closing quoteOutput:
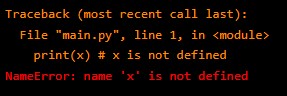
2. NameErrors – When a variable is used but not defined.
For example,
print(x) # x is not definedOutput:
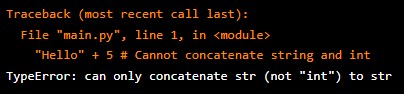
3. Type Errors – These happen when an operation or function is applied to an object of an inappropriate type.
For example:
"Hello" + 5 # Cannot concatenate string and intOutput:
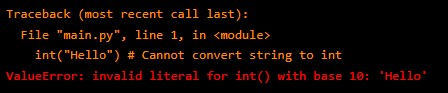
4. Value Errors – These occur when a function receives an argument of the right type but an invalid value.
For example,:
int("Hello") # Cannot convert string to intOutput:
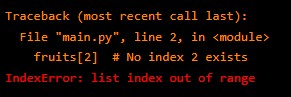
5. IndexError – This happens when you try to access a list index that does not exist.
For example,
fruits = ["Apple", "Orange"]
fruits[2] # No index 2 existsOutput:
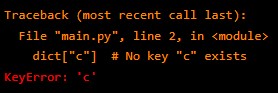
6. KeyError – This occurs when you try to access a dictionary key that is not in the dictionary. For example,
dict = {"a": 1, "b": 2}
dict["c"] # No key "c" existsOutput:
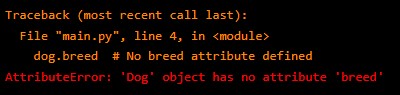
7. AttributeError – This happens when you try to access an attribute that does not exist. For example,
class Dog():
pass
dog = Dog()
dog.breed # No breed attribute definedOutput:
These are some of the most common error types.
Debugging Strategies
- Print Statements: Inserting print statements at strategic points in your code can help you understand the flow of execution and the values of variables at different stages. You can print variable values, function outputs, or custom messages to track the program’s behavior.
- Logging: The logging module in Python provides a more flexible and configurable way to track program execution. It allows you to log messages with different levels (e.g., DEBUG, INFO, ERROR) and customize logging output to files, the console, or other destinations.
- Debugger: Python has a built-in debugger called pdb (Python Debugger). You can pause code execution at specific lines with breakpoints, inspect variable values, step through the code, and interactively track the program’s flow.
- IDE Debugging Tools: Integrated Development Environments (IDEs) like PyCharm, Visual Studio Code, or Eclipse provide graphical debugging tools. These IDEs offer features like setting breakpoints, stepping through code, examining variables, and evaluating expressions during runtime.
- Exception Handling: Handling exceptions can help you recognize errors gracefully. Using try-except blocks, you can catch specific exceptions, log relevant information, and take appropriate actions to handle errors and prevent program crashes.
- Debugging Tools: Various third-party debugging tools are available for Python, such as pdbpp, ipdb, or pdb++. These tools offer enhanced features and capabilities compared to the built-in pdb debugger.
- Automated Testing: Writing unit tests and integration tests can help catch errors early and verify the correctness of your code. Test frameworks like unittest or pytest provide ways to write test cases, run them, and track failures.
Handling exceptions with try/except blocks
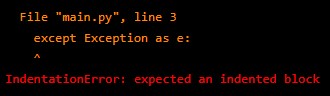
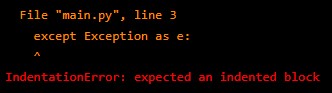
Handling Exceptions: Exceptions allow you to deal with runtime errors gracefully. You can handle exceptions using try/except blocks:
try:
# Code that may raise exception
except Exception as e:
# Handle exceptionOutput:
The try block contains code that may raise an exception. If an exception occurs, the except block is executed to handle that exception.
You can catch specific exceptions:
try:
f = open("file.txt")
except FileNotFoundError as e:
print("File not found")
except PermissionError as e:
print("Permission denied")Output:
Here we catch FileNotFoundError and PermissionError separately.
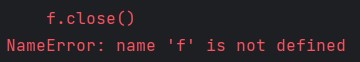
Finally, blocks let you execute cleanup code:
try:
f = open("file.txt")
finally:
f.close()Output:
Advanced Topics
Generators – Generators allow you to declare a function that behaves like an iterator. They are memory efficient and yield values one at a time.
def gen():
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3Comprehensions – List, set, and dictionary comprehensions provide concise ways to create new containers from sequences.
squares = [x*x for x in range(10)]Lambda Functions – Lambda allows you to create small anonymous functions.
add = lambda x, y : x + y
result = add(2,3)Decorators – Decorators modify functions or classes without changing their definitions.
@decorator
def func():
passRegular Expressions
Regular expressions are text patterns that match, search, and replace text.
Python’s re-module allows you to work with regular expressions. You import re and define patterns using special characters.
import re
pattern = re.compile(r'some_pattern')Common pattern characters:
- . – Any single character
- Zero or more repetitions
- […] – Matches a character in the set.
- \d – Matches a digit
- ^ – Start of string
- $ – End of string
You can search for patterns using re.search():
result = re.search(pattern, string)And replace patterns using re.sub():
new_string = re.sub(pattern, replacement, string)You can also match and extract groups.
Examples:
Match a phone number:
pattern = re.\d{3}-\d{3}-\d{4}Replace spaces with underscores:
pattern = ' '
replacement = '_'Decorators
Decorators modify functions without permanently changing them. They take a function as input and return a modified function.
A decorator is defined like this:
def decorator(func):
def wrapper():
# Add functionality
func()
return wrapperIt takes a function and returns a wrapper function.
We apply a decorator like this:
@decorator
def func():
pass,Which is equivalent to:
def func():
pass
func = decorator(func).The wrapper function is what actually gets called.
Decorators are used for:
- Logging,
- Caching results,
- Authentication,
- Timing functions,
- And more
Generators and iterators
Iterators are objects that can be used in a for loop to iterate over elements. Many built-in types in Python are iterable.
Generators are a type of iterator. Instead of yield, generator functions use the yield keyword.
def gen():
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3When a generator function is called, it returns a generator object.
g = gen()Each time the next(g) is called, the generator resumes where it left off.
next(g) # 1
next(g) # 2Generators can be iterated overusing a for loop.
Generators are memory efficient because they do not store all values in memory. They can create infinite sequences.
Generators are used to:
- Reduce memory usage
- Evaluate values lazily
- Create infinite sequences
Concurrency and Parallelism
- Concurrency: Concurrency refers to two or more tasks making progress simultaneously. In Python, concurrency can be achieved with threads or asynchronous programming.
- Threads: Threads are lightweight processes that can run concurrently. The threading module allows you to create multiple threads that run simultaneously.
- Asynchrony: Asynchronous programming uses callbacks and events to notify the completion of tasks. The asyncio module provides asynchronous I/O capabilities.
- Parallelism: Parallelism refers to tasks running simultaneously using multiple CPUs. Python does not support true parallelism, but libraries like multiprocessing can emulate it.
FAQ’s
Q1. What are the main features of Python?
Ans: Python is characterized by its simple syntax, dynamic typing, automatic memory management, large standard library, and support for a variety of programming paradigms, including object-oriented, procedural, and functional programming.
Q2. What is a virtual environment in Python?
Ans: A virtual environment is a directory that includes a Python interpreter and a set of libraries, all contained within it. It enables you to manage dependencies and isolate various projects so they do not conflict. Venv and virtualenv are popular tools for generating virtual environments.
Q3. What is the difference between ‘==’ and ‘is’ in Python?
Ans: The == operator determines whether the values of two variables are equal, whereas the is operator determines whether two variables belong to the same object in memory.
Conclusion
Python is a powerful, versatile, and simple-to-learn programming language that has grown in popularity due to its ease of use and readability. Its vast standard library and strong community support make it appropriate for a wide range of applications, including web development, data science, and more. Python’s future as a widely used language.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “Python Programming” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.